| Title | Pages |
|---|---|
| Prominence of Curcumin in Anticancer Strategies and İnnovation in Bioimaging Curcumin (CUR), a natural polyphenol derived from the rhizomes of Curcuma longa (turmeric), has garnered significant attention in recent years for its multifaceted potential in anticancer therapy and bio-imaging applications. This review article comprehensively explores the diverse anticancer properties of CUR, encompassing its potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-proliferative effects, as well as its ability to induce apoptosis and inhibit angiogenesis, making it a promising candidate in the fight against cancer. In addition to its therapeutic potential, CUR's unique physicochemical properties have enabled its utility as a versatile imaging agent for various bio-imaging modalities, including fluorescence imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET). We investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying CUR's bio-imaging capabilities and discuss its various applications in cancer diagnosis, monitoring treatment responses, and elucidating biological processes. This comprehensive review provides valuable insights into the dual role of CUR as an anticancer agent and a bio-imaging tool, elucidate its potential in the development of novel cancer therapies and diagnostic approaches. The amalgamation of CUR's bio-imaging and therapeutic properties suggests its future as a pivotal player in personalized medicine and precision oncology.
|
1 - 11 |
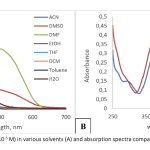
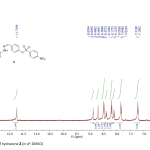
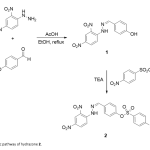
| Synthesis of Hydrazone Based Ion Sensor and Photophysical Characterization Hydrazone compounds are susceptible to nucleophilic attacks of anions such as fluoride or cyanide due to their tendency toward deprotonation of hydrogen bonded to nitrogen atom in the structure and found applications as ion sensors. In this work, from the condensation reaction of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, phenolic hydrazone compound was obtained and the following substitution reaction with 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride was studied to synthesize a new hydrazone compound with elongated conjugation. Structures of the synthesized compounds were accomplished with 1H NMR, 13C NMR an UV-Vis absorption spectroscopic techniques. According to the spectroscopic data, absorption maximum of the new hydrazone compound was found to shift bathochromically with ca. 120 nm in the presence of nucleophilic fluoride, cyanide, acetate, hydroxide and dihydrogenphosphate anions. 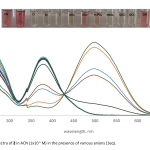
|
13 - 18 |
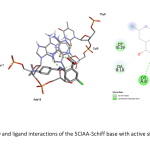
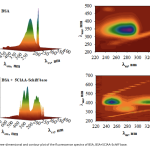
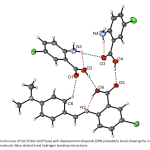
| 5-Chloroanthranilic Acid Schiff Base: Crystal structure, DNA/BSA Interactions, Molecular Docking and Antioxidant Activity A novel 5ClAA-Schiff base (Schiff base derived from the condensation of 5-chloroanthranilic acid and 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde) has been synthesized. The structure of the 5ClAA-Schiff base was clarified by CHN analysis, FTIR, electronic absorption spectroscopy, ESI-MS, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods. In biological activity studies, the interactions of the 5ClAA-Schiff base with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) were examined using fluorescence spectroscopy. The interactions of the 5ClAA-Schiff base with bovine serum albumin (BSA) were investigated using electronic absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy techniques, and the BSA quenching mechanism was found. The molecular docking simulation was analyzed to explore the interactions between the 5ClAA-Schiff base and biomolecules such as DNA and BSA using in silico techniques. Results confirmed that the 5ClAA-Schiff base was inserted into DNA via a minor groove and into BSA with subdomain IIA. The antioxidant activity of the 5ClAA-Schiff base was also investigated in comparison with the compounds used as standard. 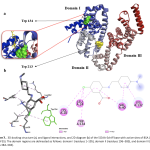
|
19 - 30 |
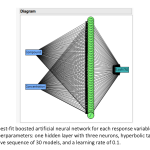
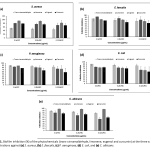
