Cyanide is a hazardous substance and a toxic contaminant but it is found in the environment as a natural product of industrial activities. Biological methods are an alternative and promising potential approach to the conversion and destruction of other toxic byproducts that can be formed by both cyanide and chemical treatment. It is known that a lot of fungi, bacteria and some plants are used in biological treatment works. Trichoderma is a genus of fungi that has enzymes for cyanide destruction. It is known that microbial activity under aerobic conditions cyanide can be converted to ammonia and then nitrate by oxidation. Cryogels are gel matrices synthesized at temperatures below zero using monomeric or polymeric precursors. Polymeric network occurs while the solvent forms ice crystals. After the ice crystals melt, polymeric matrices with large pores are formed. Cryogels are used in a variety of areas of biotechnology, including chromatographic materials, carriers for immobilization of molecules and cells. In this study, poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA)-based Triccoderma spp. embedded supermacroporous cryogels were synthesized for cyanide destruction. The polymeric materials prepared were tested for cyanide degradation at different pH, temperature and initial concentrations to examine their suitability for this purpose.
Siyanür, tehlikeli bir madde ve zehirli bir kirleticidir; ancak, endüstriyel faaliyetlerin doğal bir ürünü olarak çevrede bulunur. Biyolojik yöntemler hem siyanür hem de kimyasal işlemle oluşturulabilen diğer zehirli yan ürünlerin dönüştürülmesine ve tahrip edilmesine alternatif bir potansiyel yaklaşımdır. Biyolojik arıtma işlemlerinde birçok mantar, bakteri ve bazı bitkiler kullanıldığı bilinmektedir. Trichoderma spp., siyanür tahribatı için enzimler üreten bir mantar türüdür. Aerobik koşullar altında mikrobiyal aktivitenin siyanürün oksidasyon ile amonyak ve daha sonra nitrat haline dönüştürülebileceği bilinmektedir. Kriyojeller, monomerik veya polimerik öncülleri kullanarak sıfırın altındaki sıcaklıklarda sentezlenen jel matrisleridir. Polimer ağı, çözücü buz kristalleri oluştururken oluşur. Buz kristallerinin erimesinden sonra, büyük gözenekli polimerik matrisler oluşur. Kriyojeller, kromatografik materyaller, moleküllerin ve hücrelerin hareketsizleştirilmesi için taşıyıcılar gibi biyoteknolojinin çeşitli alanlarında kullanılır. Bu çalışmada siyanür yıkımı için poli(2-hidroksietil metakrilat) (PHEMA) bazlı, Trichoderma spp. gömülü kriyojeller sentezlenmiştir. Hazırlanan polimerik malzemelerin amaca uygun olup olmadığını belirlemek için farklı pH, sıcaklık ve başlangıç derişimlerinde siyanür yıkımı test edilmiştir.
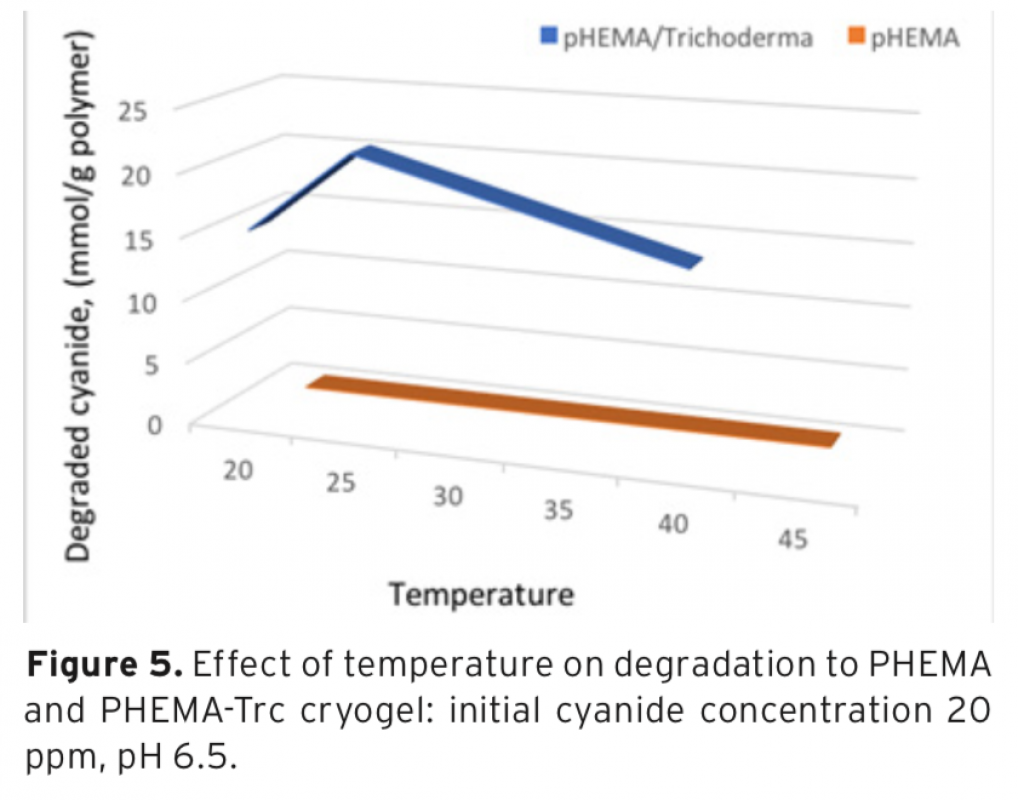
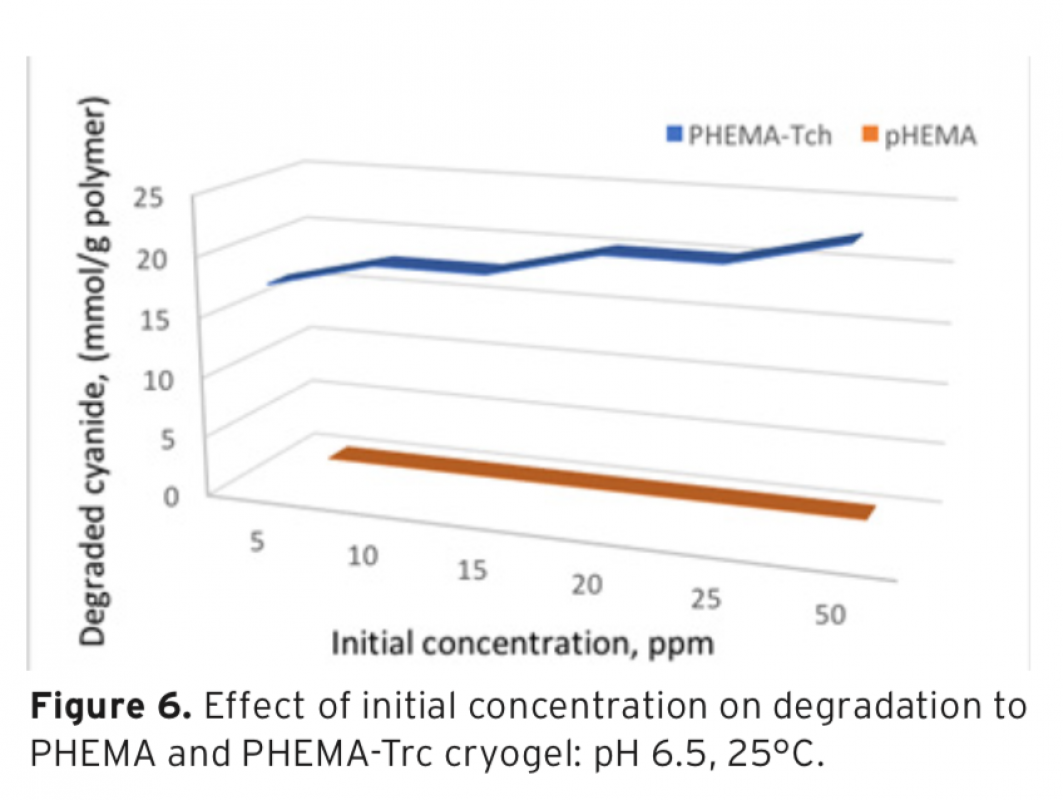
Download Article in PDF (360.1 kB)