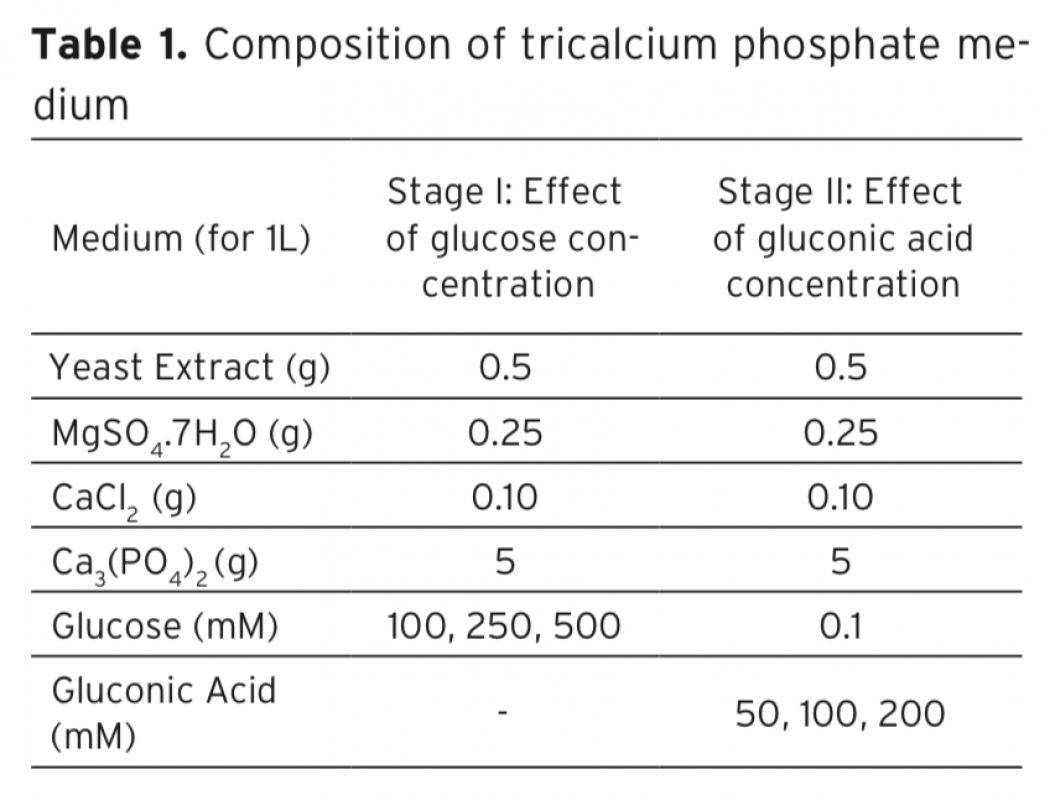
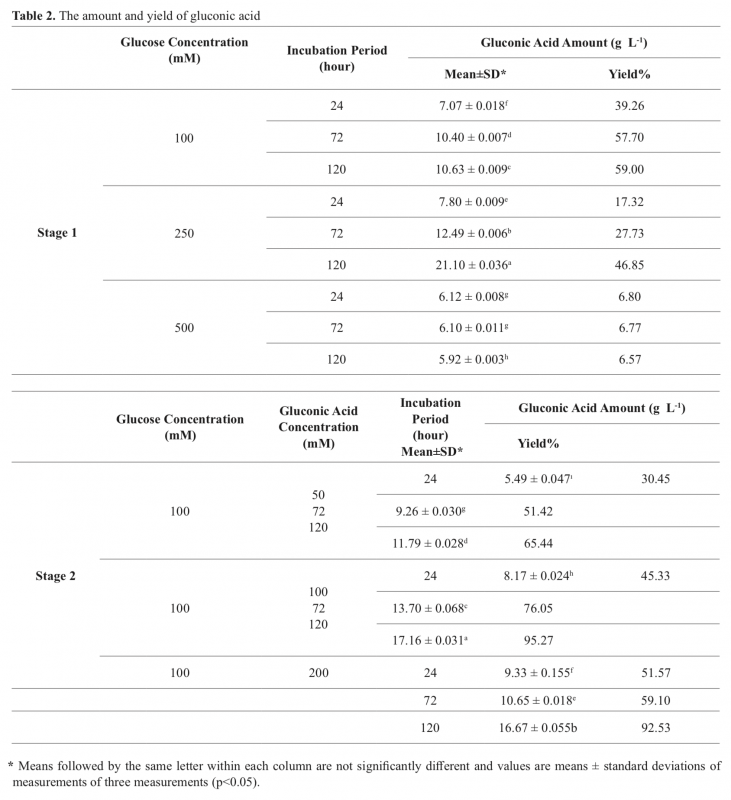
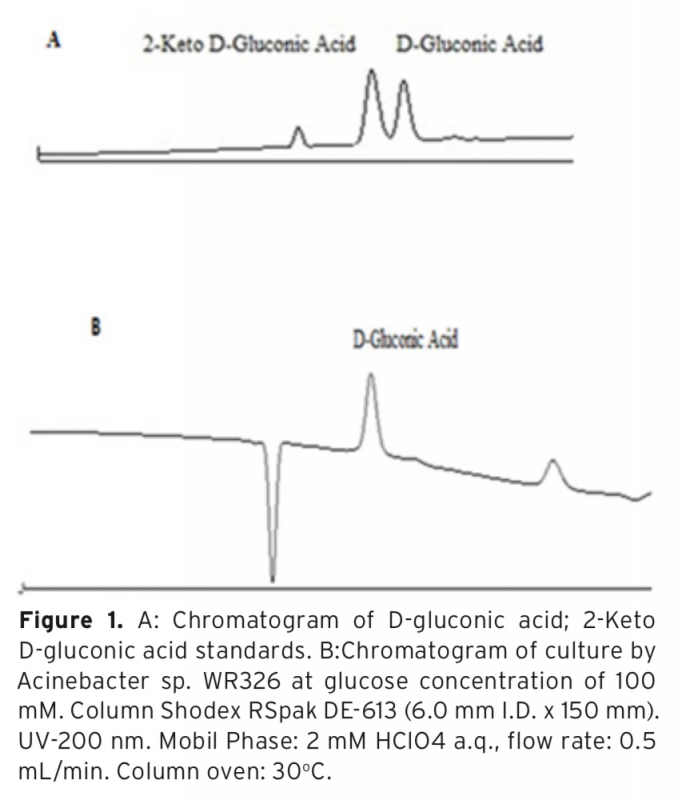
Gluconic acid, a food additive, is used in many foods to control acidity or binds metals such as calcium, iron. Acinetobacter sp. WR326, newly isolated from soil possesses high phosphate solubilizing activity and do not require pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) for glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) activity as cofactor In this study the gluconic acid production potential of this bacterium was investigated. Firstly, Acinetobacter sp. WR326 was incubated in tricalcium phosphate medium (TCP) with varying glucose concentrations (100, 250, 500 mM), at a temperature of 30°C for 5 days (120 hours). The highest gluconic acid yield (59%) was found at a glucose concentration of 100 mM. Then three different levels of gluconic acid addition to the medium (50, 100, 200 mM) were tested. When Acinetobacter sp. WR326 strain was cultivated with a 100 mM glucose and 100 mM gluconic acid the yield increased to 95.27%. In any trials 2 -keto D-gluconic acid, causes problems in processing and purification of the gluconic acid, was not detected in the medium. As a conclusion, Acinetobacter sp. WR326 may be considered novel potential bacterial strain for gluconic acid production.