| Promising Phytochemicals that Show Antibiofilm Activity at Sub-Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations: Trans-Cinnamaldehyde, Limonene, Eugenol, and Curcumin As the challenges in the treatment of infections caused by multi-drug resistant microorganisms with well-known antimicrobial agents become a serious treat for the human health in worldwide, development of novel antimicrobials with potent antimicrobial activity has garnered significant attention. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of four phytochemicals (trans-cinnamaldehyde, limonene, eugenol, and curcumin) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and a yeast. Prior to antibiofilm assays, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC), and minimum fungicidal concentrations (MFC) were determined, with significant bactericidal and fungicidal effects being observed at low phytochemical concentrations. Also, biofilm inhibition efficiency of these phytochemicals was assessed at sub-MIC values (0.5x, 0.25x, and 0.125x MIC). At least 60% biofilm inhibition was observed for most of the microorganisms at the lowest tested concentrations (0.125x MIC) of the phytochemicals. Their biofilm inhibition capacity generally increased up to 80-90% depending on the concentration. Six data-driven models and their joint optimization adopted in this study yielded validation-based high predictive accuracy and identified optimal conditions. These data analysis models were applied in the antibiofilm activity investigation of natural compounds for the first time in this study to evaluate the accuracy of the results. 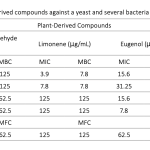

|
31 - 41 |
| Systematical Studies on the Family Cleridae (Coleoptera) in Inner Western Anatolian Region of Türkiye It was aimed to examine the morphological characteristics of the male reproductive organs in the sampled Clerid species, to discuss them with the existing literature and to contribute to the taxonomy of Cleridae by carrying out a total of 166 days of fieldwork in Inner Western Anatolia covering Afyonkarahisar, northeast of Denizli, Kütahya and Uşak provinces between May-October 2019, March-October 2021 and March-October 2022. In systematic evaluations; 16 species belonging to five genera from two subfamilies were identified by examining 992 specimens collected. The general morphologies of these species were examined, and detailed morphological descriptions were provided. Stereo microscope and Scanning Electron Microscope photographs were taken for the male reproductive organs of 15 and 14 species, respectively. Their drawings and descriptions were compared and discussed in relation to the identified species and literature data. 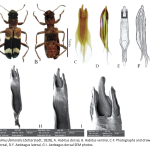



|
43 - 63 |
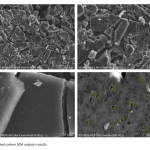
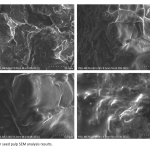
| Black Cumin Pulp-Derived Activated Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Pharmaceutical Soap Formulation In this study, we explore the utilization of black cumin pulps for the synthesis of activated carbon and its subsequent application in pharmaceutical soap formulation. Activated carbon was produced from black cumin pulps using a carbonization process followed by activation with a suitable activating agent. The synthesized activated carbon was characterized using various analytical techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Raman analysis. The results revealed the successful production of activated carbon with desirable properties for pharmaceutical applications. Subsequently, the activated carbon was integrated into soap formulations, and the resulting pharmaceutical soaps were evaluated for their antimicrobial efficacy and some chemical properties. The soap formulations exhibited effective antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms, including Candida albicans, while maintaining high skin compatibility. Moreover, the incorporation of activated carbon led to enhanced cleansing properties and biotherapeutic effects. Overall, this study highlights the potential of utilizing black cumin pulps for sustainable activated carbon production and their application in pharmaceutical soap development, contributing to both environmental and healthcare sectors. 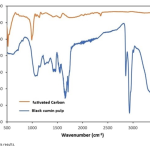
