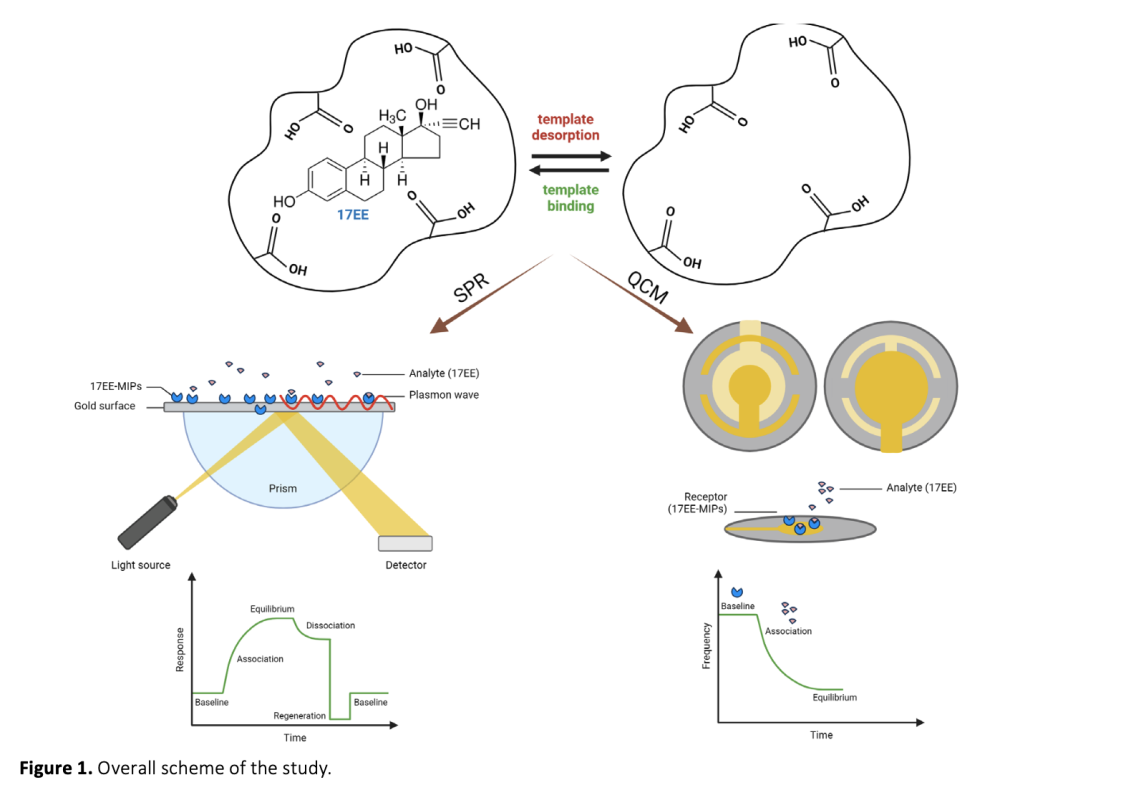
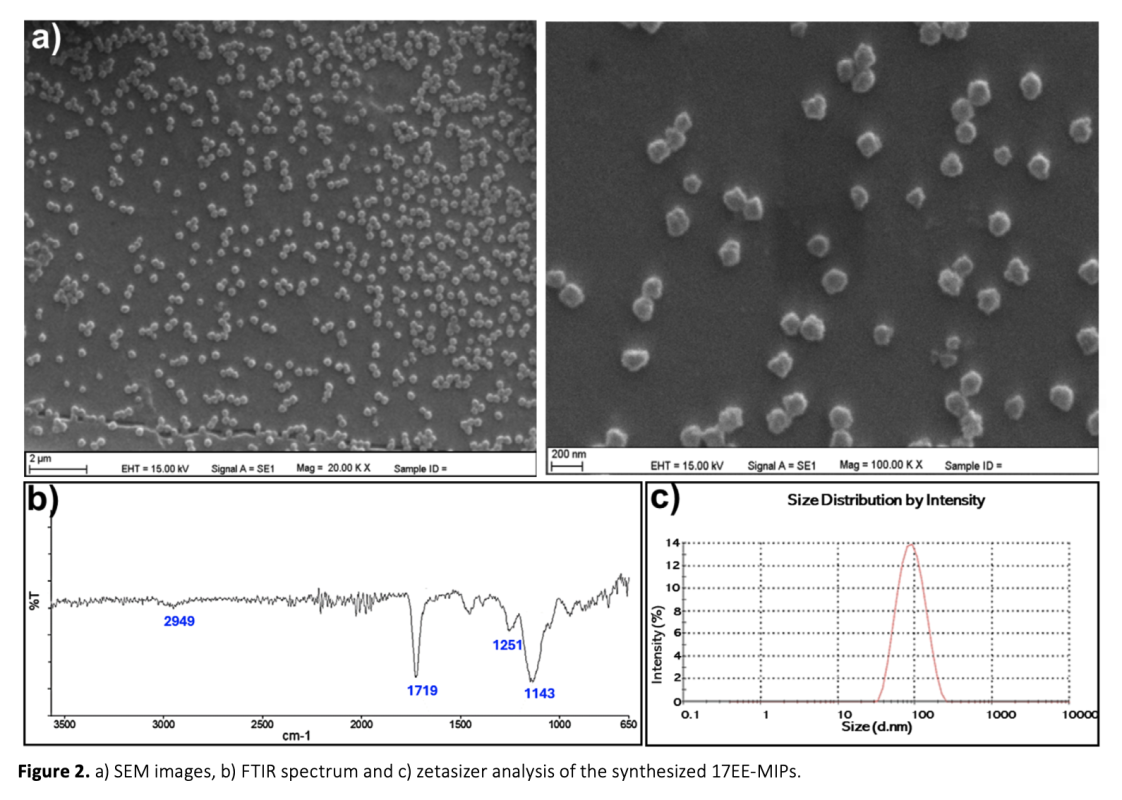
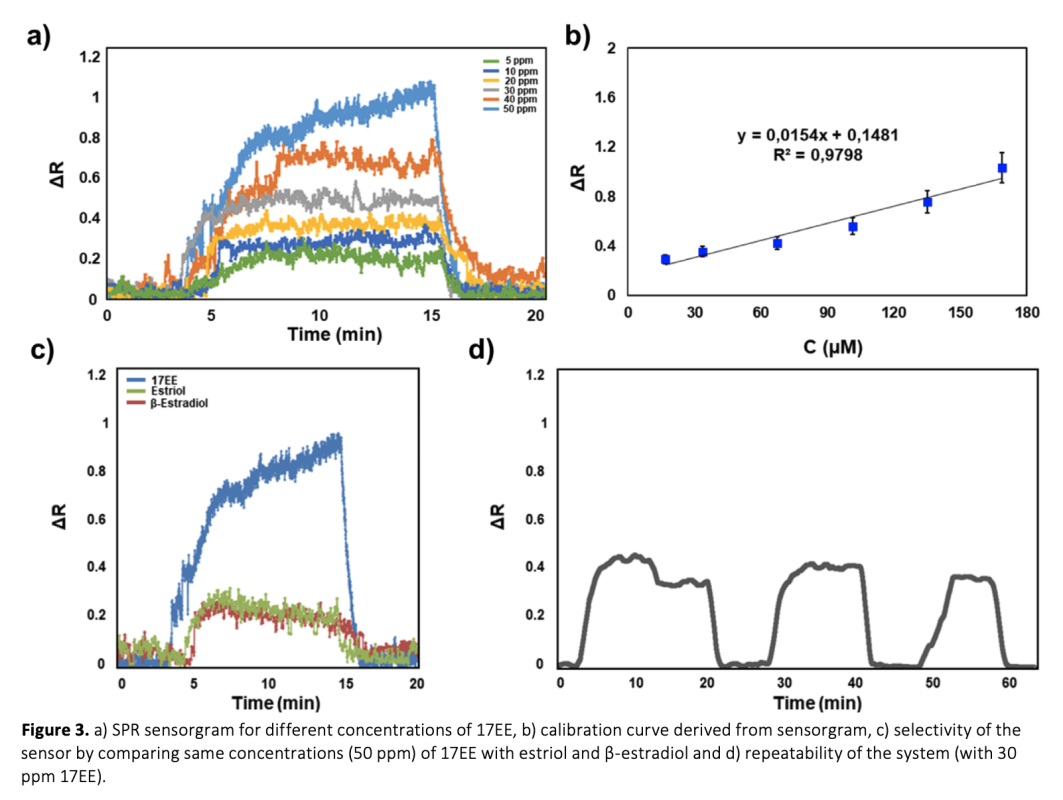
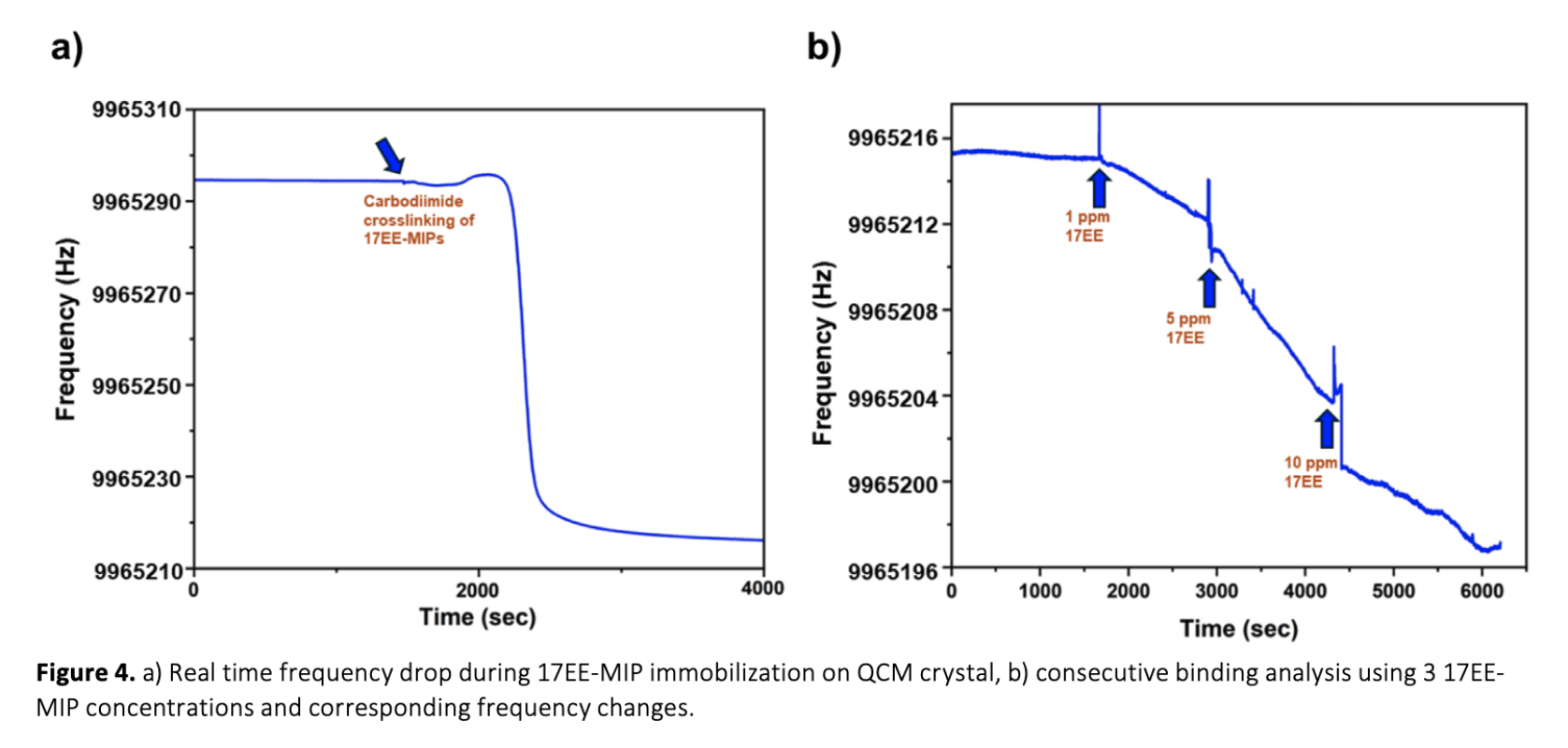
Estradiol is a critical hormone for reproductive health in both females and males, playing a key role in diagnosing conditions such as menopause, infertility, and certain cancers. However, estradiol, especially in its synthetic form, 17α-ethinyl estradiol (17EE), also represents a significant environmental threat as an endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), with serious implications for ecosystems and human health. Despite growing awareness of 17EE's role in water contamination and its potential to disrupt aquatic ecosystems and human endocrine systems, existing detection methods for 17EE are limited. Establishing reliable, rapid, and