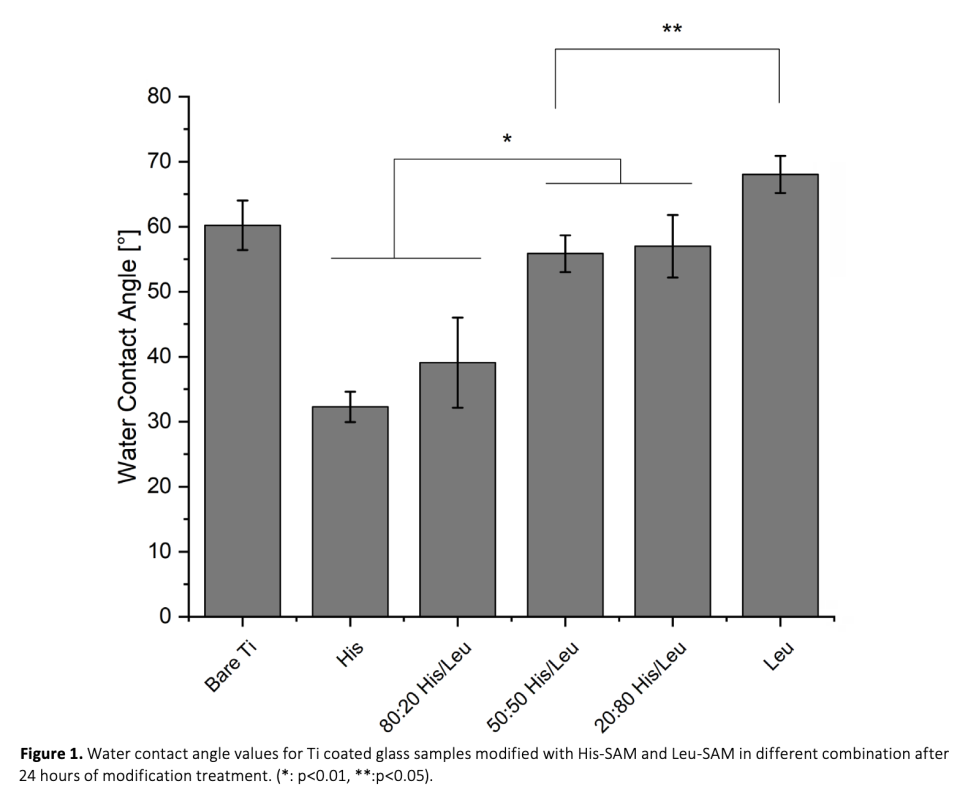
In this study, human fetal osteoblasts behavior was investigated on titanium surfaces that has been modified with amino acid conjugated self-assembled molecules. For this purpose, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was conjugated by histidine and leucine and these newly synthesized molecules were used in different combinations to modify titanium surfaces via creating amino acid conjugated self-assembled monolayers (SAM) on titanium surfaces. The modification of the surfaces to introduce hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions on the surface was achieved with varying concentrations (v/v,100:0 20:80, 50:50, 80:20, 0:100). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis and water contact angle measurements were performed for characterizing all of the modified surfaces in order to verify presence of amino acid specific bonds and wettability behavior to find suitable concentrations to support initial cell adhesion. In order to confirm that the surface modification supported cell adhesion and proliferation, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was performed. Our results have shown that, amino acid SAM modification can be used to fine tune surface wettability and adherent cells were able to proliferate at different rates using different mixture concentrations. This presented approach can prove useful for expanding fine tuning surface chemistry methods for more specific applications and research.
Bu çalışmada insan fetal osteoblast hücrelerinin amino asit konjüge edilmiş kendiliğinden oluşan tek katman molekül modifikasyonu (TKM) yapılmış titanium yüzeyler üzerindeki davranışı incelenmiştir. 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), histidine ve lösin ile konjüge edilmiş ve bu yeni moleküller değişken konsantrasyonlarda karıştırılarak titanium yüzeylerde TKMler oluşturmaları sağlanmıştır. Hidrofobik ve hidrofilik bölgeler bu amino asit konjüge moleküllerin değişken konsantrasyonlarının yüzeylere modifiye edilmesiyle elde edilmiştir (v/v, 100:0 20:80, 50:50, 80:20, 0:100). X-ray fotoelektron spekroskopisi (XPS) analizi ve yüzey su temas açısı analizleriyle modifiye edilmiş yüzeylerde amino asit konjüge moleküllerin varlığı gösterilmiş ve yüzey ıslanması değerlerine göre ilk hücre tutunmasını destekleyecek uygun karışım oranı tayin edilmiştir. Hücre tutunması ve çoğalmasının gösterilmesi ve tayini için MTT testi kullanılmıştır. Sonuçlar, amino asit TKMlerinin yüzey ıslanılabilirliğini ayarlamak için kullanılabileceğini ve farklı karışım oranlarında farklı hücre çoğalması davranışlarının görüldüğünü göstermektedir. Bu çalışmada kullanılan modifikasyon yaklaşmı, titanyum yüzeylerinin kimyasının isteğe göre ayarlabilirliğini ve bu yöntem ile daha spesifik araştırmaların yapılabileceğini göstermektedir.


Download Article in PDF (1.2 MB)