| Title | Pages |
|---|---|
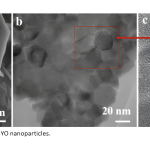
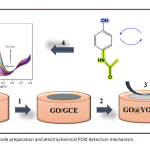
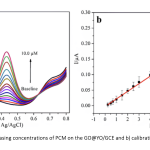
| Layered Yttrium Oxide Reinforced Graphene Oxide Electrode Surface for Voltammetric Determination of Paracetamol In this study, graphene oxide (GO) was synthesized by the Hummers method starting from graphite. Also, yttrium(III) oxide (Y2O3, YO) was synthesized with the sol-gel method and was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-Ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques. The sensor performance of the modified electrode against the paracetamol analyte was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). As a result of the optimized voltammetric methods calculated the linear working range was 0.25-10.0 μM and the limit of detection (LOD) value was 19.0 nM. With the DPV method, advanced analytical parameters such as stability, reproducibility, and selectivity were studied. Moreover, the performance of the new sensor to detect paracetamol in real tablet samples was examined. 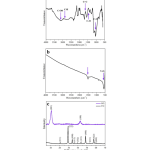
|
63 - 75 |
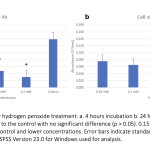
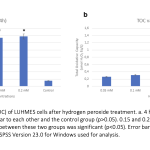
| Establishing an Oxidative Stress Model in the Human Mesencephalic Cell Line (LUHMES): an in vitro study Oxidative stress-caused neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, are widely recognized as the most prevalent brain and central nervous system disorders. This is attributed to the vulnerability of neurons to oxidative stress within the body. Although substantial research has been performed on these diseases, it is extremely difficult to establish an oxidative stress model for brain tissues. In primary cultures, it is difficult to obtain neurons and the continuity of the culture is limited for in vitro cell line models. By providing valuable insights into the mechanisms of oxidative stress-induced neurodegenerative diseases, these in vitro models can aid in the development of effective treatment strategies. Here, we developed an in vitro oxidative stress model utilizing hydrogen peroxide on the LUHMES cell line. Our study evaluated the impact of this model on LUHMES cell viability and the equilibrium between oxidants and antioxidants by assaying total oxidant capacity (TOC) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC). Our results provided evidence of oxidative effect of hydrogen peroxide in critical concentration and proved the efficacy of this model for further investigations. 

|
77 - 83 |
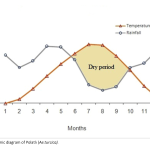
| Reclassifying the Threat Categories of Two Rare Plant Species Endemic to Central Anatolia Aethionema turcica and Astragalus beypazaricus are rare endemic plant species restricted to marly-gypsaceous soils from Ankara, Turkey. In a study in 2000, Ae. turcica and A. beypazaricus were classified under the “Least Concern” and “Critically Endangered” threat categories, respectively. This study aimed to reassess the global conservation status of these species according to the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria by using the recent findings based on their population sizes, distribution areas, and the main threats. Field research was conducted between 2016 and 2018. Additionally, physical-chemical soil tests were run, and the climatic data were utilized to draw bioclimatic conclusions. In Ankara, there are twopopulations of Ae. turcica, with 359 mature individuals covering 12 km2 AOO and 23.5 km2 EOO areas. A. beypazaricus has only one fragmented population with a total of 5700 mature individuals in Beypazarı, and both AOO and EOO were discovered to be 4 km2. Both species are on the verge of extinction due to habitat fragmentation and loss formed by intense anthropogenic activity. According to the findings, the IUCN threat categories for Ae. turcica and A. beypazaricus were suggested to be reclassified as CR based on the criteria B1ab(ii, iii) and B1ab(ii, iii)+2ab(ii, iii), respectively. 

|
85 - 95 |
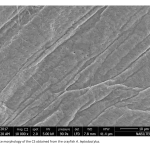
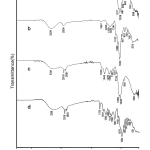
| Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Release From Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked Chitosan/Β-Cyclodextrin Hydrogel In this study, chitosan was produced from crayfish Astacus leptodactylus, and then it was used to synthesize chitosan-graft-β-cyclodextrin (CS-g-β-CD) hydrogel. The produced chitosan (CS) and the sythesized CS-g-β-CD hydrogel were characterized using a Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-NMR), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) was used as a model to investigate the antiviral drug release properties of the CS-g-β-CD hydrogel. The synthesized hydrogel had an almost homogeneous pore structure and a high swelling capacity which increases depending on the amount of β-Cyclodextrin (β-CD). The drug-loaded CS-g-β-CD hydrogels was examined by XRD, 1H-NMR, and SEM analyses. Seventy-three percent of the TDF loaded on the synthesized hydrogels was released into phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution at 37°C. The drug release behavior of all prepared CS-g-β-CD hydrogels fitted the Korsmeyer-Peppas model. The addition of β-CD into the gel improved the swelling ability and TDF release of the CS-g-β-CD hydrogel system. 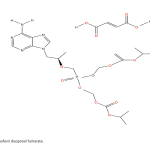

|
97 - 115 |
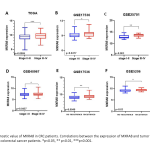
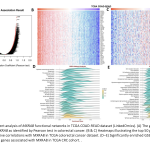
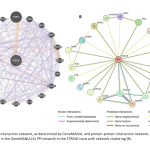
| Prognostic Implications of MXRA8 Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Its role in Tumor Progression Matrix Remodeling Associated 8 (MXRA8) is a type I transmembrane protein capable of modulating integrin-related signaling and regulating cellular interactions, and also functions as a receptor for multiple arthritogenic alphaviruses. Although limited numbers of studies have provided evidence indicating a potential role of MXRA8 in different types of cancer, the potential contrubition of MXRA8 in colorectal cancer (CRC) has not yet been fully elucidated. Therefore, our aim was to conduct a comprehensive analysis elucidating the prognostic value of MXRA8 in CRC. The results revealed that MXRA8 was highly expressed in CRC compared to normal tissue. Notably, there was a substantial correlation with the TNM stage, and elevated MXRA8 expression was indicative of a poorer prognosis in CRC cases. Furthermore, co-expression analysis indicated that MXRA8 is predominantly involved in hypoxia and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway. In conclusion, this study demonstrates the potential roles of MXRA8 in predicting CRC prognosis and contributes to the elucidation of how MXRA8 might be involved in the mechanisms underlying CRC carcinogenesis. 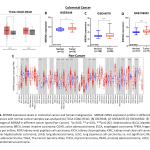
|
117 - 128 |
| Indole-Bearing Azo Compounds: Molecular Docking and in silico ADMET Analysis In this study, the interaction between the 12 indole-bearing azo compounds (a-l), which were previously synthesized by our research group, and two proteins, 2XIR and 5TGZ, was investigated using an in silico method. The ligand-protein interaction parameters and quantities were determined via molecular docking simulation studies. Since compound e has the lowest docking scores for both 2XIR and 5TGZ, it was selected for additional research on binding interactions. Both e-2XIR and e-5TGZ had docking scores that were lower than those of the control molecules. ADMET characteristics (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) were anticipated using the ADMETlab 2.0 and ProTox-II server. Compound b was categorized as having the greatest levels of toxicity, falling into the sixth toxicity class. 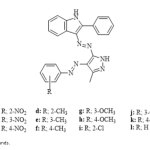

|
129 - 138 |