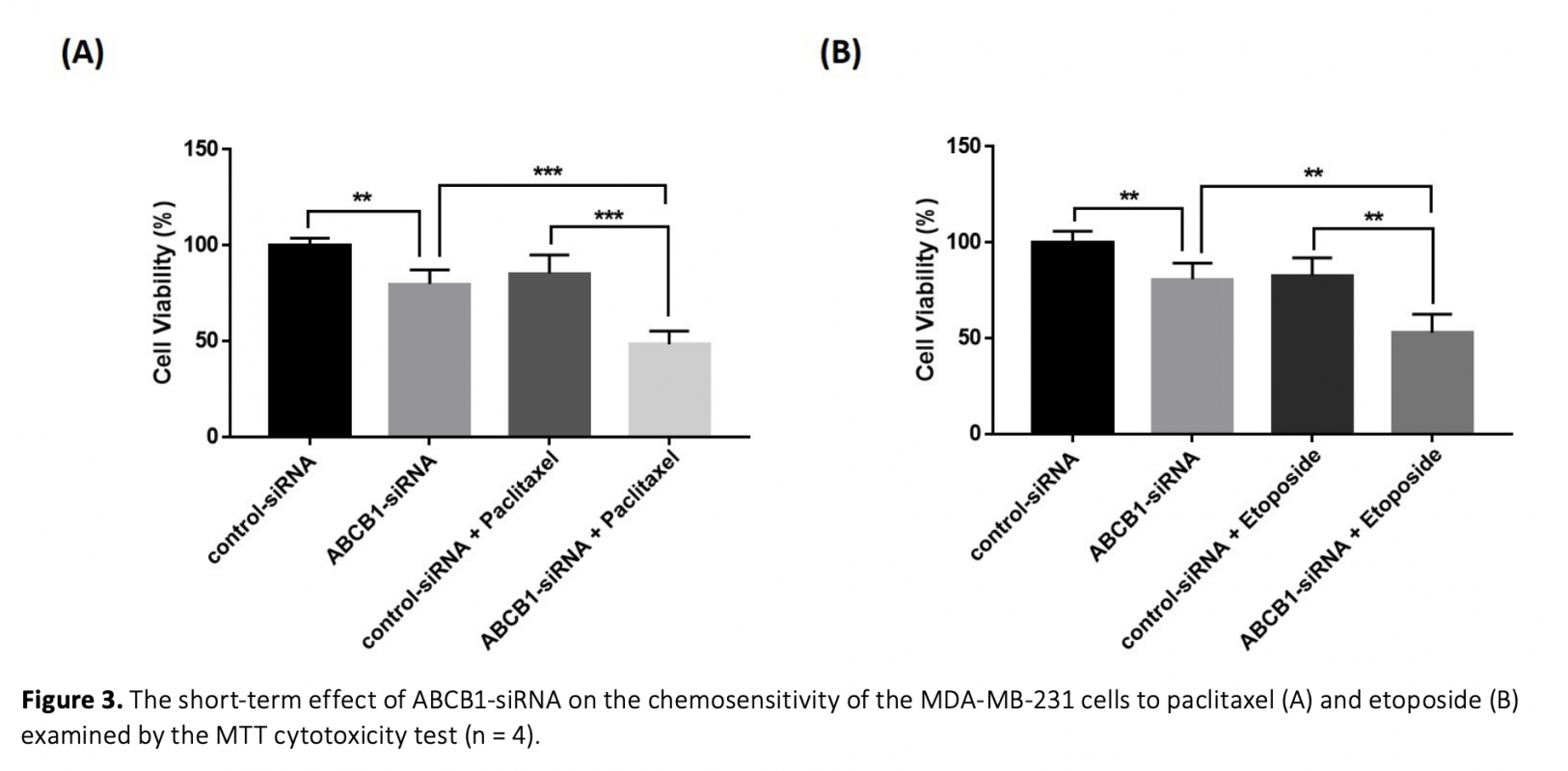
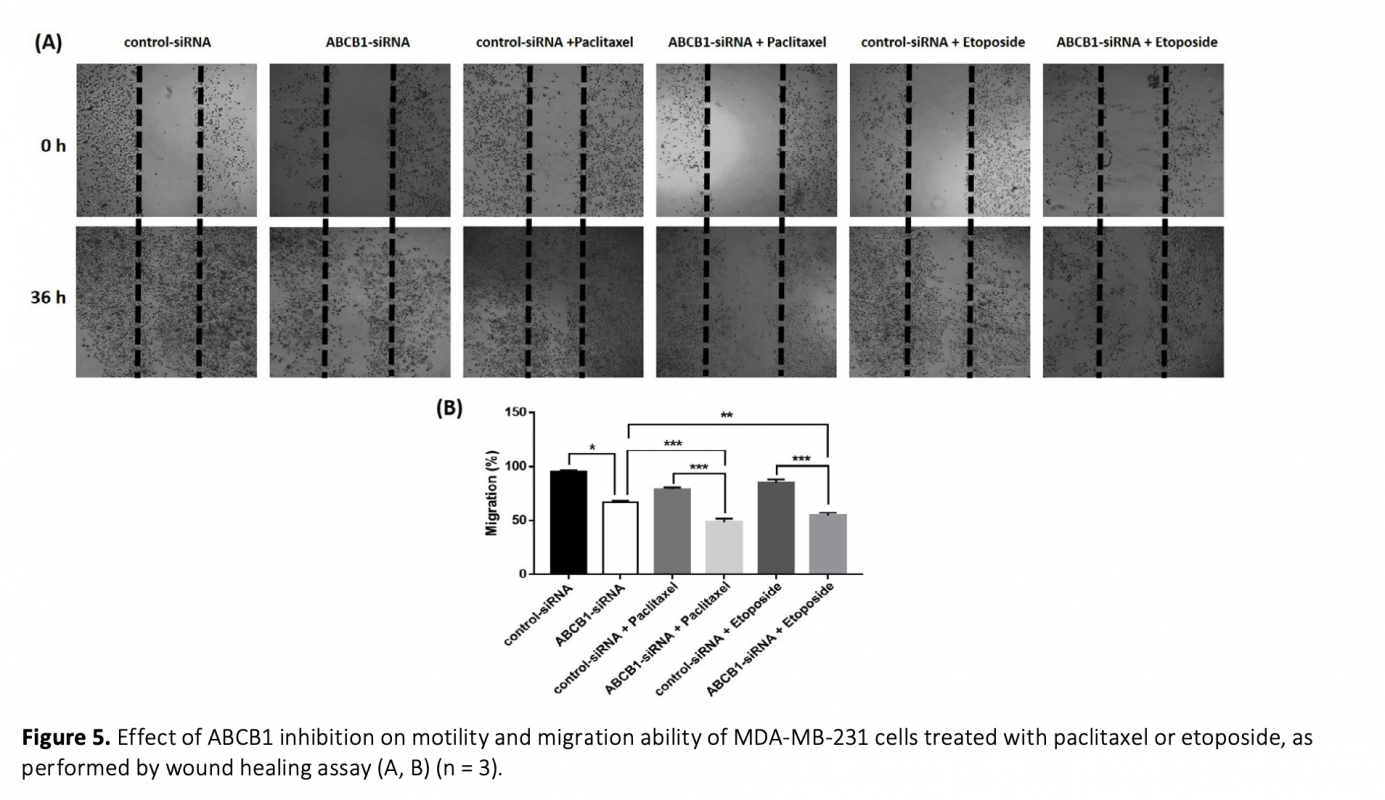
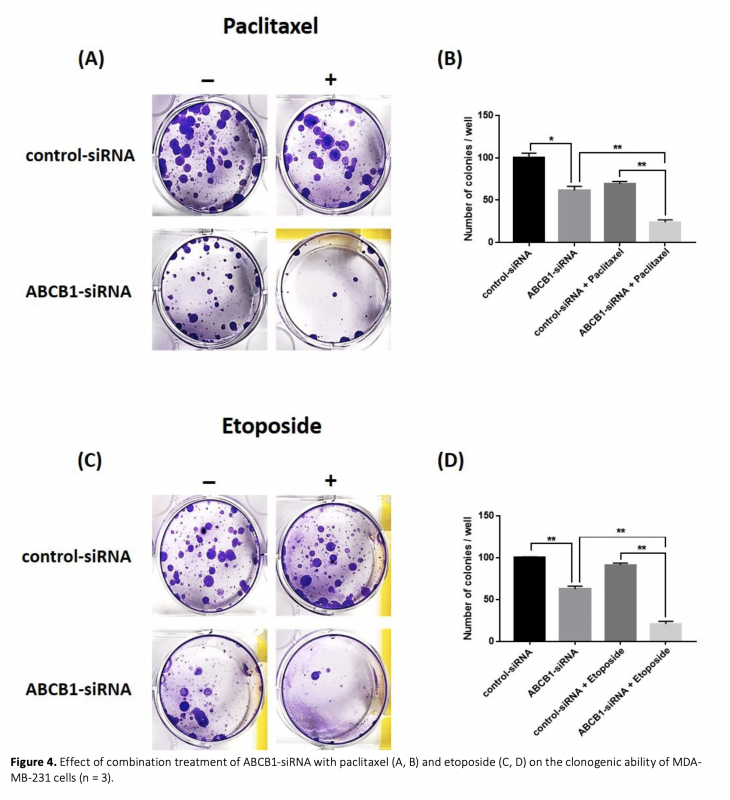
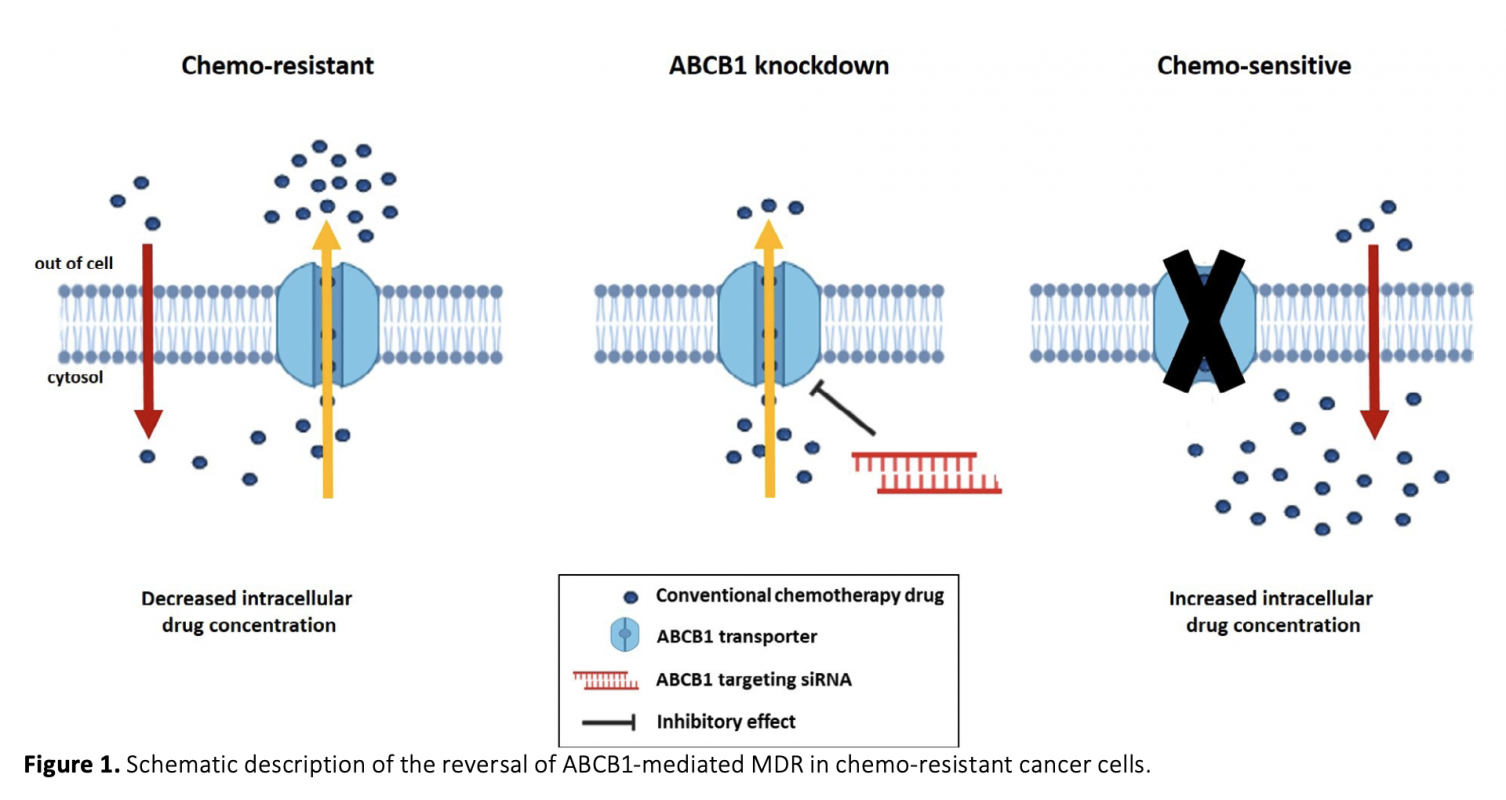
Diminishing the efficacy of chemotherapy because of multidrug resistance (MDR) is a major clinical problem for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). MDR often occurs by overexpression of ATP-binding cassette B1 (ABCB1) protein that effuses various anticancer drugs from cancer cells. One of the newly developed techniques to address MDR is to knockdown ABCB1 by RNA interference (RNAi). RNAi is a gene-silencing process in that small interfering RNA (siRNA) blocks the expression of desired genes with high efficiency/specificity. The aim of this work is to examine the impact of ABCB1 inhibition via specific