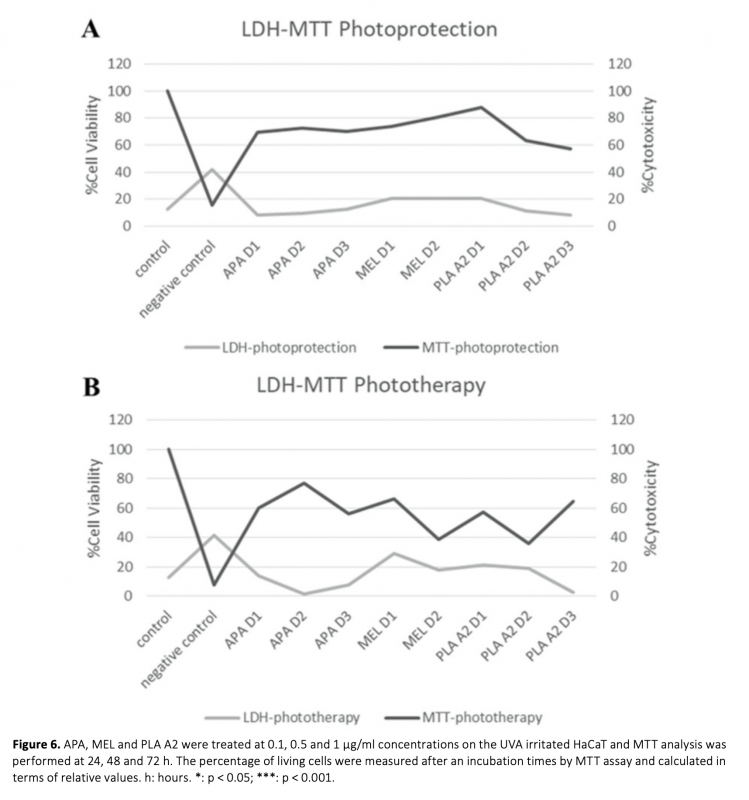
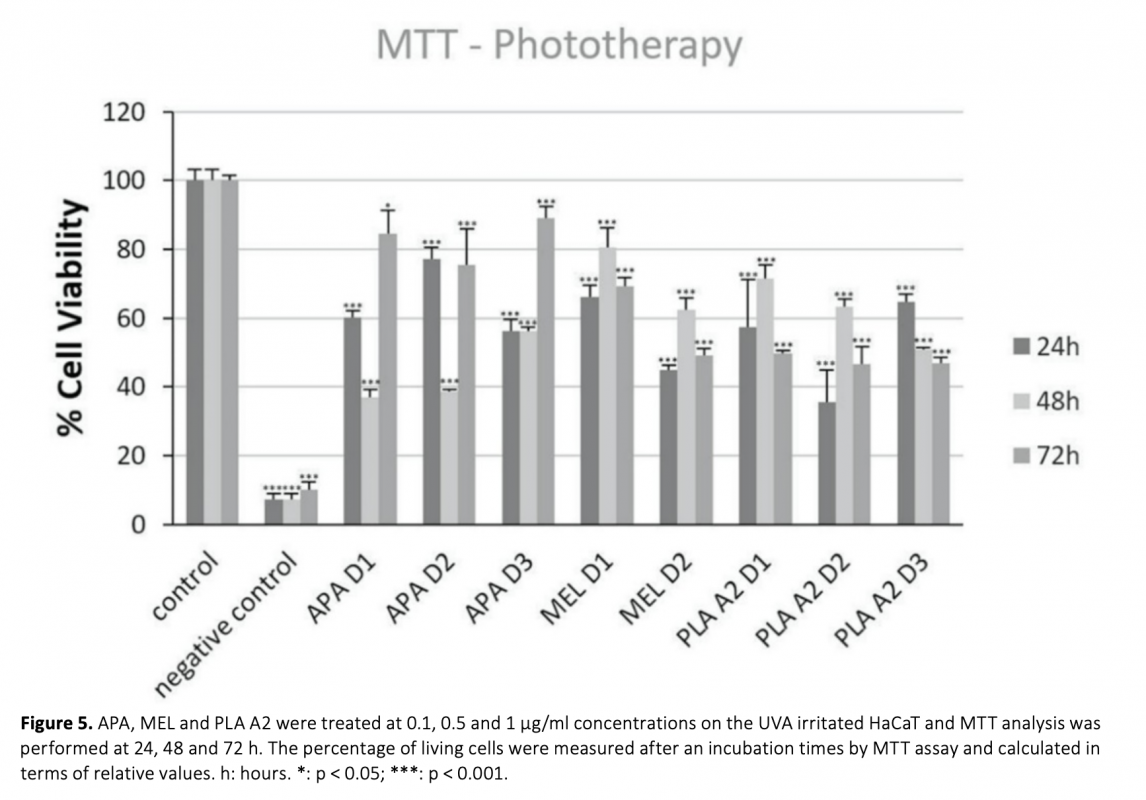
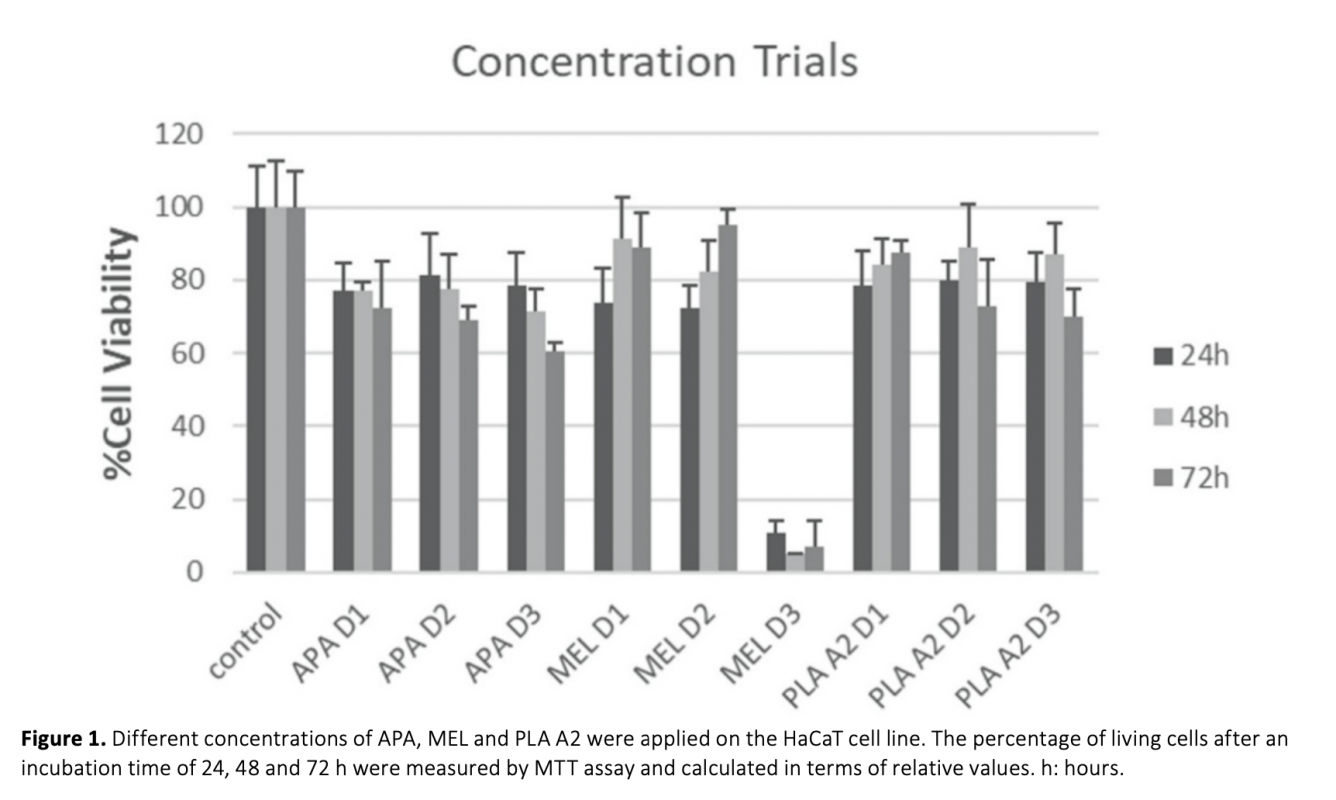
The aim of this study was to determine the protective and therapeutic properties of bee venom components Apamin, Melittin and Phospholipase A2 against UV damage in human keratinocyte cell line. The cosmetic and therapeutic effects of bee venom have been reported in previous studies, but it is not known which components of the venom are most effective. For this purpose, an in vitro UV damage model was first designed. Components of bee venom were tested at different concentrations. Cell viability, cytotoxicity and apoptotic processes were analysed on the designed model. As a result, Apamin was observed to exert a significant protective effect against UV-induced cell death at all concentrations. The photoprotective effects of Melittin were observed at all concentration times, and it was found that the photoprotective effects were increased at high concentrations. Our results showed that Phospholipase A2 can be used as a photoprotective and phototherapy agent. This study is the first to demonstrate the protective and therapeutic properties of bee venom components against UV damage. As a result, it has been shown that these components can be successful photoprotective and phototherapeutic agents against UV-induced damage, but more detailed studies should be done to minimize their toxic effects on cells.