|
65 - 75 |
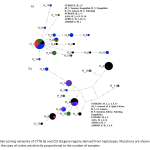
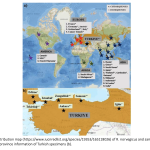
| Revealing the Genetic Differentiation of Rattus norvegicus (Berkenhout 1769) Populations by Analyzing Two Mitochondrial Markers Rattus norvegicus (Brown rat) has a significant importance for public health and economy due to its close association with human populations. However, there have been very few molecular systematic studies on global populations of R. norvegicus. In this study, sequences obtained from Türkiye, Europe, Asia, Africa, and America regions were analyzed using mitochondrial Cytochrome-b and Cytochrome oxidase-I gene regions and genetic differentiation levels between these populations were revealed. Accordingly, samples belonging to the studied populations did not split in Bayesian Inference trees and Median-joining networks; these samples also formed common haplotypes, and the mean genetic distance and fixation index values were generally low. The results of the study showed that gene flow between these populations may continue due to human transportation activity. 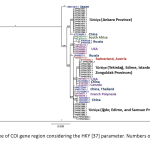

|
77 - 86 |
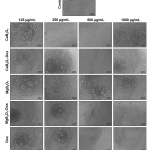
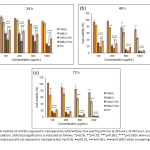
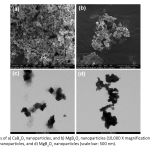
| Effect of Doxorubicin-Loaded Tetraborate Nanoparticles on HUVEC Behavior for Tumor Angiogenesis Angiogenesis supports tumor growth and facilitates metastasis to nearby tissues, making its inhibition a key target in cancer therapy. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) are commonly used for in vitro angiogenesis studies due to their role in forming blood vessels. This study investigates the effects of doxorubicin (Dox)-loaded calcium tetraborate nanoparticles (CaB4O7-Dox) and magnesium tetraborate nanoparticles (MgB4O7-Dox) on HUVEC behavior, aiming to inhibit cell proliferation and enhance the cancer treatment efficiency. CaB4O7 and MgB4O7 nanoparticles have approximately 200 nm and 300 nm sizes, respectively. Cytotoxicity studies showed that the IC50 of Dox was determined to be approximately 350 ng/mL (440 nM) for HUVECs. Dox-loaded calcium and magnesium tetraborate nanoparticles significantly outperformed free Dox and control groups in inhibiting HUVEC proliferation. Additionally, these nanoparticles significantly changed cell morphology and disrupted the tendency to tube formation, indicating their anti-angiogenic effect. These findings indicate that Dox-loaded tetraborate nanoparticles effectively modulate HUVEC behavior and angiogenesis, highlighting their potential as a nanoparticle-based system to improve the efficacy of cancer therapies. 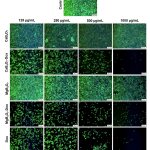
|
87 - 96 |
| Multifunctional Gelatin Hydrogel Microspheres Delivering Phages and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor The aim of this study is to prepare gelatin hydrogel microspheres (GELs) delivering phages (as antibacterial agents) and/or basic fibroblast growth factor (as a potent angiogenic factor) as multifunctional pharmaceuticals to be used in healing of infected wounds. T4 phages were propagated and tested by using E.coli as the host and the target. GELs with different crosslinking degrees were prepared by a two step process from basic and/or acidic gelatins by using different amounts of glutaraldehyde as the crosslinker. Acidic and enzymatic degradations were studies. T4 phages and/or basic fibroblast growth factor were loaded within these microspheres and release kinetics/modes were investigated/optimized. 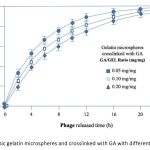
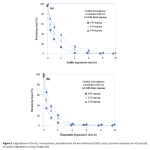
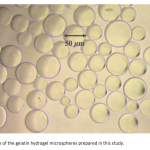
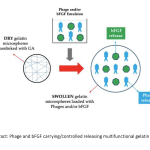
|
97 - 108 |
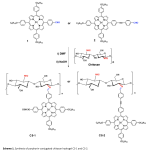
