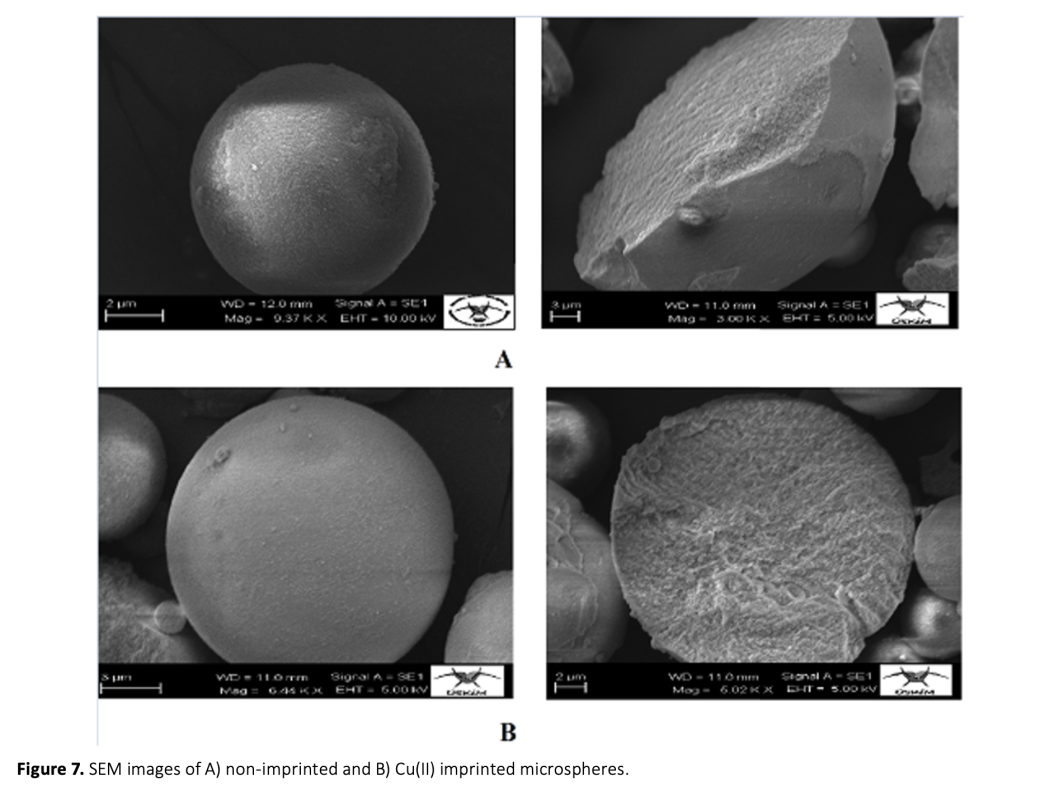
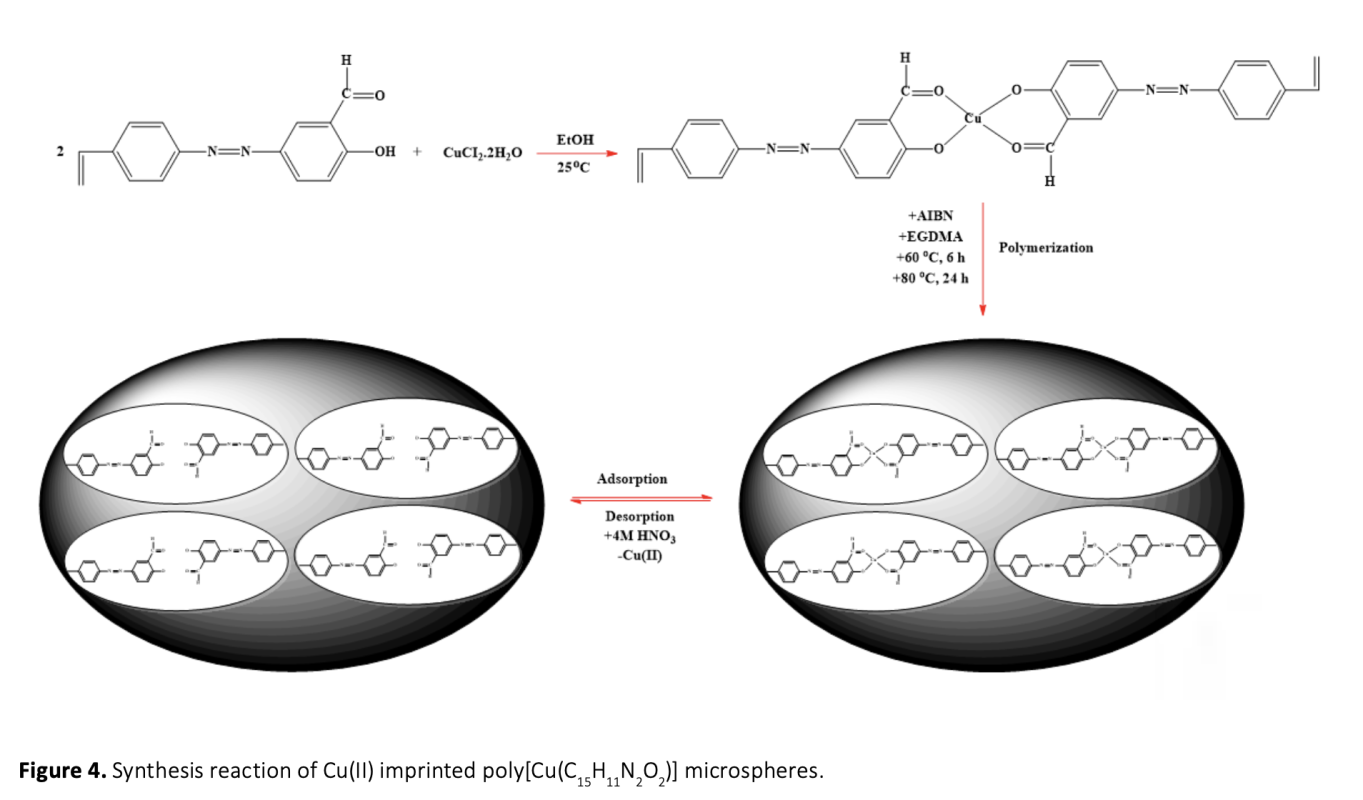
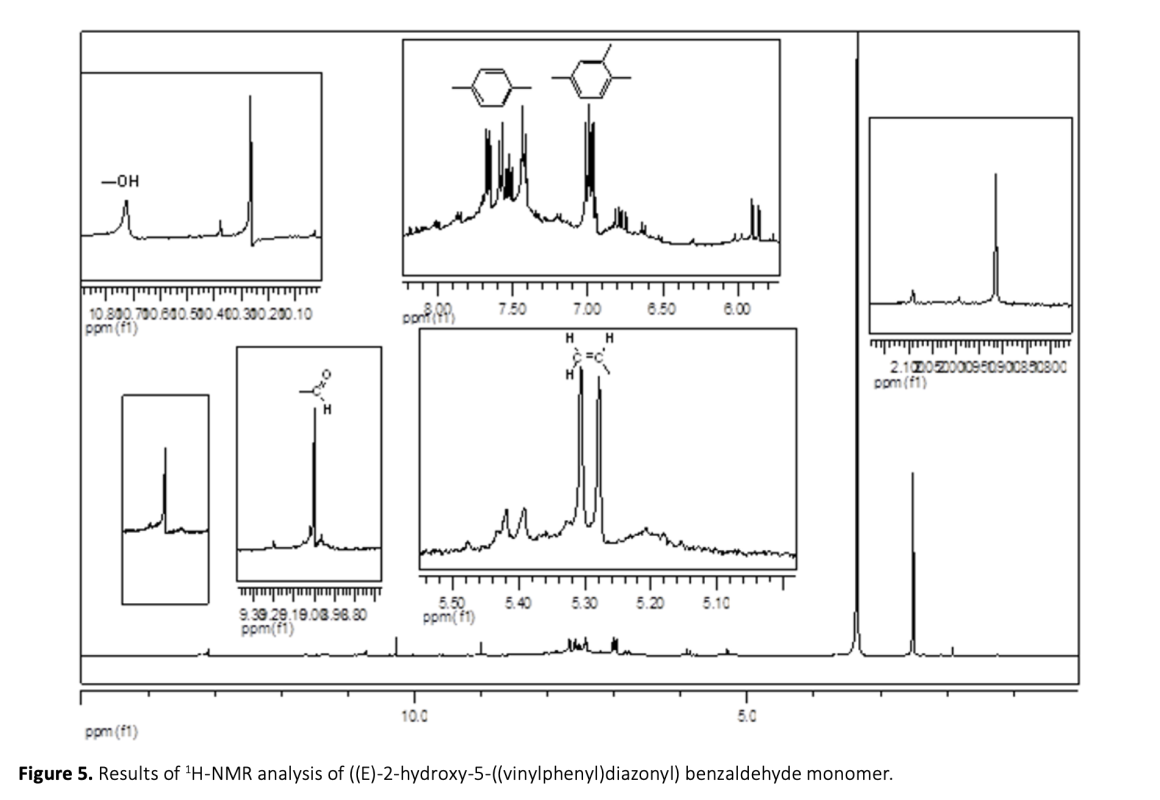
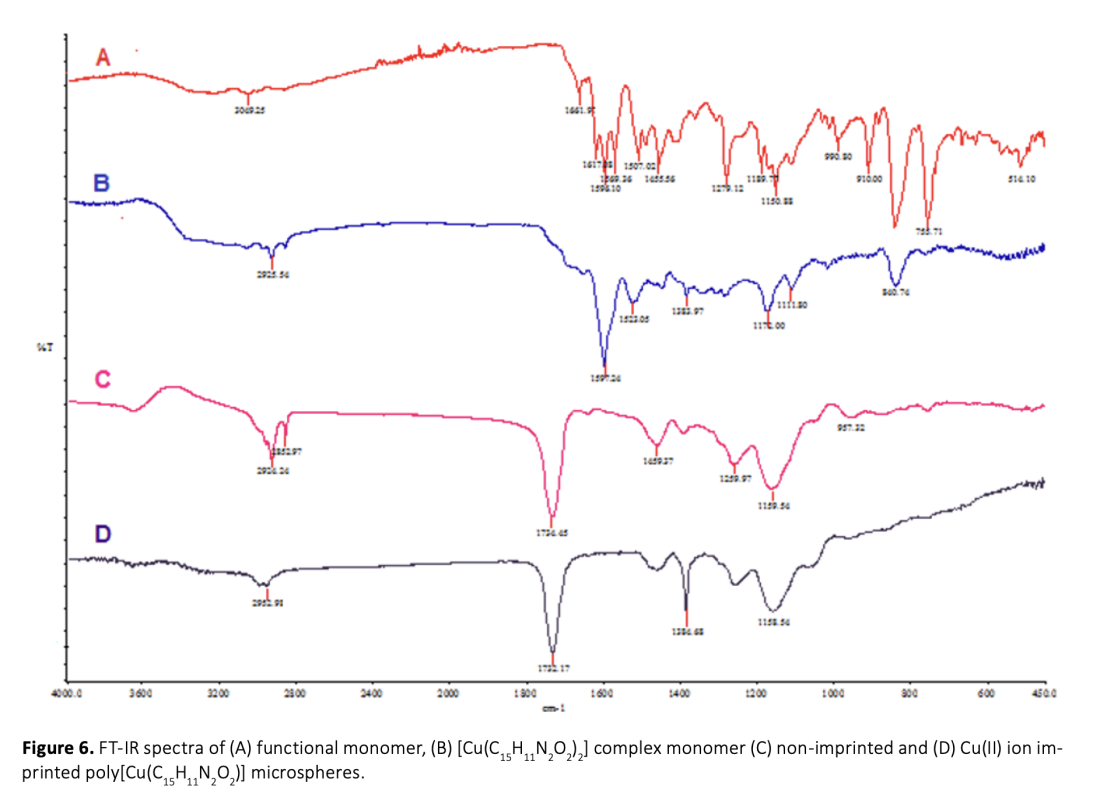
In this study, ion-imprinted polymers were prepared. These polymers can be used for the selective removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions. To this end, (E)-2-hydroxy-5-((vinylphenyl)diazonyl) benzaldehyde was used as a functional monomer in the synthesis stage of the polymeric adsorbent. Cu(II) imprinted poly[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] microspheres have been synthesized by dispersion polymerization technique through the interaction of the template molecule Cu(II) ion with the functional monomer. The specific surface area of Cu(II) imprinted poly[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] microspheres was 374.26 m2/g. The