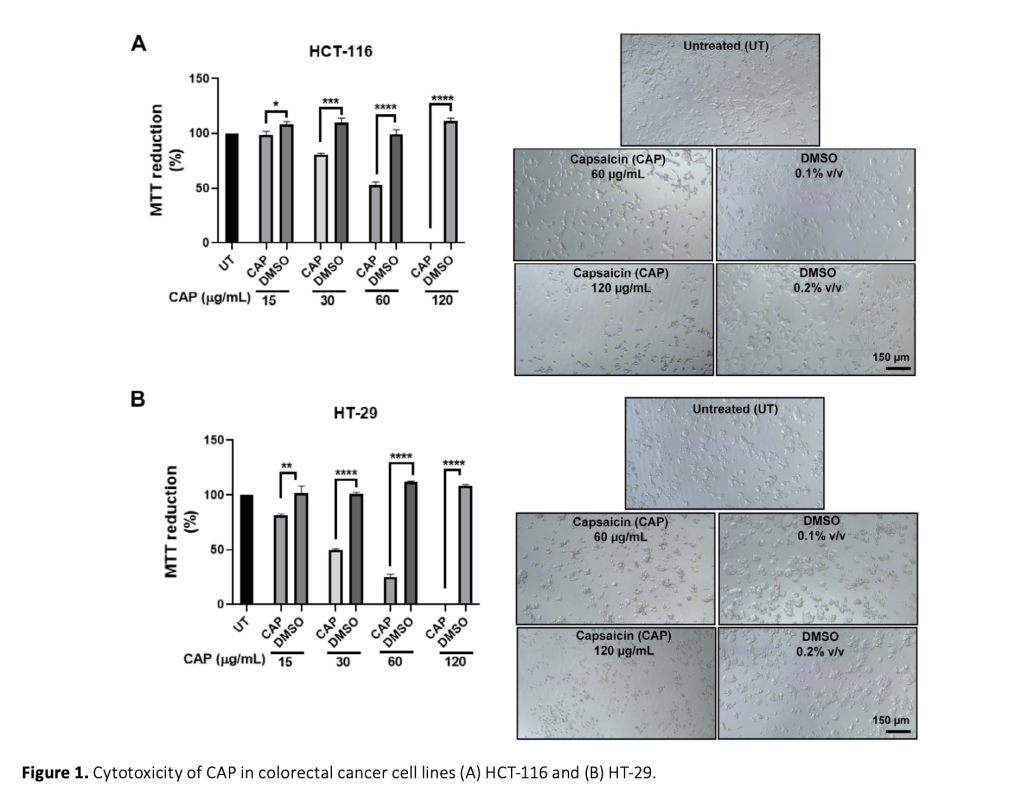
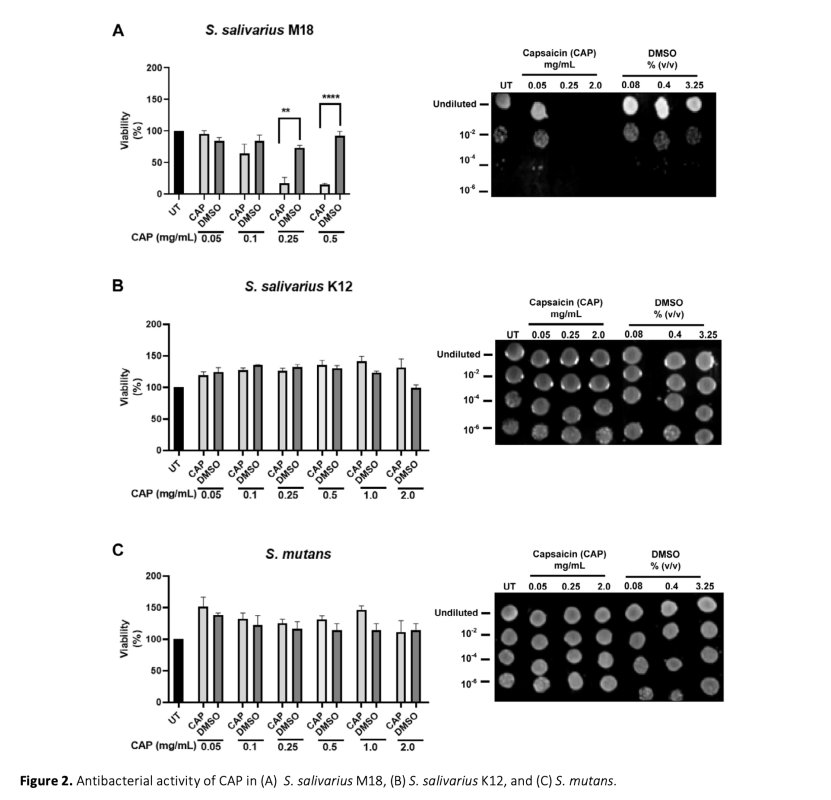
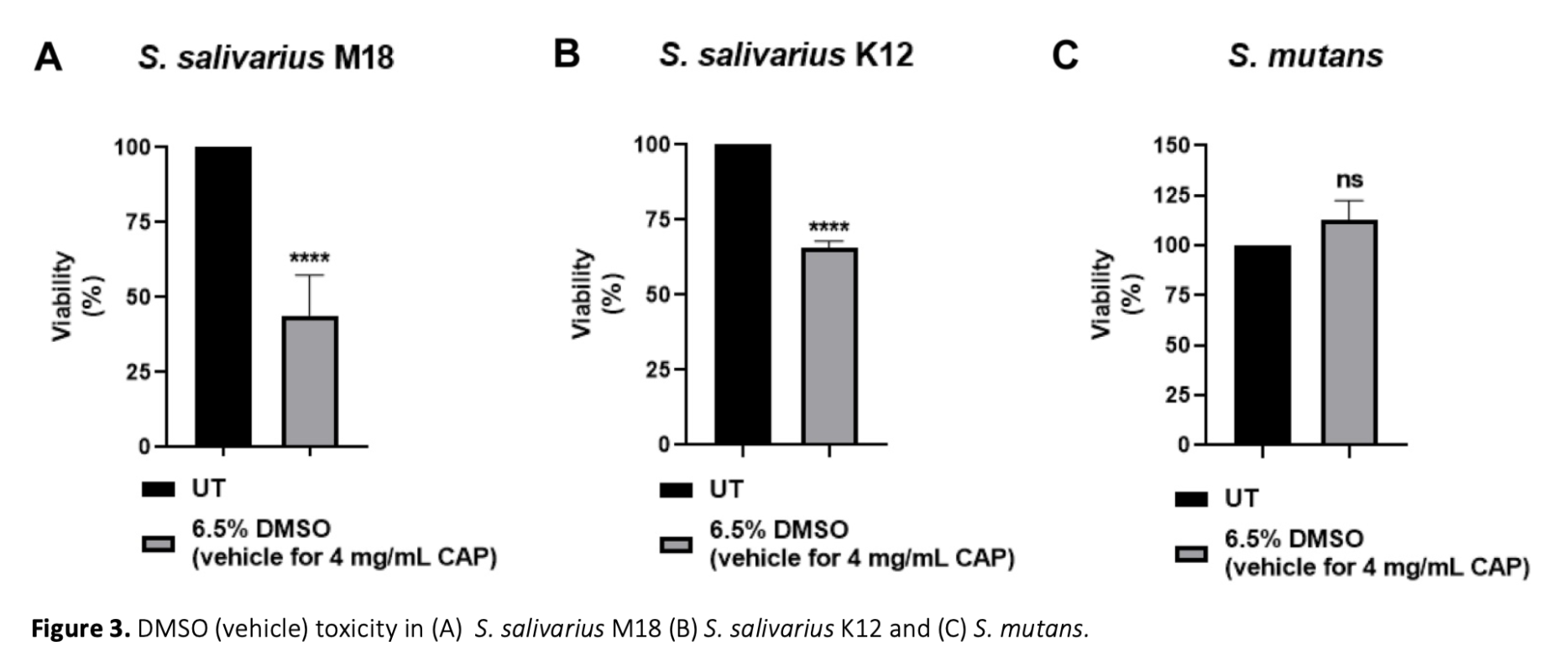
Extensive research has investigated capsaicin (CAP), the primary bioactive compound in chili peppers, to explore its diverse pharmacological and physiological properties. Recently, the focus has shifted to understanding the potential effects of CAP on gut microbiota due to the strong link between gut bacterial profile and diet. However, there has been no research on the effects of CAP on oral microbiota. Therefore, our study aimed to explore the antibacterial effects of CAP on two oral probiotics, Streptococcus salivarius M18, and S. salivarius K12, along with the oral pathogen S. mutans. Previously, the anti-cancer activity of CAP had been demonstrated, and in accordance with these findings, here, we show its growth inhibitory activity on colorectal cancer cell lines. However, this study is the first to examine the impact of CAP on specific oral microorganisms while considering the oral consumption of CAP and the interconnectedness of the oral and gut microbiomes. The findings revealed that CAP exhibited antibacterial properties against the M18 strain at concentrations exceeding 100 μg/mL. Surprisingly, it did not show any growth-inhibitory effects on S. salivarius K12, even at a concentration of 2 mg/mL. Similarly, CAP did not inhibit the growth of S. mutans, a significant factor in dental caries. These results suggest that CAP's effects are species and strain-specific, indicating potential changes in the oral microbiota upon CAP consumption.
