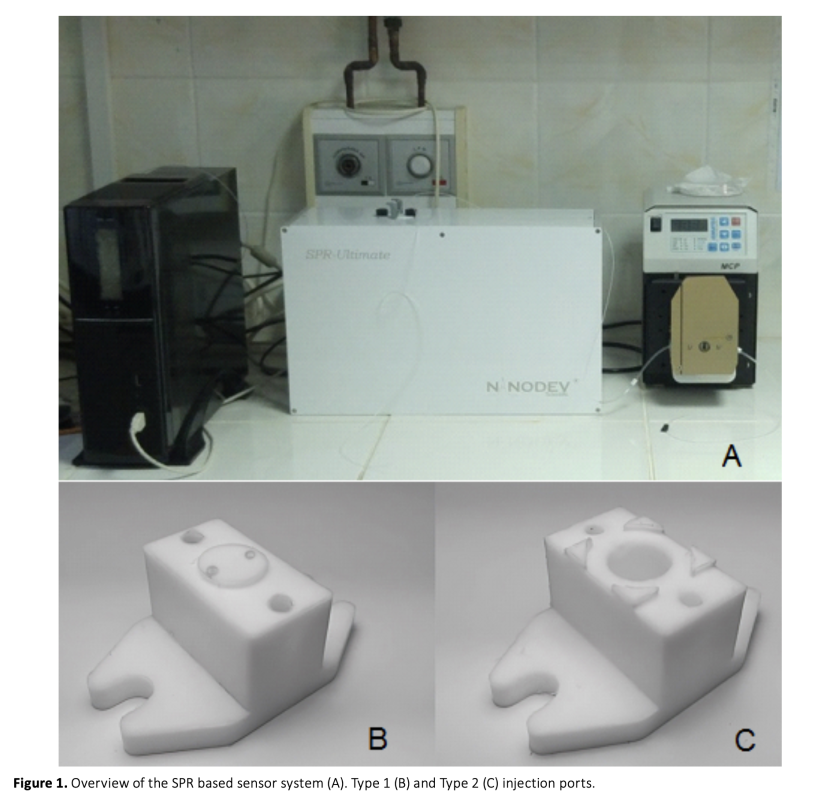
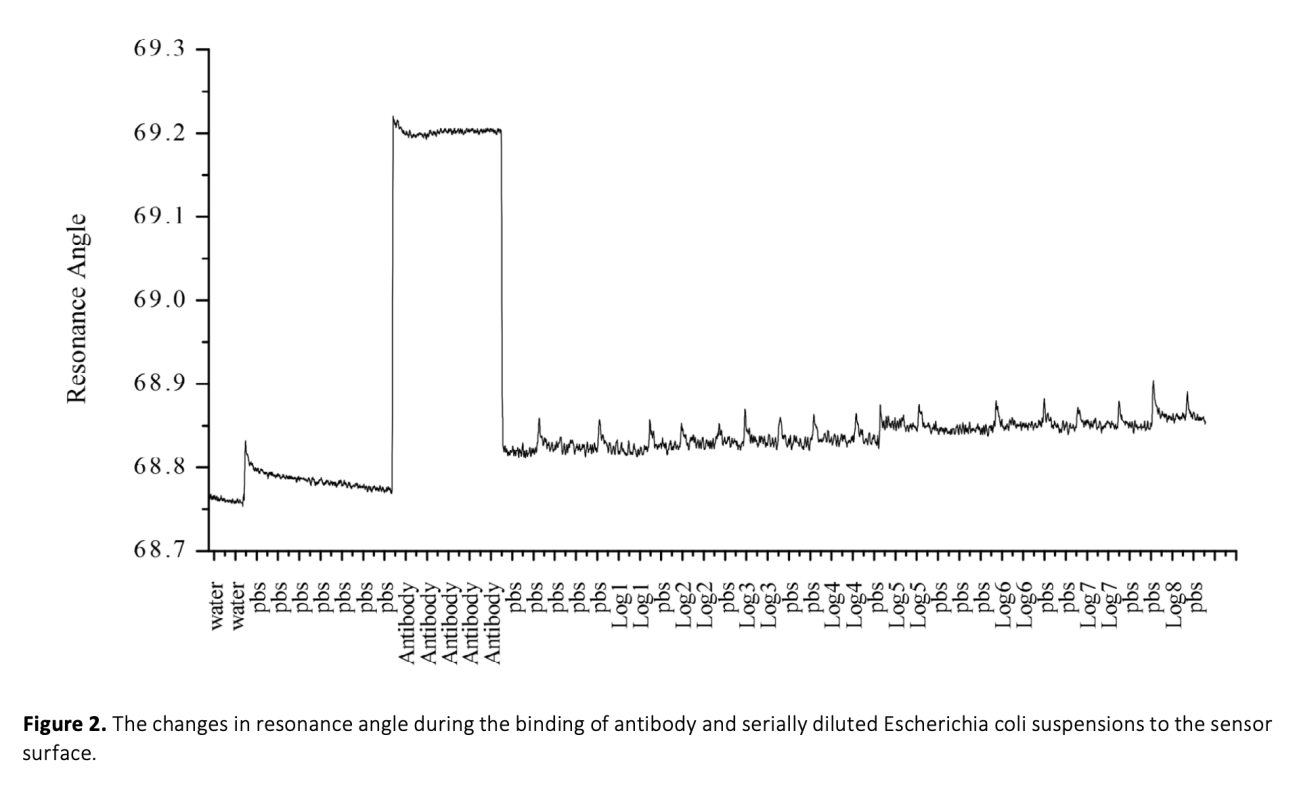
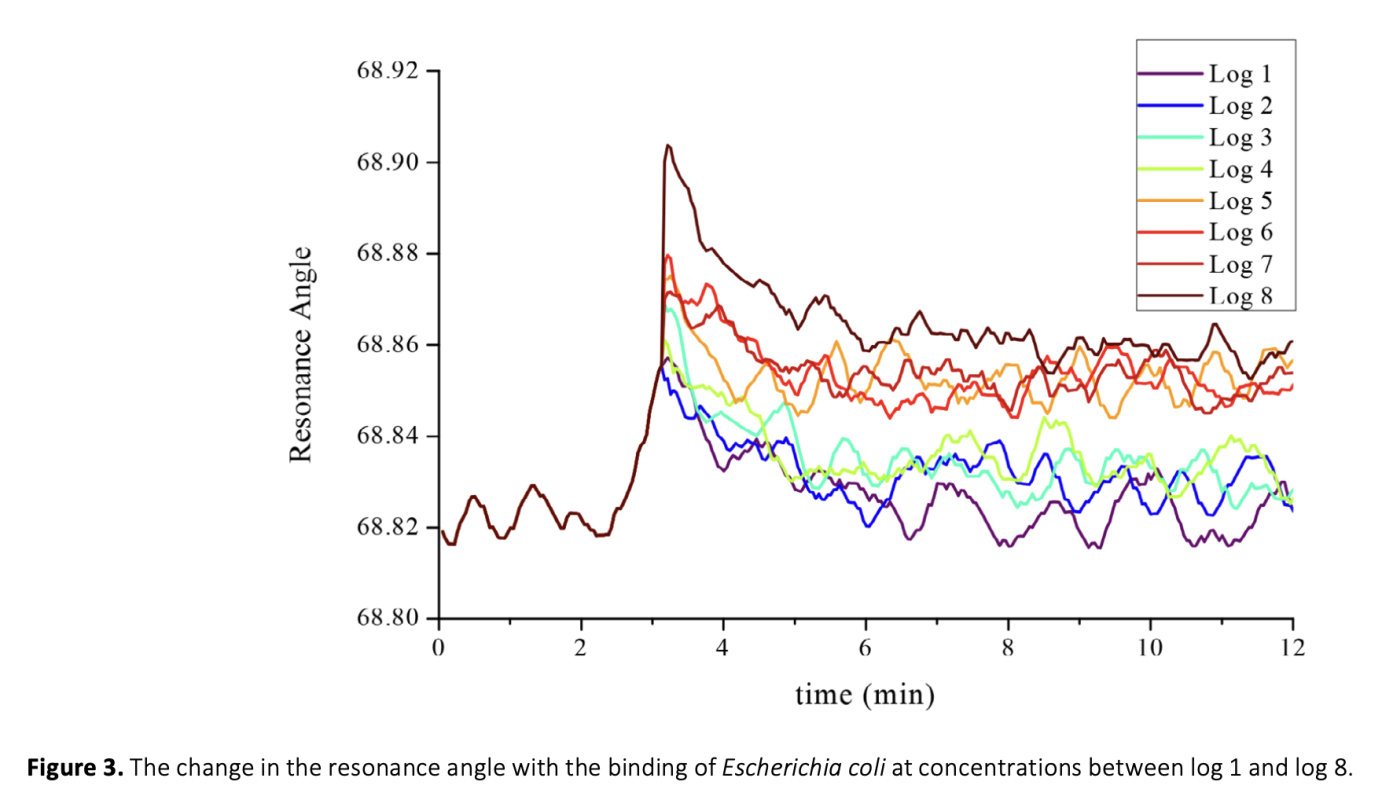
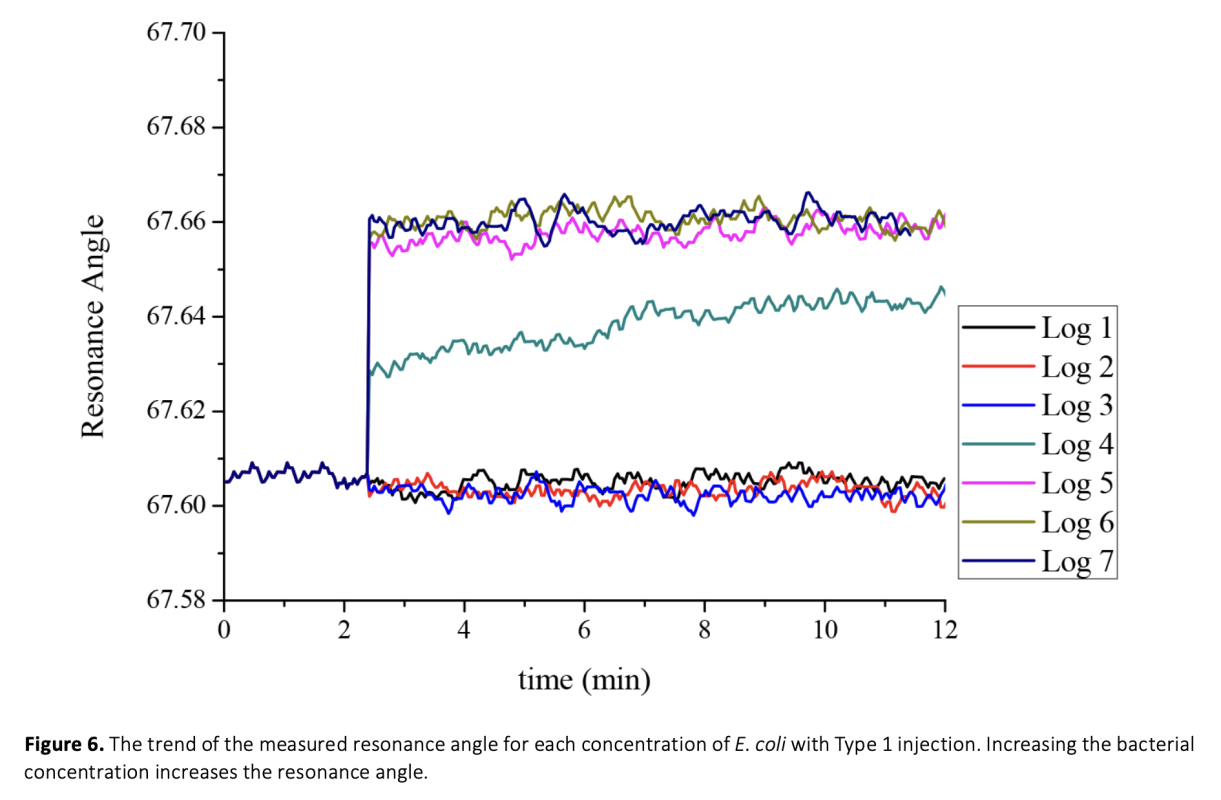
The detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria remains a significant challenge, and the need for fast and sensitive detection methods is becoming increasingly important. Escherichia coli is a prevalent bacteria associated with foodborne illness, and this study aimed to evaluate the ability of a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) based biosensor to detect E. coli O157:H7 at low levels in pure culture and artificially contaminated bay leaves (Laurus nobilis) using different injection methods. To develop a biological sensing surface, the sensor surface was functionalized with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), and polyclonal antibodies were immobilized on the surface for bacteria