Bu çalışmanın amacı, arı zehiri bileşenleri olan Apamin, Melittin ve Fosfolipaz A2’nin insan keratinosit hücre hattındaki UV hasarına karşı koruyucu ve tedavi edici özelliklerini belirlemektir. Arı zehirinin kozmetik ve tedavi edici etkileri önceki çalışmalarda bildirilmiştir, ancak zehirin hangi bileşenlerinin en fazla etkiye sahip olduğu bilinmemektedir. Bu amaçla ilk olarak bir in vitro UV hasar modeli tasarlandı. Arı zehirinin bileşenleri farklı konsantrasyonlarda test edildi. Hücre canlılığı, sitotoksisite ve apoptotik süreçler tasarlanan model üzerinde analiz edildi. Sonuç olarak, Apamin’in tüm konsantrasyonlarda UV ile indüklenen hücre ölümüne karşı önemli bir koruyucu etki gösterdiği gözlendi. Melittin’in ışık koruyucu etkileri tüm konsantrasyon sürelerinde gözlendi ve yüksek konsantrasyonda ışık koruyucu etkilerinin arttığı tespit edildi. Sonuçlarımız, Fosfolipaz A2’nin bir fotokoruyucu ve fototerapi ajanı olarak kullanılabileceğini gösterdi. Bu çalışma, arı zehiri bileşenlerinin UV hasarına karşı koruyucu ve tedavi edici özelliklerini gösteren ilk çalışmadır. Sonuç olarak, bu bileşenlerin UV kaynaklı hasara karşı başarılı fotokoruyucu ve fototerapötik ajanlar olabileceği gösterilmiştir, ancak hücreler üzerindeki toksik etkilerini en aza indirmek için daha detaylı çalışmalar yapılmalıdır.

Download Article in PDF (1.8 MB)