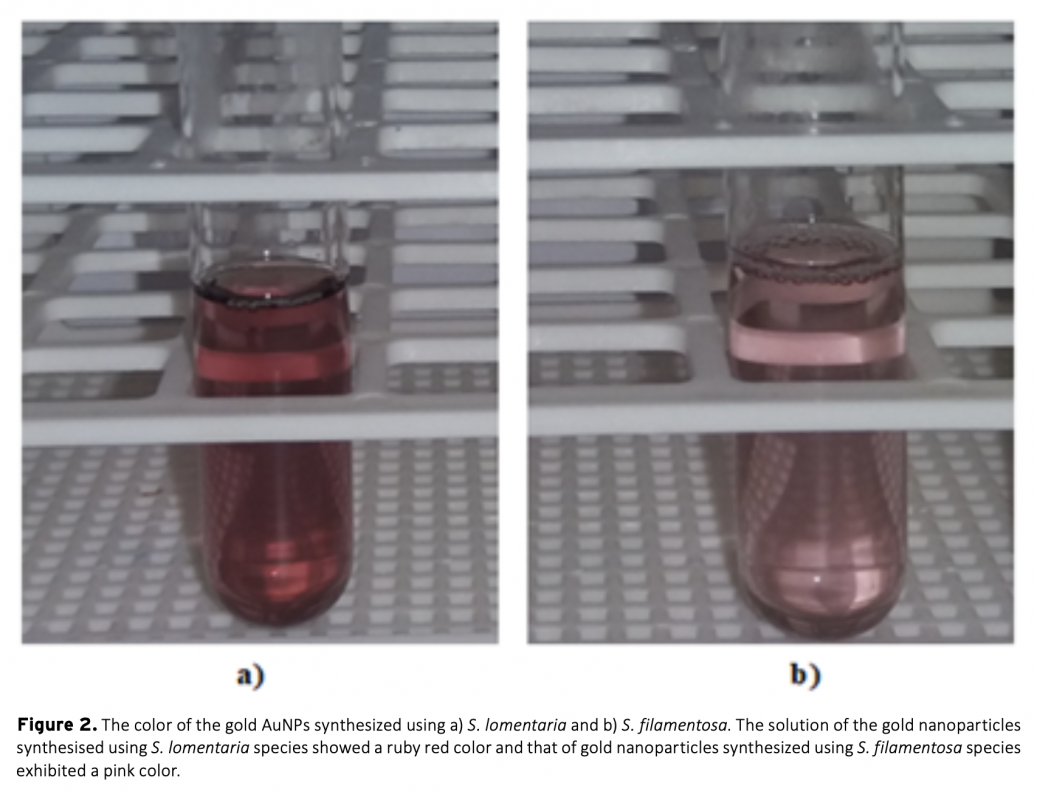
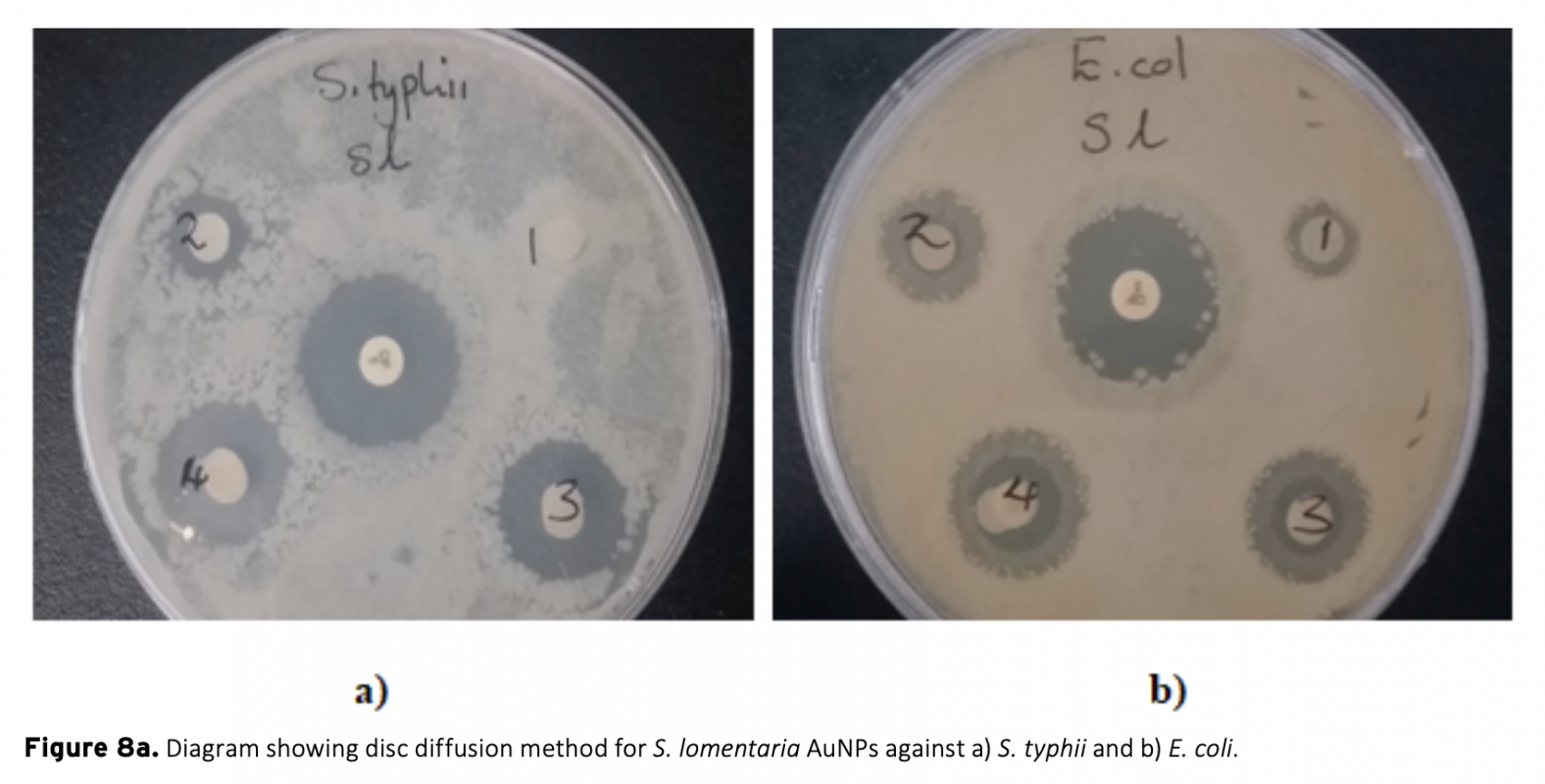
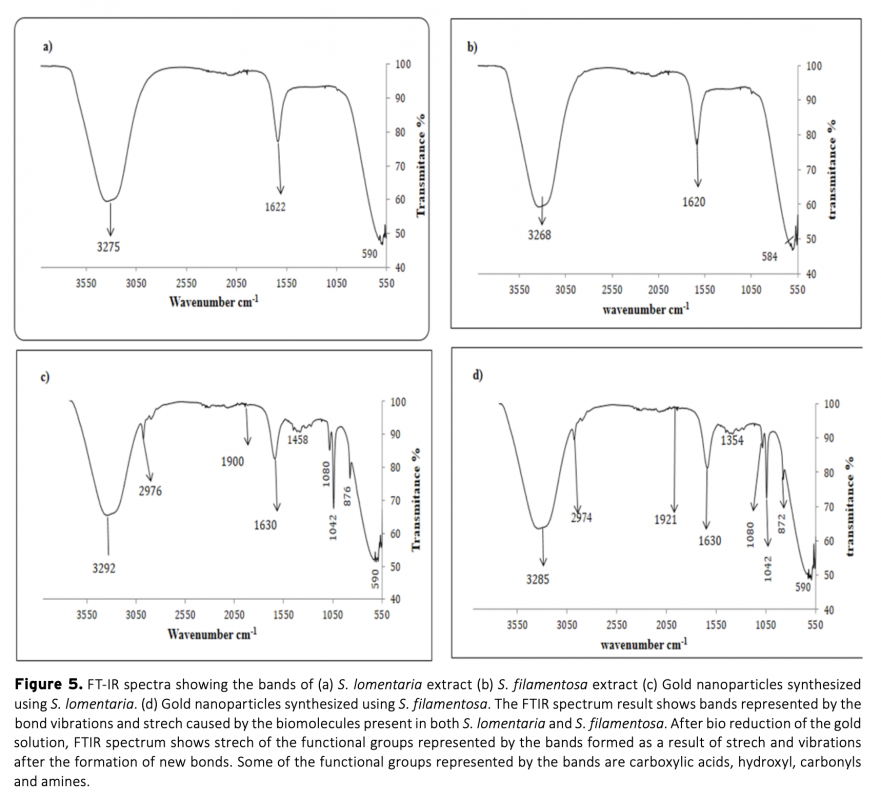
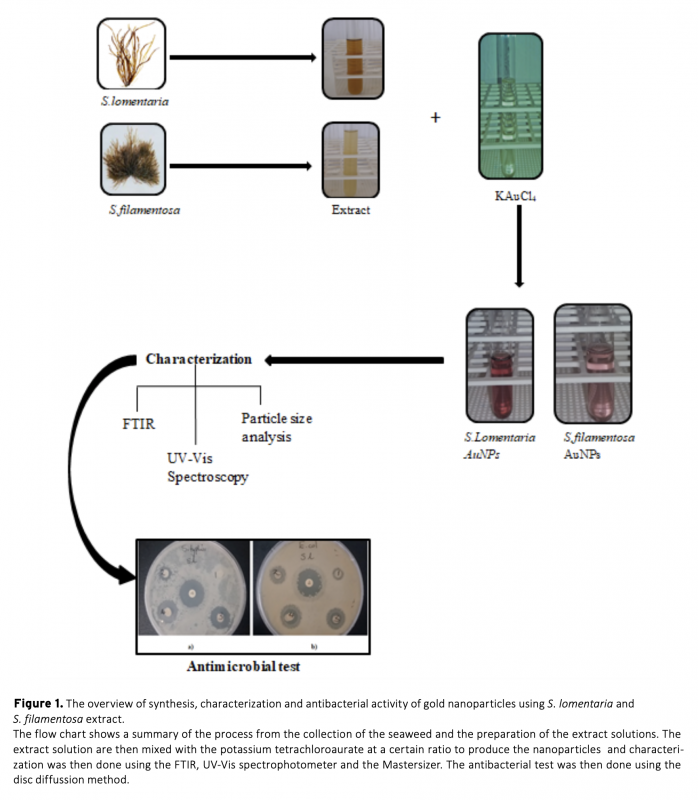
This study was carried out for biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by using Scytosiphon lomentaria (brown algae) and Spyridia filamentosa (red algae) and compared. Synthesized gold nanoparticles were characterized using the UV-Vis spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and Master Sizer analysis. Macro algae extract involvement in the stabilization of the gold nanoparticles was confirmed by the presence of UV-Vis peak at 540 nm and is an indication of the presence of the gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Strech in peaks of the FTIR showed that the biomolecules present in the seaweed extract reduced the gold ions. Master sizer results for AuNPs were within the range of 15-55 nm. Antioxidant activity carried out