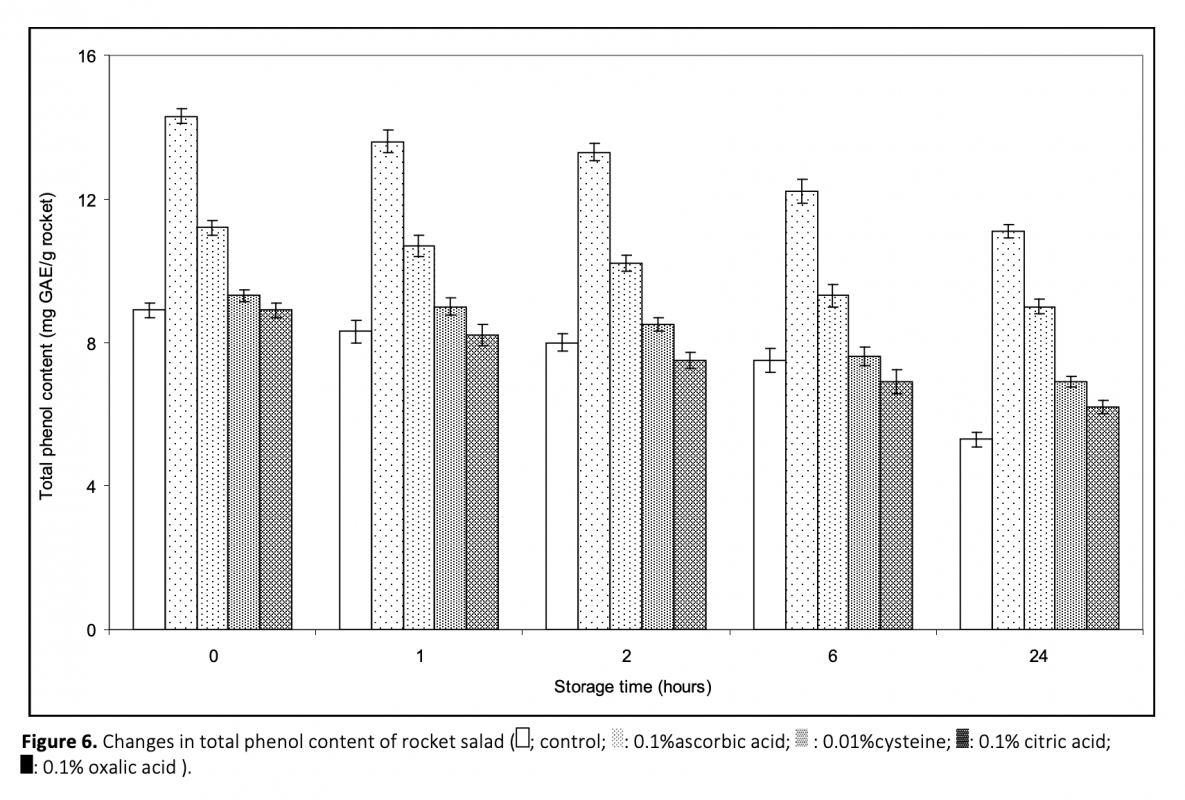
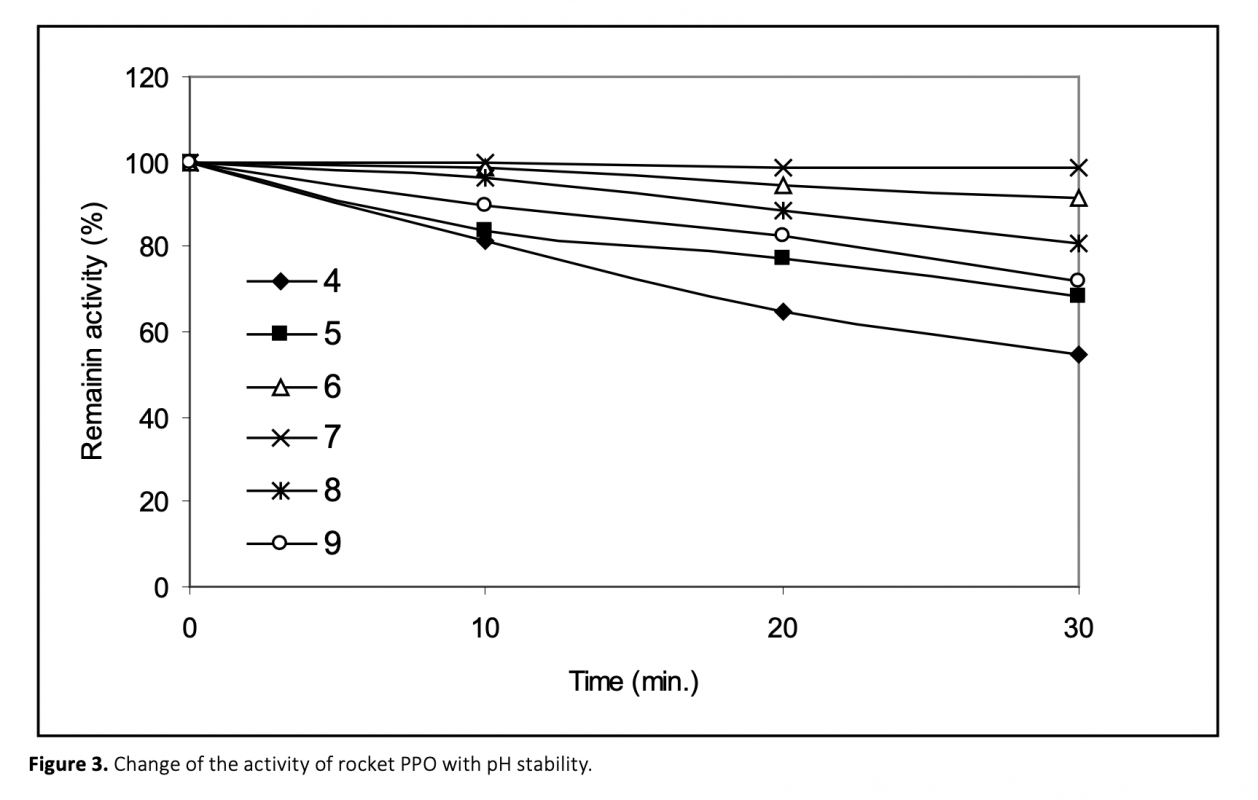
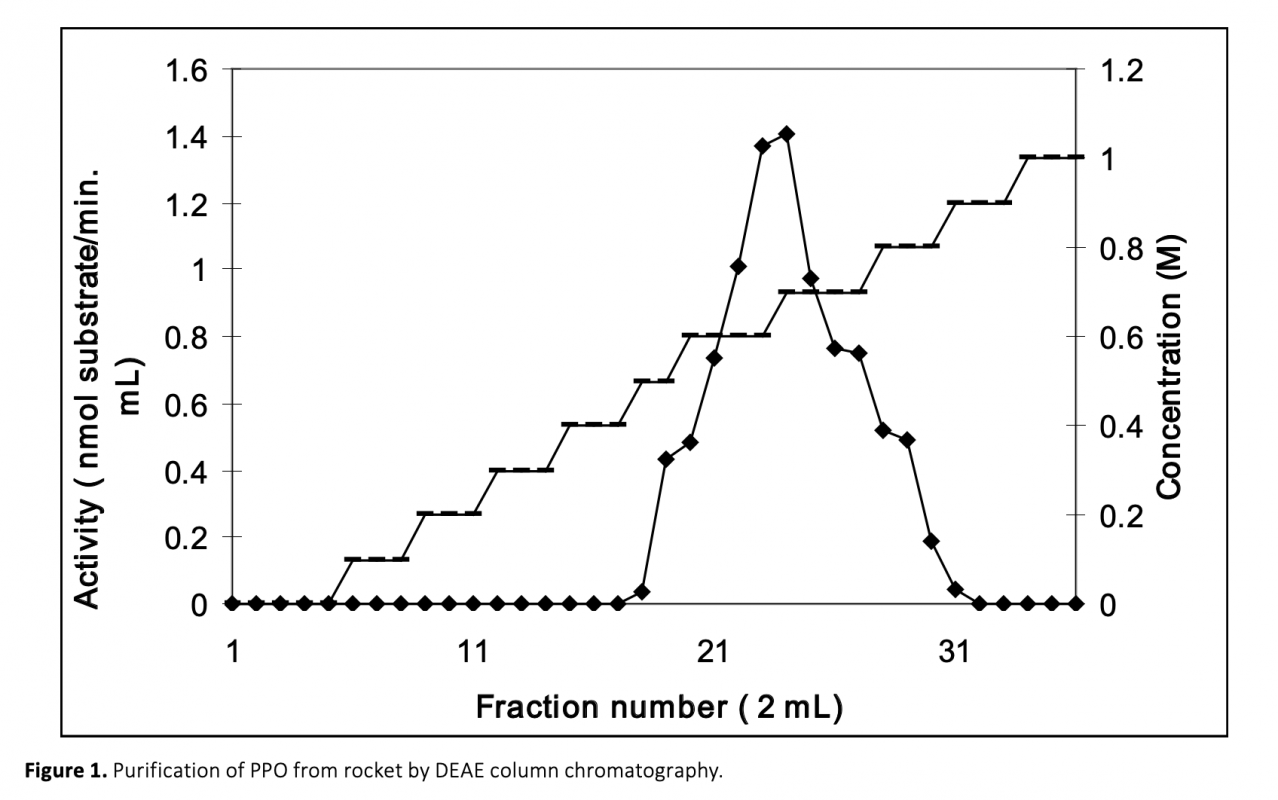
In this study, polyphenol oxidase (PPO) was extracted and partially purified by ion-exchange chromatography on a column packed with diethyaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE) from fresh rocket salad. Its optimum temperature and pH were found to be 30°C and 6.0, respectively. Rocket PPO was shown to the greatest substrate specificity with catechol among the substrates used. Ascorbic acid, cysteine, oxalic acid and citric acid were tested as potential inhibitors of rocket PPO. Cysteine was found as the most effective inhibitor. While ascorbic acid increased the total antioxidant activity of rocket significantly, Rocket phenolics were protected from oxidation by the treatments of these inhibitors.
Bu çalışmada, taze roka salatasında bulunan polifenoloksidaz (PPO), dietilaminoetil selüloz (DEAE) ile doldurulmuş kolon üzerinden kısmen saflaştırılmıştır. Optimum sıcaklığı 30°C ve pH 6.0 olarak bulunmuştur. Roka PPO, en yüksek substrat spesifikliğini kullanılan substratlar arasında kateşol ile göstermiştir. Askorbik asit, sistein, okzalik asit ve sitrik asit potansiyel inhbitörler olarak test edilmiştir. En etkili inhibitor sistein olarak belirlenmiştir. Askorbik asit toplam antioksidan aktiviteyi arttırken, kullanılan inhibitörlerin Rokada bulunan fenolik bileşiklerin oksidasyonunu önlediği tespit edilmiştir.

Download Article in PDF (475.3 kB)