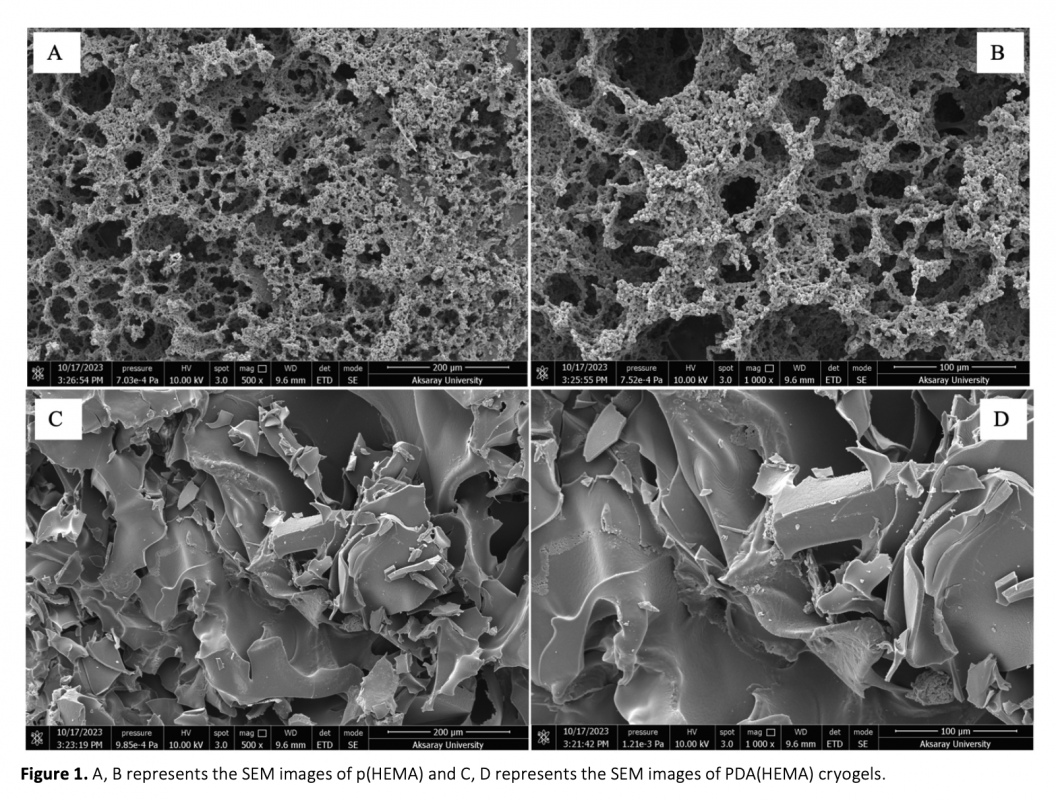
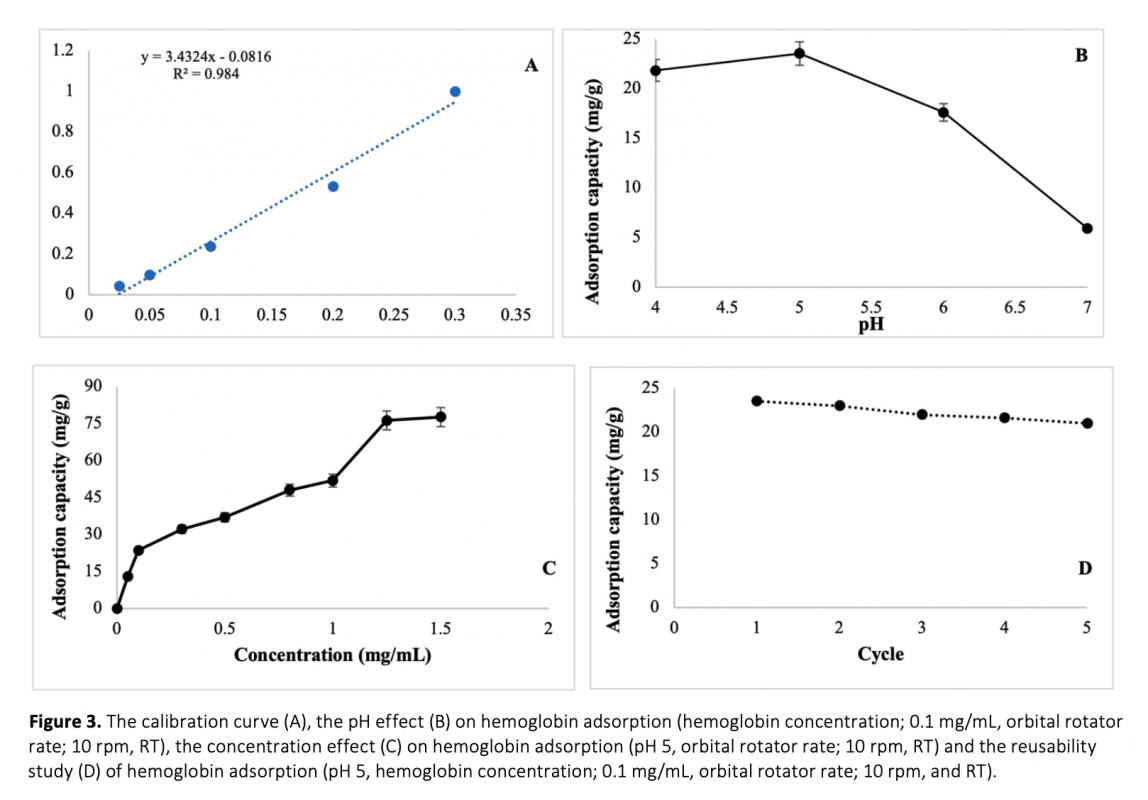
Nickel ions were were utilized in this study due to forming of strong complexes with histidine and its ability to interact with histidine-containing proteins and for this goal, an affinity adsorbent of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (p(HEMA) was developed to purify hemoglobin with the assistance of Ni ions. Initially, cryogel membranes of p(HEMA) were prepared and their surfaces were modified with the dopamine monomer to create polydopamine (PDA) modified p(HEMA) cryogel PDA(HEMA) membranes. After the modification, the nickel (Ni) ions were immobilized on PDA(HEMA) for Hb purification in the aqueous solution. According to experimental findings, at pH 5, the adsorbent successfully adsorbed 23.5 mg/g of Hb. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm model was found to accurately describe this adsorption process, as evidenced by the high R2 and q max values. Furthermore, it was observed that the adsorption capacity of the prepared adsorbent remained consistent without significant decreases, even after multiple uses.