detection. Bacterial attachment to the antibodies resulted in a change in resonance angle. The biosensor was able to discriminate between cellular concentrations of 103 to 107 CFU/mL and showed potential in detecting different pathogens in various food samples. Before the SPR detection, the sample preparation step was optimized to ensure complex food matrices were suitable for SPR analysis. Additionally two different injection ports were compared to investigate the impact of flow rate on binding events at the sensor surface. In one of these ports, solutions were pumped onto the sensor surface at a flow rate of 1.6 μL/s, while in the other method, without any flow, a volume of 10 μL of sample was transferred to the chip surface using a pipette and kept for 10 minutes, after which the signal dynamics were examined. The results suggest that the SPR based biosensor is a promising tool for the rapid detection of foodborne pathogens in complex food matrices.
Gıda kaynaklı patojenik bakterilerin tespiti önemli bir zorluk olmaya devam etmektedir ve hızlı ve hassas tespit yöntemlerine olan ihtiyaç giderek daha zorunlu hale gelmektedir. Escherichia coli, gıda kaynaklı hastalıklarla ilişkili yaygın bir bakteridir ve bu çalışma, yüzey plazmon rezonansı (SPR) temelli bir biyosensörün, saf kültürde ve yapay olarak kontamine olmuş defne yapraklarında (Laurus nobilis) düşük seviyelerde E. coli O157:H7'yi farklı enjeksiyon yöntemleri kullanarak saptama yeteneğini değerlendirmeyi amaçlamıştır. Biyolojik bir algılama yüzeyi geliştirmek için sensör yüzeyi, bakteri tespiti için 3-aminopropiltrietoksisilan (APTES) ile işlevselleştirilmiş ve yüzey üzerine poliklonal antikorlar immobilize edilmiştir. Antikorlara bakteriyel bağlanma, rezonans açısında bir değişikliğe neden olmuştur. Biyosensör, 103 ile 107 CFU/mL arasındaki hücresel konsantrasyonları ayırt ederek ve çeşitli gıda örneklerinde patojenleri tespit etme potansiyeli göstermiştir. Ayrıca SPR tespitinden önce, karmaşık gıda matrislerinin SPR analizi için uygun olmasını sağlamak için numune hazırlama adımı optimize edilmiştir. Ek olarak, akış hızının sensör yüzeyindeki bağlanma olaylarına etkisinin karşılaştırılması için iki farklı enjeksiyon portu kullanılmıştır. Bu portlardan birinde 1,6 μL/s akış hızında solüsyonların sensör yüzeyine pompalanmasına imkan tanınırken diğer yöntemde herhangi bir akış söz konusu olmadan 10 μL hacmindeki örnek pipet yardımı ile çip yüzeyine aktarılıp 10 dk bekletilerek ve sinyal dinamikleri incelenmiştir. Elde edilen sonuçlar, SPR tabanlı biyosensörün, karmaşık gıda matrislerinde gıda kaynaklı patojenlerin hızlı tespiti için umut verici bir araç olduğunu göstermektedir.
Download Article in PDF (2.1 MB)