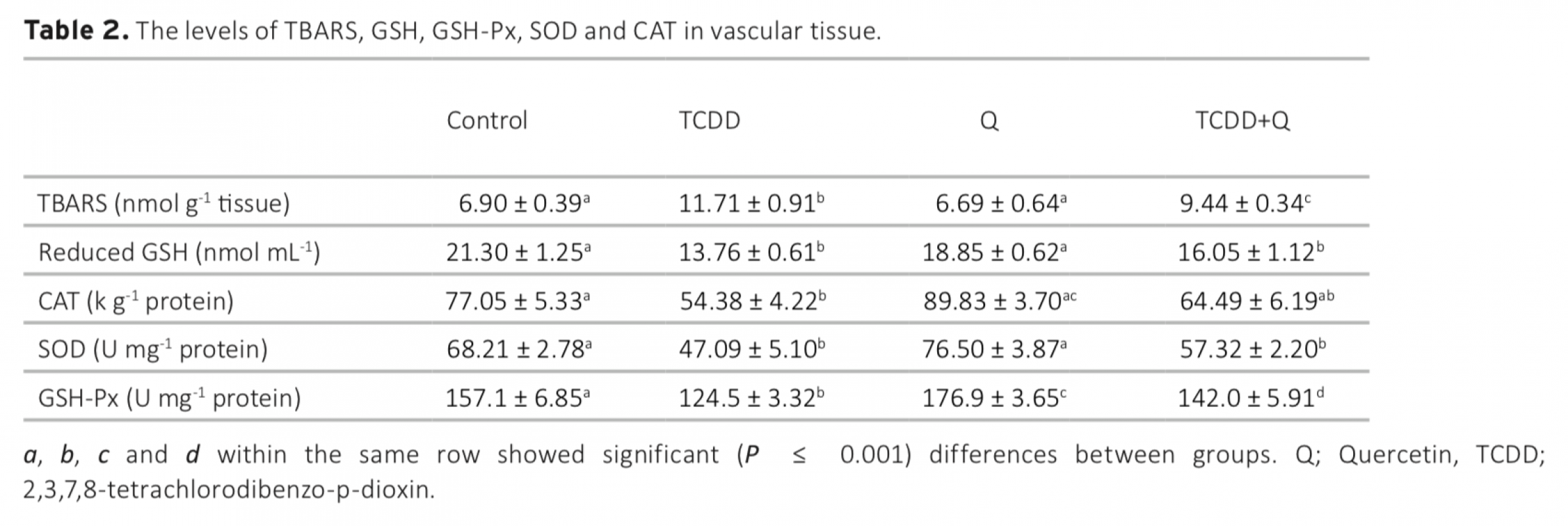
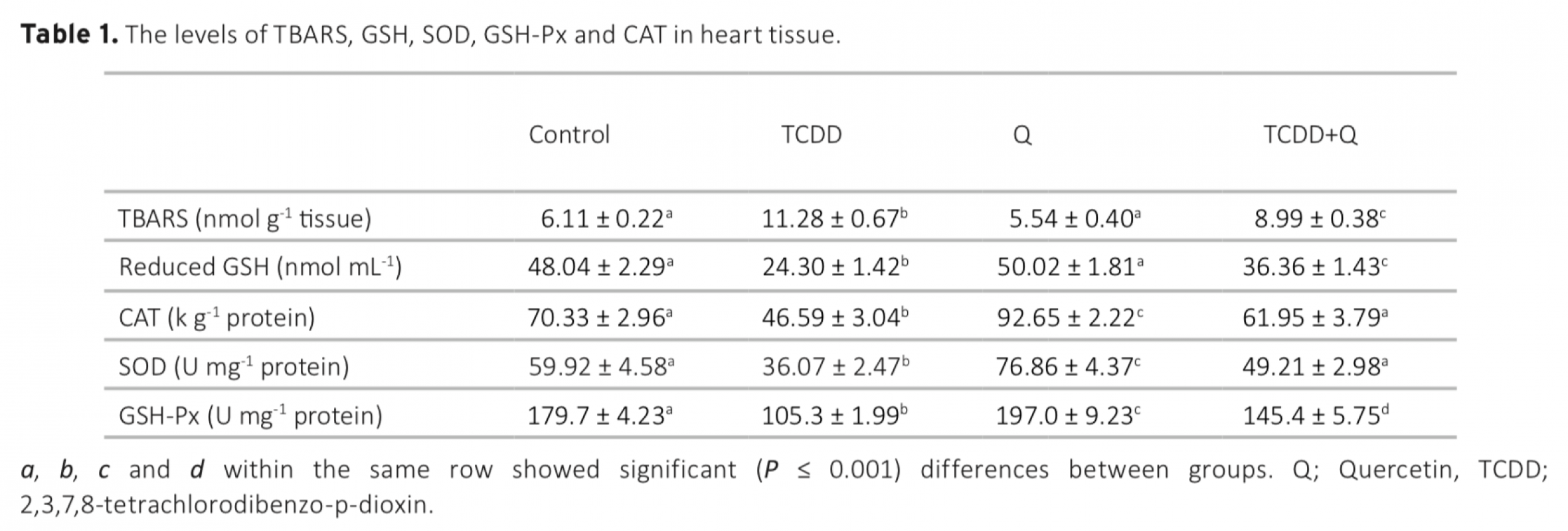
In this study, 28 Wistar Albino male rats were randomly divided into four equal groups. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p- dioxin (TCDD) was intraperitoneally administered at the dose of 2 μg/kg/week, quercetin was administered at the dose of 20 mg/kg/day by gavages, and quercetin+TCDD were intraperitoneally administered at the doses of 20 mg/kg/day and 2 μg/kg/week, respectively. All applications were performed for 8 weeks. At the end of the eighth week, the rats were sacrificed and their heart and vascular tissues were taken for biochemical analysis (reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) levels) by spectrophotometric method. As a result of the study, TCDD significantly decreased antioxidant activities and increased lipid peroxidation in rats. In contrast, quercetin significantly prevented the toxic effects of TCDD via increasing SOD, CAT, GSH and GSH-Px levels but decreased the formation of TBARS. Therefore, it can be suggested that quercetin has the potential for treatment against the toxicity caused by TCDD or other environmental contaminants and can decrease the risk of mortality due to cardiovascular diseases, especially in humans.