siRNAs on the efficacy of paclitaxel or etoposide in TNBC cells. The toxicity of increasing paclitaxel and etoposide concentrations on MDA-MB-231 cells was assessed using the MTT test. Cells were then cotreated with paclitaxel or etoposide in combination with ABCB1-siRNA, followed by cytotoxicity, colony formation, and migration assays. The administration of ABCB1-siRNA with paclitaxel or etoposide exhibited a synergistic effect and siRNA-drug treatments markedly reduced viability, clonogenicity, and migration of TNBC cells compared to siRNA or drug alone. Overall, these results indicate that TNBC cells become vulnerable even to sub-toxic doses of paclitaxel and etoposide after ABCB1-siRNA transfection, representing a promising approach to enhance the influence of chemotherapy in TNBC.
Çoklu ilaç direnci (MDR) nedeniyle kemoterapinin etkinliğinin azalması, üçlü-negatif meme kanseri (TNBC) için önemli bir klinik sorundur. MDR sıklıkla, kanser hücrelerinden çeşitli antikanser ilaçları dışarı sızdıran ATP bağlayıcı kaset B1 (ABCB1) proteininin aşırı ekspresyonu ile oluşur. MDR'yi ele almak için yeni geliştirilen tekniklerden biri, ABCB1'i RNA interferans (RNAi) ile devre dışı bırakmaktır. RNAi, küçük interfere edici RNA'nın (siRNA) istenen genlerin ekspresyonunu yüksek verimlilik/spesifite ile bloke ettiği bir gen susturma mekanizmasıdır. Bu çalışmanın amacı, spesifik siRNA'lar aracılığıyla ABCB1 susturmasının TNBC hücrelerinde paklitaksel veya etoposidin etkinliği üzerindeki etkisini incelemektir. MDA-MB-231 hücrelerinde artan paklitaksel ve etoposid konsantrasyonlarının toksisitesi MTT testi ile değerlendirilmiştir. Hücreler daha sonra ABCB1-siRNA ile kombinasyon halinde paklitaksel veya etoposid ile birlikte muamele edilmiş, ardından sitotoksisite, koloni oluşumu ve göç deneyleri yapılmıştır. ABCB1-siRNA'nın paklitaksel veya etoposid ile uygulanması sinerjistik bir etki sergilemiş ve siRNA-ilaç tedavileri, siRNA veya tek başına ilaca kıyasla TNBC hücrelerinin canlılığını, klonojenisitesini ve göçünü belirgin şekilde azaltmıştır. Genel olarak, bu sonuçlar, TNBC hücrelerinin, ABCB1-siRNA transfeksiyonundan sonra alt-toksik paklitaksel ve etoposid dozlarına karşı bile savunmasız hale geldiğini ve TNBC'de kemoterapinin etkisini iyileştirmek için umut verici bir stratejiyi temsil ettiğini göstermektedir.
Download Article in PDF (2.3 MB)