swelling rate was 80%. The maximum adsorption capacity, the optimum pH, and the adsorption equilibrium time were determined to be 153.03 mg/g, in the range of 8-10, and 30 min, respectively. According to the elemental analysis results, before imprinting; C%: 55.72, H%: 6.756, N%: 0.555 were found to be C%: 58.81, H%: 6.998, N%: 0.570 after imprinting. The increase in the percentages of C, H and N showed that the remaining molecule moved away from the structure. The relative selectivity coefficients of the imprinted microspheres were found to be 13.09, 57.88, 44.72, and 35.01 for the ion pairs as Cu(II)/Ni(II), Cu(II)/Pb(II), Cu(II)/Zn(II) and Cu(II)/Co(II), respectively. These results showed that the Cu(II)-imprinted microspheres were more selective with respect to Cu(II) ions. Reproducibility studies showed that Cu(II) imprinted poly[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] microspheres can be used repeatedly without a significant decrease in adsorption capacity.
Bu çalışmada, sulu çözeltilerden Cu(II) iyonlarının seçici olarak uzaklaştırılması için kullanılabilecek iyon baskılanmış polimerler hazırlanmıştır. Bu amaçla, polimerik adsorbentin sentez aşamasında fonksiyonel monomer olarak (E)-2-hidroksi-5-((vinilfenil)diazonil) benzaldehit kullanılmıştır. Kalıp molekül Cu(II) iyonu ile fonksiyonel monomer etkileştirilerek dispersiyon polimerizasyon tekniği ile Cu(II) baskılanmış poli[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] mikroküreleri sentezlenmiştir. Cu(II) baskılanmış poli[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] mikrokürelerinin spesifik yüzey alanı 374,26 m2/g ve şişme oranı %80 olarak bulunmuştur. Maksimum adsorpsiyon kapasitesi, optimum