Acı biberin ana aktif maddesi olan Kapsaisin (CAP), bugüne kadar çoklu farmakolojik ve fizyolojik özellikleri açısından araştırılmıştır. Bağırsak bakteri profilinin beslenme ile güçlü bir ilişkisi olduğundan, CAP'in bağırsak mikrobiyotası üzerinde etkileri giderek daha fazla ilgi çekmektedir. CAP’in anti-kanser etkileri daha once çalışılmış olup, bu makalede de önceki verilerle uyumlu olarak CAP’in kolorektal kanser hücrelerinde büyüme inhibe edici etkisi olduğu gösterilmektedir. Öte yandan, CAP'in ağız mikrobiyotası üzerindeki etkilerini inceleyen mevcut herhangi bir araştırma bulunmamaktadır. CAP'in oral tüketimi ve oral ve bağırsak mikrobiyomları arasındaki karşılıklı etkileşim göz önüne alınarak, burada, literatürde ilk kez olarak CAP’inin, iki oral probiyotik olan Streptococcus salivarius M18 ve S. salivarius K12 ve oral patojen S. mutans üzerindeki antibakteriyel etkisini araştırmayı amaçladık. Sonuçlar, CAP'in M18 suşu üzerinde antibakteriyel etkiye sahip olmasına rağmen (konsantrasyon 100 μg/mL'den yüksek), 2 mg/mL olarak uygulandığında dahi S. salivarius K12 üzerinde herhangi bir büyüme inhibe edici etki göstermediğini ortaya koymuştur. Benzer şekilde CAP muamelesi, diş çürüklerinde önemli bir etiyolojik faktör olan S. mutans'ın büyümesini de engellemememiştir. Bu veriler, CAP'in tür ve suşa özgü aktivite gösterdiğini ortaya koymakta olup, ayrıca CAP tüketimi sonucu ağız mikrobiyotasında olası değişikliklere dikkat çekmektedir.
Download Article in PDF (1.8 MB)