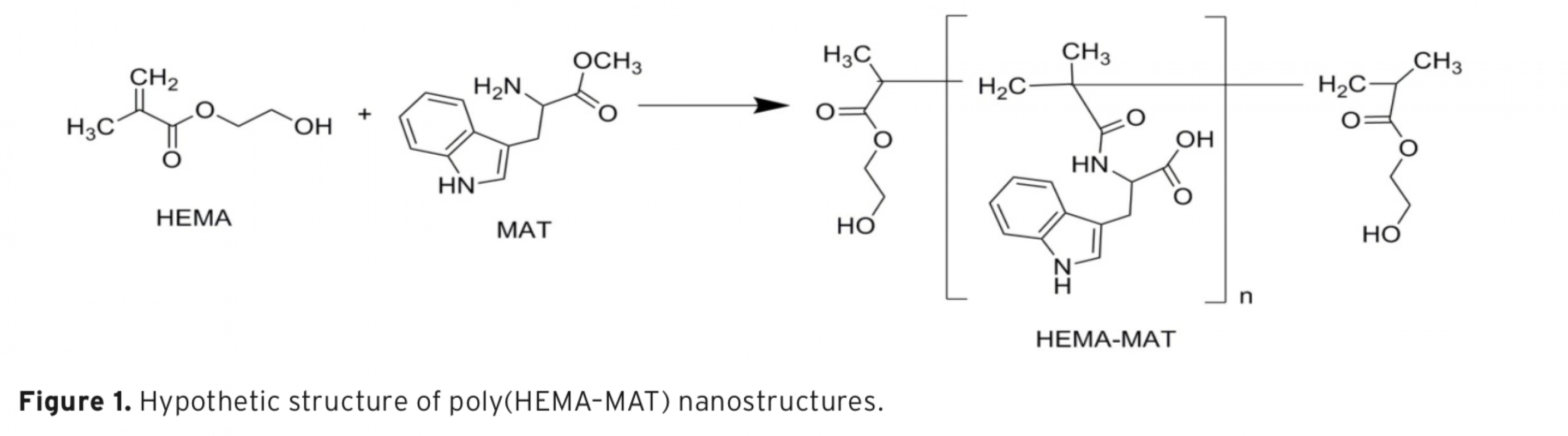
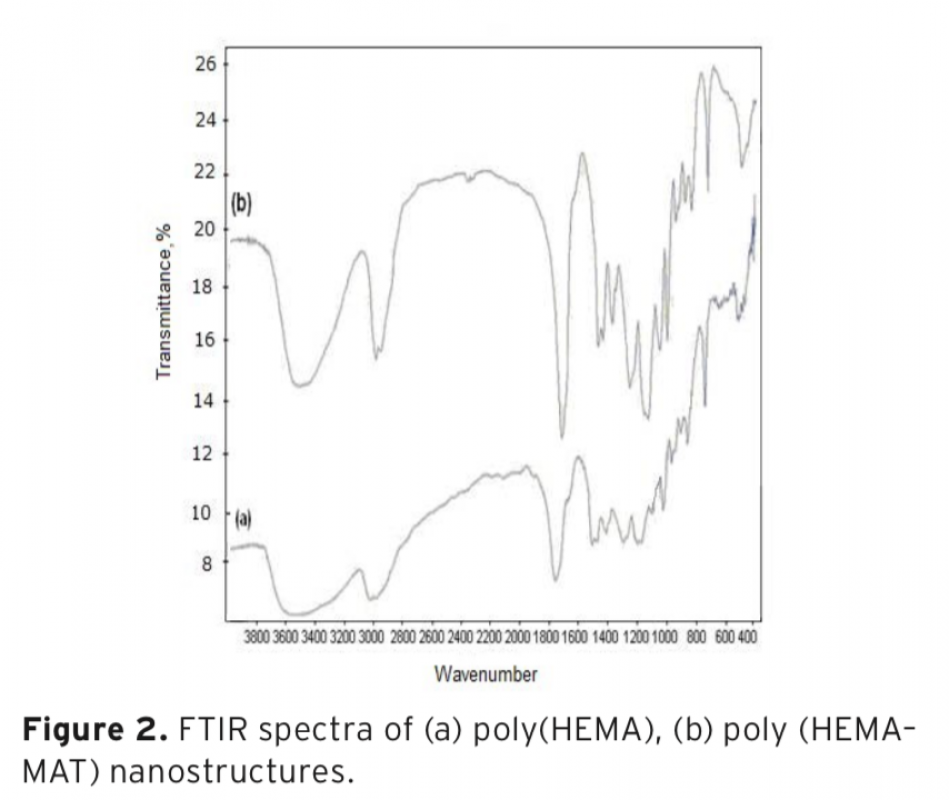
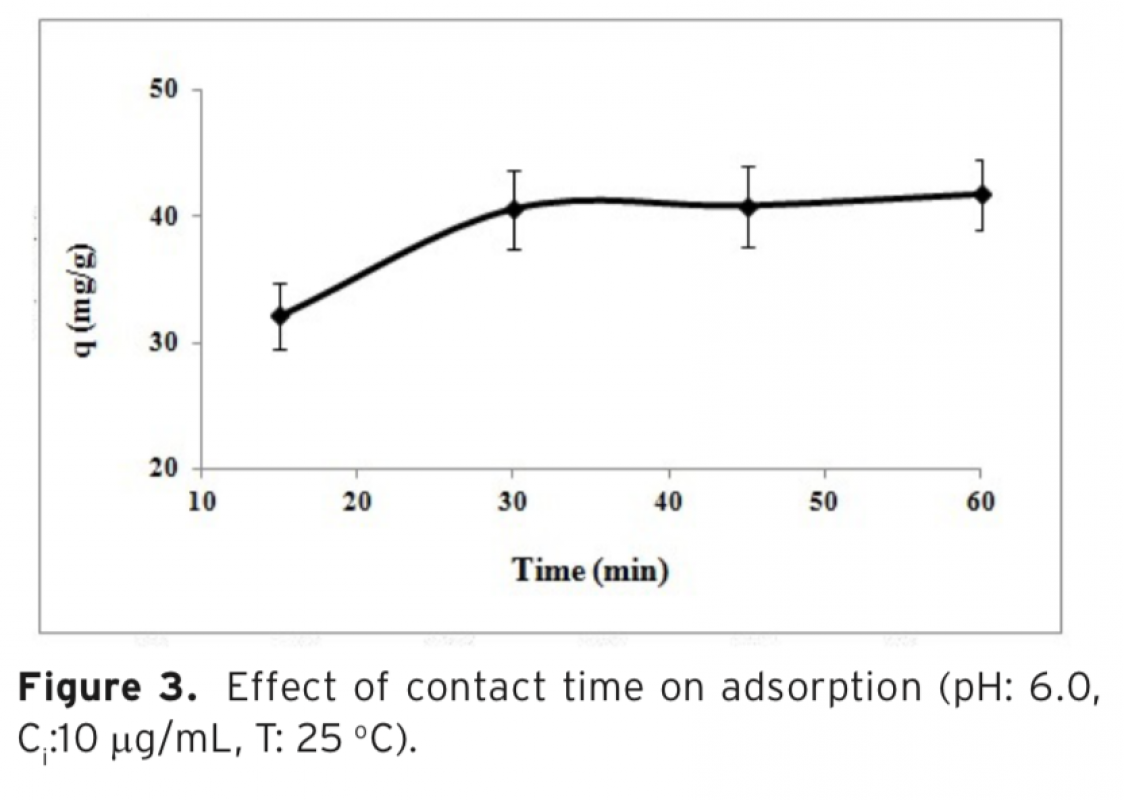
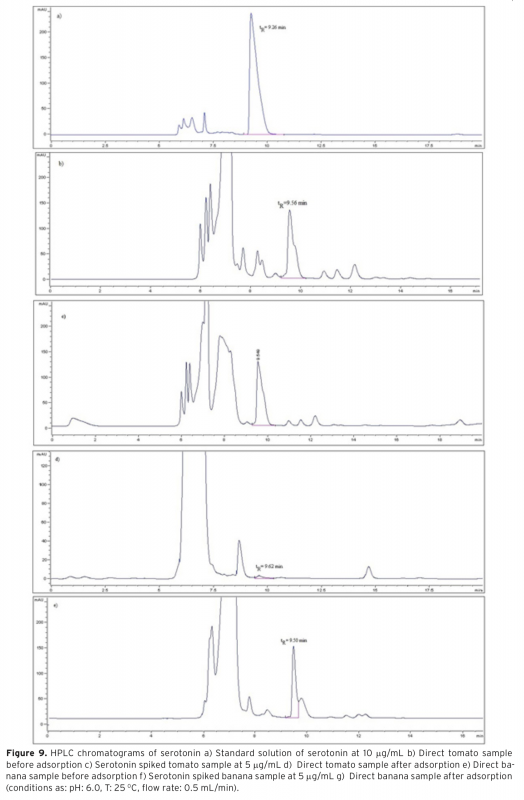
The aim of this study was to evaluate the extraction performance of poly(hydroxyethyl methacry-late-methacryloyl-(L)-tryptophan methyl ester) poly(HEMA–MAT)] nanostructures for serotonin from edible plants by a series of batch experiments. Average size of nanostructures was found as 100 nm with polydispersity index of 1.189 using zeta size analysis results. Maximum serotonin uptake capacity of the nanostructures was found to be 2901.4 ± 65.9 mg/g at pH 6.0. Applicabil-ity of this nanosorbent for the extraction of serotonin in banana and tomato before HPLC analysis was also studied and the level of serotonin was determined as 86.26 mg/g for banana and 36.02 mg/g for tomato samples.
Bu çalışmanın amacı, bir seri kesikli sistem deneyle poli (hidroksietil metakrilat-metakriloil- (L) -triptofan me- til ester) poli (HEMA-MAT)] nano-yapılarının yenilebilir bitkilerden serotonin için ekstraksiyon performan- sını değerlendirmektir. Polidispersiyon indeksi 1.189 olan nanoyapıların ortalama boyutu, zeta boyut analizi so- nuçlarına göre 100 nmdir. Nanoyapıların maksimum seroto-nin adsorpsiyon kapasitesi, pH 6.0’da 2901.4 ± 65.9 mg/ g olarak bulunmuştur. Bu nanosorbentin, HPLC analizi öncesi muz ve domatesde serotonin ekstraksiyonu için uygulanabilirliği de araştırılmış ve serotonin seviyesi muz için 86.26 mg/g, domates numuneleri için 36.02 mg/g olarak tespit edilmiştir.
Download Article in PDF (668.2 kB)