Glukonik asit asitliği kontrol etmek veya kalsiyum, demir gibi metalleri bağlamak için çoğu gıdada kullanılan bir gıda katkı maddesidir. Topraktan yeni izole edilen Acinetobacter sp. WR326, yüksek fosfat çözme aktivitesine sahiptir ve glukoz dehidrojenaz (GDH) aktivitesi için pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) kofaktörüne gereksinim duymamaktadır. Bu çalışmada bu bakterinin glukonik asit üretme potansiyeli araştırılmıştır. İlk önce, Acinetobacter sp. WR326 farklı glukoz konsatrasyonlarında (100, 250, 500 mM) 30°C sıcaklıkta 5 gün boyunca (120 saat) trikalsiyum fosfat (TCP) besiyerinde inkübe edilmiştir. En yüksek glukonik asit verimi (%59) 100 mM lık glukoz derişimi içeren kültürde bulunmuştur. Sonra besiyerine glukonik asit ilavesi üç farklı derişimde (50, 100, 200 mM) araştırılmıştır. Acinetobacter sp. WR326 suşu 100 mM glukoz ve 100 mM glukonik asit ilavesinde kültüre alındığında verim %95,27 oranına yükselmiştir. Hiçbir koşulda glukonik asidin işlenmesi ve saflaştırılmasında problemlere neden olan 2 -keto D-glukonik asit tespit edilmemiştir. Sonuç olarak, Acinetobacter sp. WR326 suşunun glukonik asit üretiminde yeni potansiyel bakteri suşu olarak kullanılabileceği düşünülmektedir.
Download Article in PDF (132.4 kB)