| Photochemical and Sono-Photochemical Studies of Zn (II) Porphyrin-conjugated Chitosan Hydrogels for Enhanced Singlet Oxygen Generation This study investigates the synthesis, characterization, and photochemical properties of porphyrin-chitosan hydrogels. These hydrogels, developed for potential use in photodynamic therapy (PDT) and sono-photodynamic therapy (SPDT), efficiently produce singlet oxygen, an essential reactive oxygen species (ROS) for therapy. Zinc (II) porphyrins 1 and 2 were synthesized by metal insertion to free based porphyrins and covalently linked to chitosan via Schiff-base reaction to produce chitosan hydrogel CS-1 and CS-2 (conjugation via phenylacetylene spacer). Spectroscopic analysis confirmed successful conjugation of the porphyrins, with SEM imaging showing an even distribution of porphyrins within the hydrogel. Photophysical and photochemical properties, including ground state absorption and singlet oxygen generation, were evaluated for both porphyrin complexes and chitosan-conjugated hydrogels in DMSO. The porphyrin-hydrogel structures showed superior singlet oxygen generation efficiency. Sono-photochemical studies showed further enhanced singlet oxygen generation, with the highest quantum yield (ΦΔ= 0.81) observed for the chitosan hydrogel CS-2. The results demonstrated enhanced singlet oxygen generation in the hydrogel structures, particularly under simultaneous ultrasound and light irradiation, indicating their potential efficacy in PDT and SPDT applications. Additionally, photo degradation studies revealed the stability of the synthesized compounds under light irradiation. These findings highlight the potential of porphyrin-conjugated chitosan hydrogels as effective photosensitizers for PDT and SPDT applications. 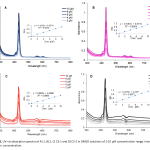


|
109 - 125 |
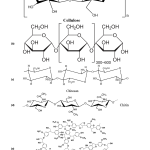
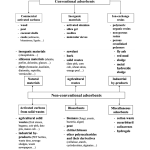
| Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Starch, Cellulose, Chitin, Chitosan and Lignin Biological Macro Molecule: Review Article Contaminant removal from sewage is a serious difficulty on the subject of water contamination. Adsorption is a direct and efficient technique for eliminating contaminants that involves the use of solid materials known as adsorbents. Mineral, organic, or biological adsorbent materials can be utilized. At the industrial scale, activated carbon is the favored traditional material. Activated carbon is widely used to remove contaminants from wastewater streams and to absorb them from groundwater, rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, which are all sources of potable water. However, because of its expensive cost, activated carbon is not widely used. Several ways of utilizing non-conventional adsorbents have been investigated over the last three decades to generate cheaper and more effective adsorbents to remove contaminants at trace levels. This article provides an overview of liquid-solid adsorption techniques for pollution removal that use low-cost polymer adsorbents. The paper discusses the fundamentals of adsorption and provides a classification for adsorbent materials as well as numerous low-cost biological macromolecule adsorbents, includes cellulose, starch, chitin, chitosan, lignin, and their heavy metal removal capability. 
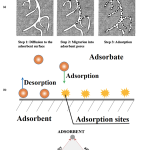
|
127 - 158 |
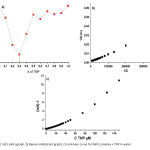
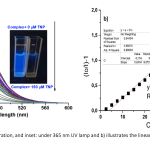
| Schiff Base-Nickel(II) Complex: A Robust Luminescent Probe For The Detection Of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol İn An Aqueous Medium This study delved into the fluorescence properties of a Ni(II) Schiff base complex towards nitroaromatic compounds, such as dinitrobenzene (DNB), 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), 2,4-dinitrotoluene (DNT), 2-nitrophenol (2-NP), 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP), and 1,3,5-trinitrophenol (TNP),. Remarkably, the compound exhibited exceptional sensitivity in detecting TNP, with a notable Ksv value of 40.5 × 103 M-1 . LOD value of the targeted compound was found to be 0.134 μM, encompassing a linear working range of 2.50–50.00 μM.. Furthermore, the synthesized Ni(II) complex proved effective in the fluorescence quenching-based detection of TNP in water solutions, demonstrating both high selectivity and sensitivity. Through fluorescence titrations (Job's plot), the stoichiometry between the compound and TNP was found to be 2/1 (complex/TNP). This finding underlines the potential utility of the complex as a promising tool in environmental monitoring or related fields where the detection of TNP is crucial. 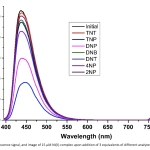
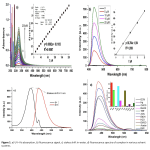
|
159 - 168 |