pH ve adsorpsiyon denge zamanı sırasıyla 153,03 mg/g, 8-10 aralığı ve 30 dakika olarak tespit edilmiştir. Elementel analiz sonuçlarına göre baskılama öncesi; C%: 55.72, H%:6.756, N%:0.555 baskılama sonrası C%:58.81, H%:6.998, N%:0.570 olarak bulunmuştur. C, H ve N yüzdelerindeki artış yapıdan kalıp molekülün uzaklaştığını göstermiştir. Baskılanmış mikrokürelerin bağıl seçicilik katsayısı Cu(II)/Ni(II), Cu(II)/Pb(II), Cu(II)/Zn(II) ve Cu(II)/Co(II) için sırasıyla 13,09, 57,88, 44,72 ve 35,01 olarak bulunmuştur. Bu sonuçlar; Cu(II) baskılanmış mikrokürelerin Cu(II) iyonlarına karşı daha seçici olduğunu göstermiştir. Yapılan tekrarlanabilirlik çalışmaları Cu(II) baskılanmış poli[Cu(C15H11N2O2)] mikrokürelerin adsorpsiyon kapasitesinde önemli bir azalma olmaksızın tekrar tekrar kullanılabilir olduğunu göstermiştir.

Download Article in PDF (1.6 MB)