sensitive biosensors for estradiol detection is thus essential for both environmental monitoring and healthcare. In this study, 17EE-imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (17EE-MIPs) were synthesized using mini-emulsion polymerization and characterized. The synthesized 17EE-MIPs were evaluated using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) and Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) platforms. SPR analysis yielded equilibrium and binding kinetic parameters, with the Freundlich model providing the best fit for the 17EE-MIP based system. Following this, 17EE-MIPs were covalently attached to a QCM crystal, where consecutive 17EE concentrations were tested. Both platforms demonstrated high linearity in detecting low concentrations of 17EE, with detection limits of 11.57 µM and 1.335 µM for SPR and QCM, respectively. These results underscore the potential of using MIPs to develop highly sensitive biosensors for hormone detection, with applications in both environmental and healthcare fields.
Estradiol, hem kadın hem de erkeklerde üreme sağlığı için kritik bir hormondur. Estradiol seviyelerinin izlenmesi, menopoz, kısırlık ve bazı kanser türleri gibi çeşitli durumların teşhisinde yardımcı olabilir. Ayrıca estradiol, ekosistemler ve insan sağlığı üzerinde çeşitli etkileri olan bir endokrin bozucu kimyasal türüdür. Tarımsal akış, kanalizasyon ve endüstriyel atıklar yoluyla çevreye girebilir. Bu iki perspektif göz önüne alındığında, estradiol tespiti için biyosensörlerin geliştirilmesi büyük önem taşır. Bu çalışmada, 17-α-etinilestradiol baskılanmış polimerik nanopartiküller (17EE-MBP) mini-emülsiyon polimerizasyonu kullanılarak sentezlenmiş ve karakterize edilmiştir. Kuartz Kristal Mikrobalans (KKM) analizinden önce, 17EE-MBP Yüzey Plazmon Rezonansı (YPR) ile test edilmiştir. Elde edilen verilerden denge ve bağlanma kinetiği analizleri ile denge izoterm modelleri çıkarılmıştır. Freundlich modeli, 17EE-MBP tabanlı YPR platformunu en iyi şekilde temsil etmiştir. Daha sonra, 17EE-MBP KKM kristaline kovalent olarak bağlanmış ve farklı 17EE derişimleri ardışık olarak test edilmiştir. Her iki sistem de yüksek doğrusal sonuçlar vermiştir. YPR ve KKM sensörlerinin tespit limitleri sırasıyla 11.57 ve 1.335 µM olarak hesaplanmıştır. Burada, iki algılama platformu 17EE-MBP'in performansını doğrulamak için kullanılmış ve düşük konsantrasyonlara yüksek tutarlılıkla tepki verdikleri doğrulanmıştır.
Download Article in PDF (1.9 MB)