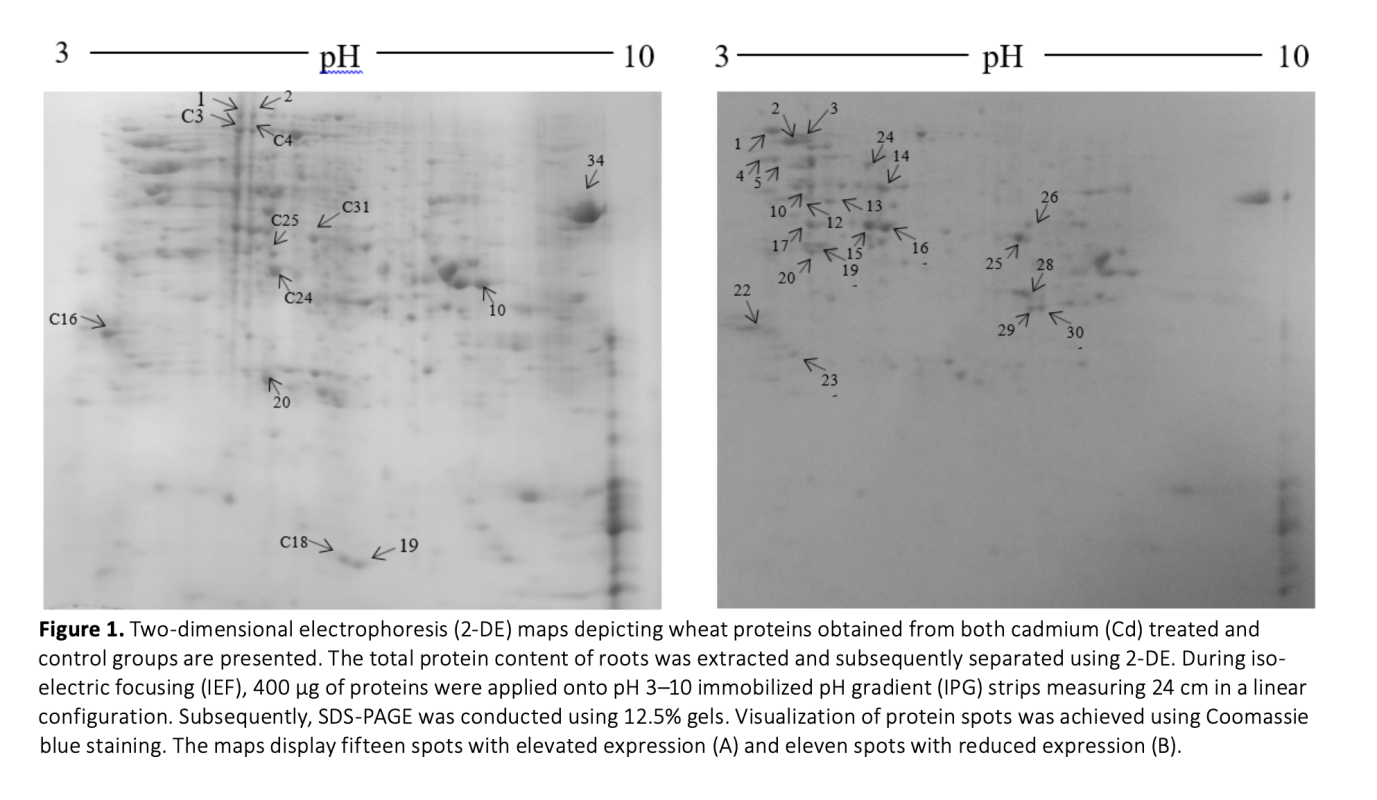
The current study aims to assess the changes in protein abundance in wheat roots upon exposure to cadmium, using a proteomic approach. Wheat seeds were cultivated in a nutrient solution comprised specific macro and micronutrients under controlled environmental conditions and treated with 30 μM Cd for three days. In order to comprehend the impact of Cd stress on the protein level in wheat, a differential proteomics investigation was conducted utilizing two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-DE). Fifty two protein spots were clearly identified and exhibited a consistent and significant alteration between the control and stressed samples. Out of the fifty two proteins, twenty seven exhibited changes in abundance following Cd stress, with seventeen proteins being up-regulated and ten proteins being down-regulated. Differentially regulated proteins were selected after image analysis and identified using MALDI-TOF MS. The identified differential proteins were primarily associated with stress response (41%) and metabolism (35%). These proteins were discovered to play a role in various processes, including protein biosynthesis, carbon metabolism, transportation, and stress response. The findings from our proteomics analysis indicate that Cd stress significantly impacts the stress response in wheat. This study provides novel insights that contribute to an enhanced comprehension of the molecular mechanisms implicated in the plant's reaction to cadmium-induced stress.
Bu çalışma, proteomik bir yaklaşım kullanarak, kadmiyuma maruz kaldıktan sonra buğday köklerindeki protein bolluğundaki değişiklikleri değerlendirmeyi amaçlamaktadır. Buğday tohumları kontrollü çevre koşulları altında belirli makro ve mikro besin maddelerinden oluşan bir besin çözeltisinde yetiştirilmiş ve 3 gün boyunca 30 μM Cd ile muamele edilmiştir. Cd stresinin buğdaydaki protein seviyesi üzerindeki etkisini anlamak için, iki boyutlu poliakrilamid jel elektroforezi (2-DE) kullanılarak bir diferansiyel proteomik araştırması yapılmıştır. Elli iki protein beneği açıkça tanımlanmış ve kontrol ve stres altındaki örnekler arasında tutarlı ve önemli bir değişiklik sergilemiştir. Bu elli iki proteinden yirmiyedisi Cd stresini takiben bollukta değişiklik göstermiş, onyedi protein yukarı regüle edilirken 10 protein aşağı regüle edilmiştir. Diferansiyel olarak regüle edilen proteinler görüntü analizi ile seçildikten sonra MALDI-TOF MS kullanılarak tanımlandı. Tanımlanan farklı proteinler öncelikle stres (%41) ve metabolizma (%35) ile ilişkilendirilmiştir. Bu proteinlerin protein biyosentezi, karbon metabolizması, taşıma ve stres tepkisi dahil olmak üzere çeşitli süreçlerde yer aldığı bulunmuştur. Proteomik analizimizden elde edilen bulgular, Cd stresinin buğdaydaki stres tepkisini önemli ölçüde etkilediğini göstermektedir. Bu çalışma, bitkinin kadmiyum stresine verdiği yanıtın altında yatan moleküler mekanizmaların daha iyi anlaşılmasına katkıda bulunan yeni bilgiler sağlamaktadır.


Download Article in PDF (566.4 kB)