Bu çalışmada histidin ile güçlü kompleksler oluşturması ve histidin içeren proteinlerle etkileşime girme yeteneğinden ötürrü nikel iyonları kullanılmış ve bu amaçla, Ni iyonlarının yardımıyla hemoglobini saflaştırmak için poli(2-hidroksietilmetakrilat) (p(HEMA) aesaslı bir afinite adsorbenti geliştirilmiştir. İlk olarak, p(HEMA) kriyojel membranlar sentezlenmiş ve yüzeyleri dopamin monomeri kullanılarak polidopamin (PDA) kriyojeller PDA(HEMA) hazırlanmıştır. Modifikasyon sonrasında, nikel (Ni) iyonları PDA(HEMA) üzerine sulu çözeltiden hemoglobin (Hb) saflaştırılması için immobilize edilmiştir. Deney sonuçlarına göre pH 5 de, adsorbent tarafından 23.5 mg/g Hb’ni adsorpladığı görülmüştür. Langmuir adsorpsiyon isoterm modeli yüksek R2 değeri ve q maks değerlerine doğrultusunda bu adsorpsiyon işlemi için uygun olarak bulunmuştur. Ayrıca, birçok kez tekrar kullanım sonunda, hazırlanmış olan adsorbentin adsorpsiyon kapasitesinde önemli kayıpların olmadığı görülmüştür.

Download Article in PDF (2.0 MB)