Dried Cydonia oblonga, Persea americana, Malus domestica and Citrus sinensis peels were used as low-cost biosorbents in crude oil removal. Among them, Citrus sinensis was selected as the most effective biosorbent with a removal rate of 83.81% and the effect of adsorption parameters such as pH (4.0-10.0), adsorbent dose (0.1-0.5 g/50mL) and crude oil concentration (0.25-2.5%) were also investigated. Maximum removal rate of 94.37% (qe=1.81) was found at pH=7.0, 0.25 g/50 mL adsorbent dose and 1% crude oil concentration. And 25.91% removal rate (qe=0.49) was determined at the end of the 6th cycle of re-used peels. The kinetics of this adsorption was described by Pseudo-second order model (R2=0.8167) and the equilibrium modelling were well fitted with Langmuir isotherm (R2=0.9403). Characteristic bands of cellulose and hemicellulose in the lignocellulotic structure of dried peels were determined by FTIR. Thermogravimetric profile was resulted as a residual weight of 17.5% even at 1000 ̊C with high resistance to increasing temperature. Therefore,C. sinensis peels, which is a common domestic and an industrial food waste, can be used as a low-cost, easily available, biodegradable and environmentally friendly adsorbent in crude oil removal.
Kurutulmuş Cydonia oblonga, Persea americana, Malus domestica ve Citrus sinensis kabukları, ham petrolün uzaklaştırılmasında düşük maliyetli biyosorbanlar olarak kullanıldı. Bunlardan Citrus sinensis, %83.81'lik giderim oranı ile en etkili biyosorban olarak seçildi ve pH (4.0-10.0), adsorbent dozu (0.1-0.5 g/50 mL) ve ham petrol konsantrasyonu (0.25-2.5%) parametrelerinin adsorpsiyona etkisi araştırıldı. Kurutulmuş C. sinensis kabukları kullanılarak ham petrol uzaklaştırma için en yüksek uzaklaştırma oranı (%94.37, qe=1.81), pH=7.0, 0.25 g/50 mL adsorbent dozu ve %1 ham petrol konsantrasyonu olarak bulundu. Kabukların tekrar kullanımı ile 6. döngünün sonunda %25.91 uzaklaştırma oranı (qe=0.49) gözlendi. Bu adsorpsiyonun kinetiği, Pseudo-ikinci derece modeli ile açıklandı (R2=0.8167) ve denge modelleme Langmuir izotermi ile uyumlu bulundu (R2=0.9403). Kurutulmuş kabukların lignoselülozik yapısındaki selüloz ve hemiselulozun karakteristik bantları FTIR ile belirlendi. Termogravimetrik profil, 1000 ̊C'de bile %17.5'lik bir kalıntı ağırlığı ile yüksek sıcaklığa karşı direnç gösterdi. Sonuç olarak, yaygın bir evsel ve endüstriyel gıda atığı olan C. sinensis kabuklarının, ham petrol uzaklaştırmada düşük maliyetli, kolayca bulunabilir, biyobozunur ve çevre dostu bir adsorban olarak kullanılabilirliği gösterildi.
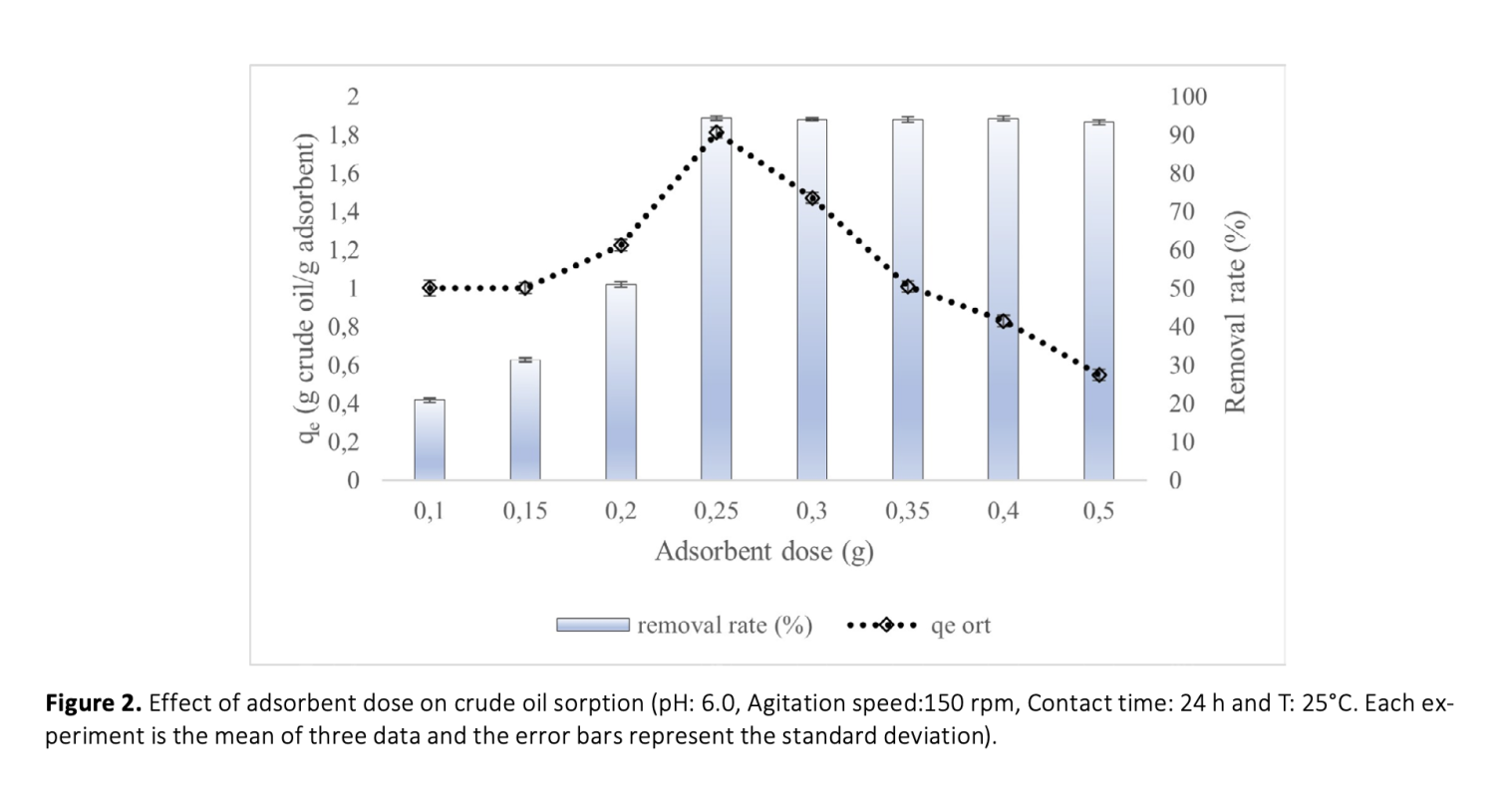
Download Article in PDF (1.4 MB)