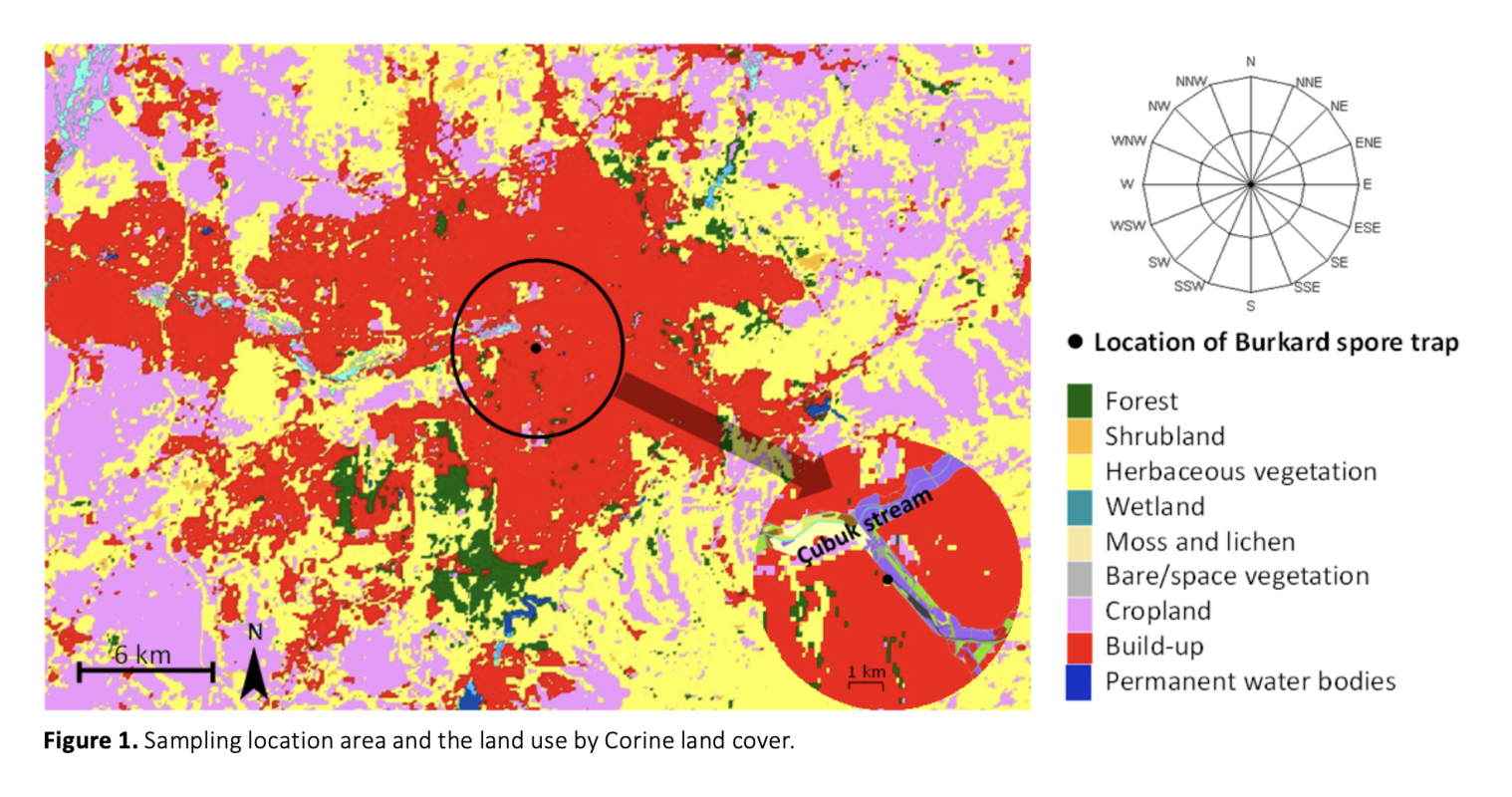
The objective of the research was to examine how meteorological conditions and air pollution affect the levels of Salicaceae pollen in the Ankara province. Salicaceae, a plant family encompassing willows and poplars, generates pollen that may contribute to respiratory allergies. The study employed a Burkard volumetric 7-day spore trap for airborne pollen monitoring throughout the pollen season, spanning from March to June in the year 2023. The relations between pollen concentrations, various meteorological parameters and air pollutants were revealed by correlation and regression analysis. While, the wind direction was found to be positively correlated with Populus pollen concentration, there was also a positive relationship between relative humidity and Salix pollen loads. Additionally, air pollutants, including PM10, PM2.5 and nitrogen oxides, were found be positive impact on the abundance of Populus pollen. Understanding these relationships is crucial for assessing the potential health risks associated with airborne pollen and for developing strategies to mitigate the impact of urban environmental factors on pollen concentration.
Bu çalışmada Ankara ilinde meteorolojik faktörlerin ve hava kirliliğinin Salicaceae polen konsantrasyonuna etkisinin araş- tırılması amaçlandı. Bu familyayı oluşturan söğüt ve kavak ağaçlarının polenleri solunum yolu alerjilerini tetikleyebilmektedir. Havadaki polen izlemesi, 2023 yılının Mart ayından Haziran ayına kadar polen mevsimi boyunca Burkard volumetric spor tuzağı kullanılarak gerçekleştirildi. Polen konsantrasyonları, çeşitli meteorolojik parametreler ve hava kirleticileri arasındaki ilişkiler korelasyon ve regresyon analizi ile ortaya çıkarıldı. Rüzgar yönü ile Populus polen konsantrasyonu arasında pozitif korelasyon bulunurken, bağıl nem ile Salix polen yükü arasında pozitif ilişki bulunmuştur. Ayrıca PM10, PM2.5 ve nitrojen oksitler de dahil olmak üzere hava kirleticilerinin Populus poleninin bolluğu üzerinde olumlu etkisi olduğu tespit edildi. Bu ilişkilerin anlaşılması, havadaki polenlerle ilişkili potansiyel sağlık risklerinin değerlendirilmesi ve kentsel çevresel faktörlerin polen konsantrasyonu üzerindeki etkisini hafifletmeye yönelik stratejiler geliştirilmesi açısından çok önemlidir.



Download Article in PDF (1.9 MB)