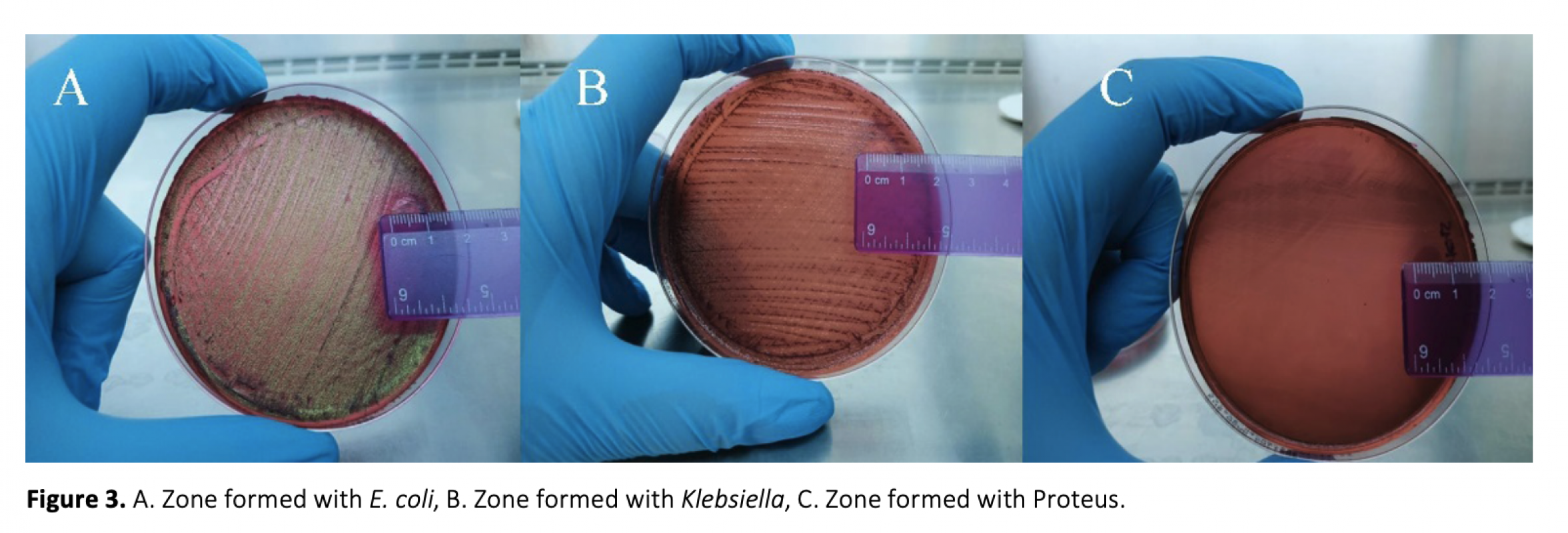
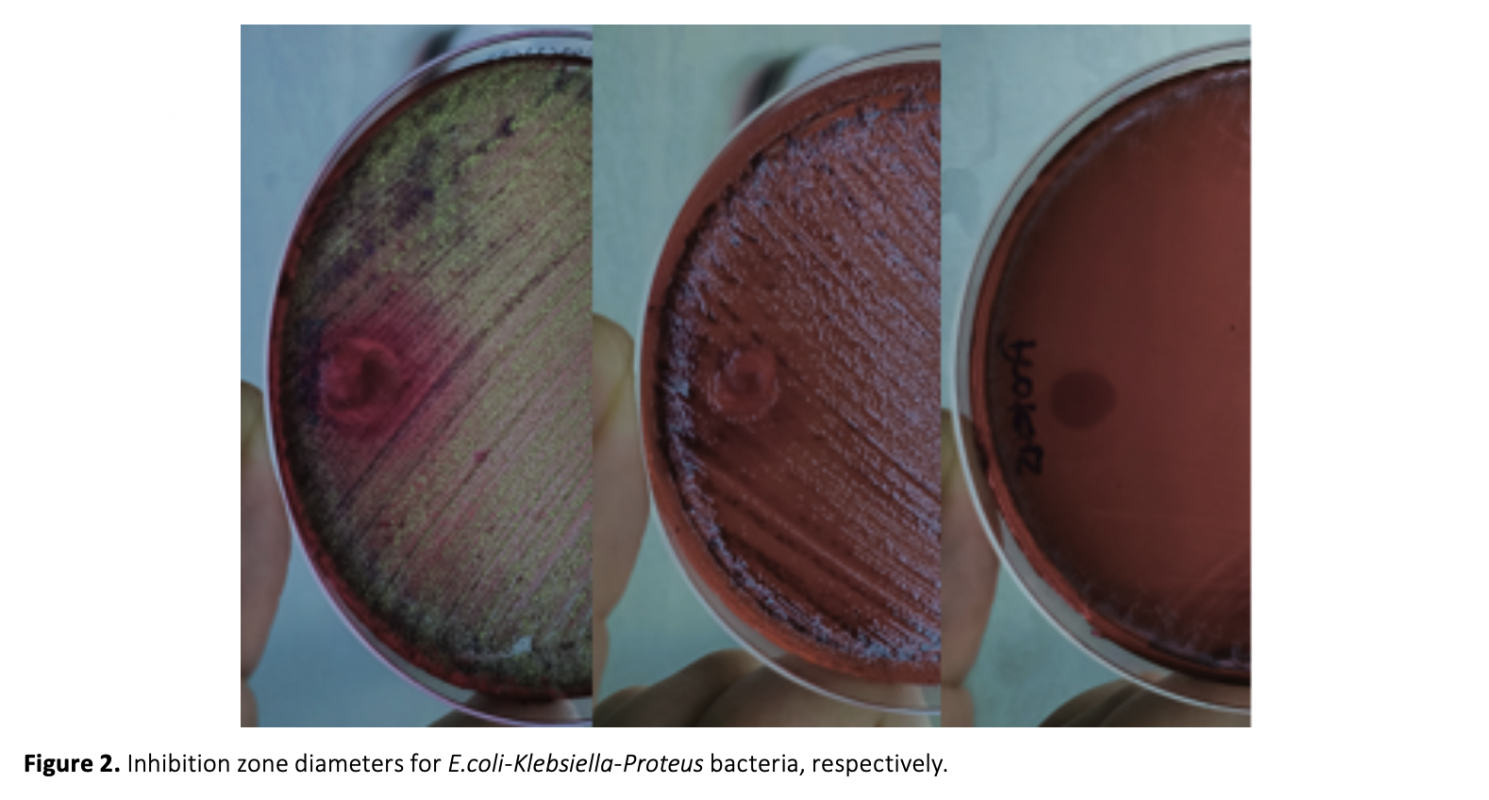
Scorpion venom, is a neurotoxic secretion produced by the venom glands in telson of scorpions, consisting of many proteins, peptides, and biologically active compounds, and it is commonly used in catching and digesting prey. The peptides within scorpion venoms hold significant pharmacological importance, particularly in the fields of cancer treatment, analgesics, and anesthesia. In recent years, bacteria developing resistance to antibiotics drew a significant level of interest. The present study investigates the antibacterial activity of the venom obtained from Aegaeobuthus gibbosus (Brulle, 1832). The antibacterial effects were observed by applying crude venom by using the dripping method on Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, and Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria in suitable environments. As a result, it was determined that the venom of Aegaeobuthus gibbosus is effective against Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, and Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria.
Akrep zehri, akreplerin telsonlarında bulunan zehir bezleri tarafından üretilen, birçok protein, peptid ve biyolojik yönden etkin bileşiklerden oluşan nörotoksik etkili bir salgı olup, genellikle avını yakalamada ve sindirimde kullanılır. Akrep zehirlerinin içerisindeki peptidler farmakolojik olarak oldukça önemlidir. Özellikle kanser, ağrı kesiciler grubu ve anestezide yararlanılmaktadır. Son yıllarda antibiyotiklere karşı direnç kazanan bakteriler dikkat çekmektedir. Bu çalışmada A. gibbosus (Brulle, 1832) türüne ait zehrin antibakteriyel aktivitesi araştırılmıştır. Araştırmada Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris ve Klebsiella pneumoniae bakterilerine uygun ortamda damlatma yöntemi ile ham zehir uygulanarak antibakteriyel etkileri gözlemlenmiştir. Sonuç olarak A. gibbosus zehrinin Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris ve Klebsiella pneumoniae bakterilerine karşı etkili olduğu tespit edilmiştir.


Download Article in PDF (1.2 MB)