using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging activity revealed significant activity for both AuNPs. Biosynthesized AuNPs also showed antimicrobial activity against S. typhii and E. coli. The S. lomentaria AuNPs exhibited inhibition against E. coli, whereas S. filamentosa gold nanoparticles showed antibacterial activity against S. typhi. Synthesized AuNPs using S. lomentaria and S. filamentosa extracts as stabilizing agents showed convincing antioxidant and antimicrobial activity against gram negative and gram positive bacteria.
Bu çalışma, Scytosiphon lomentaria (kahverengi yosun) ve Spyridia filamentosa (kırmızı yosun) kullanılarak altın nanopartiküllerinin (AuNPs) sentezi için yürütülmüş ve bu iki türden kullanılarak sentezlenen naopartiküllerin karşılaştırması yapılmıştır. Altın nanoparçacıklar daha sonra UV-Vis spektrofotometre, FTIR ve Mastersizer kullanılarak karakterize edilmiştir. UV-Vis kullanılarak altın nanopartiküllerin oluşumu 540 nm’de oluşan pik ile görülmektedir. FTIR’daki gerilme, deniz yosunu ekstraktında bulunan biyomoleküllerin altın iyonlarını azalttığını göstermiştir. Mastersizer sonuçları, nanoparçacıkların 15-55 nm aralığında geniş bir dağılım göstermektedir. 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) serbest radikal yöntemi kullanılarak gerçekleştirilen antioksidan aktivitesi, her iki nanopartikül için de önemli aktiviteler göstermiştir. S. typhii ve E. coli kullanılarak antimikrobiyal etkileri araştırılmıştır. S. lomentaria altın nanoparçacıklar E. coli’ye karşı inhibisyon sergilerken, S. filamentosa altın nanopartiküllerı S. typhi’ye karşı inhibisyon göstermiştir. Stabilize edici ajan olarak kullanılan S. lomentaria ve S. filamentosa özütleri ile sentezlenen altın nanoparçacıklar, hem gram negatif hem de gram pozitif bakterilere karşı ikna edici antioksidan ve antimikrobiyal aktivite göstermiştir.

Download Article in PDF (1.8 MB)