Bu çalışmada, 28 adet Wistar Albino erkek sıçan rastgele dört eşit gruba ayrıldı. 2,3,7,8-tetraklorodibenzo-p-dioksin (TCDD) 2 μg/kg/hafta dozda intraperitonal olarak uygulandı, kuersetin 20 mg/kg/gün dozda gavajla uygulandı, ve kuersetin+TCDD birlikte sırasıyla 20 mg/kg/gün ve 2 μg/kg/hafta dozlarda uygulandı. Tüm uygulamalar sekiz hafta boyunca gerçekleştirildi. Sekizinci haftanın sonunda sıçanlar sakrifiye edildi ve kalp ve damar dokuları spektrofotometrik yöntemle biyokimyasal analizler (redükte glutatyon (GSH), glutatyon peroksidaz (GSH-Px), katalaz (CAT), süperoksit dismutaz (SOD) ve tiyobarbitürik asit reaktif sübstansları (TBARS) düzeyleri) için alındı. Çalışmanın sonucunda, TCDD sıçanlarda antioksidan aktiviteleri önemli ölçüde azaltmış ve lipid peroksidasyonunu arttırmıştır. Aksine, kuersetinin artan SOD, CAT, GSG ve GSH-Px düzeyleri ile TCDD’nin toksik etkisini önemli ölçüde engellediği ancak TBARS oluşumunu azalttığı belirlenmiştir. Bu nedenle, kuersetinin TCDD ve diğer çevresel kirleticiler tarafından oluşan toksisiteye karşı tedavi potansiyeline sahip olduğu ve özellikle insanlarda kardiyovasküler rahatsızlıklara bağlı ölüm riskini azaltabileceği önerilebilir.
Download Article in PDF (399.5 kB)