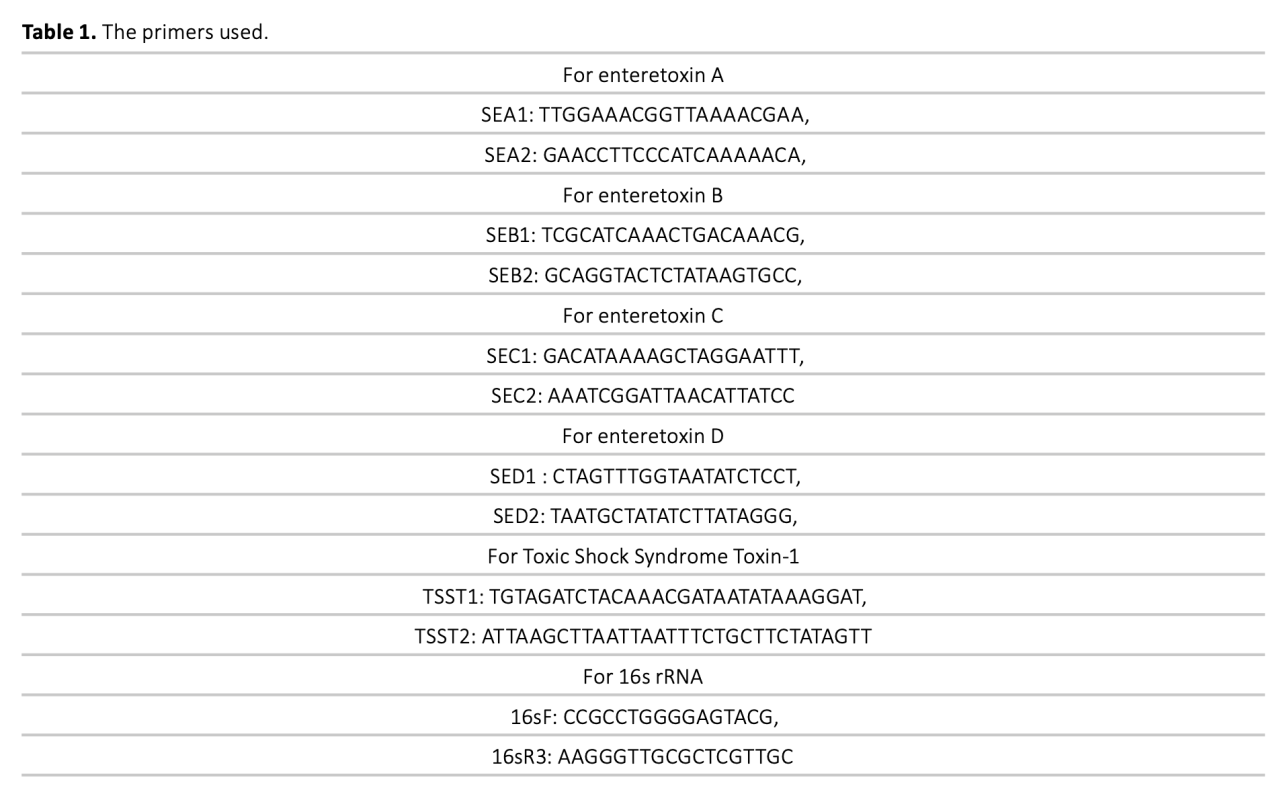
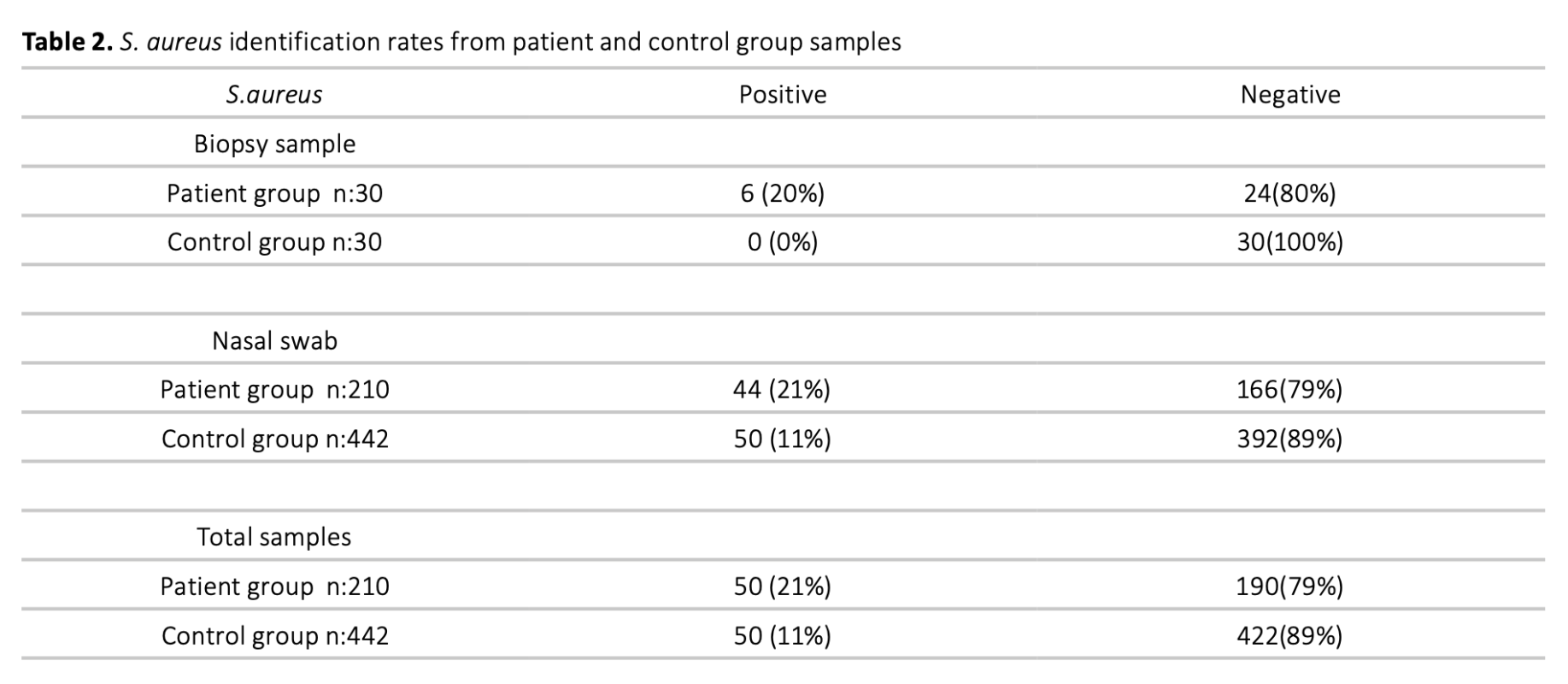
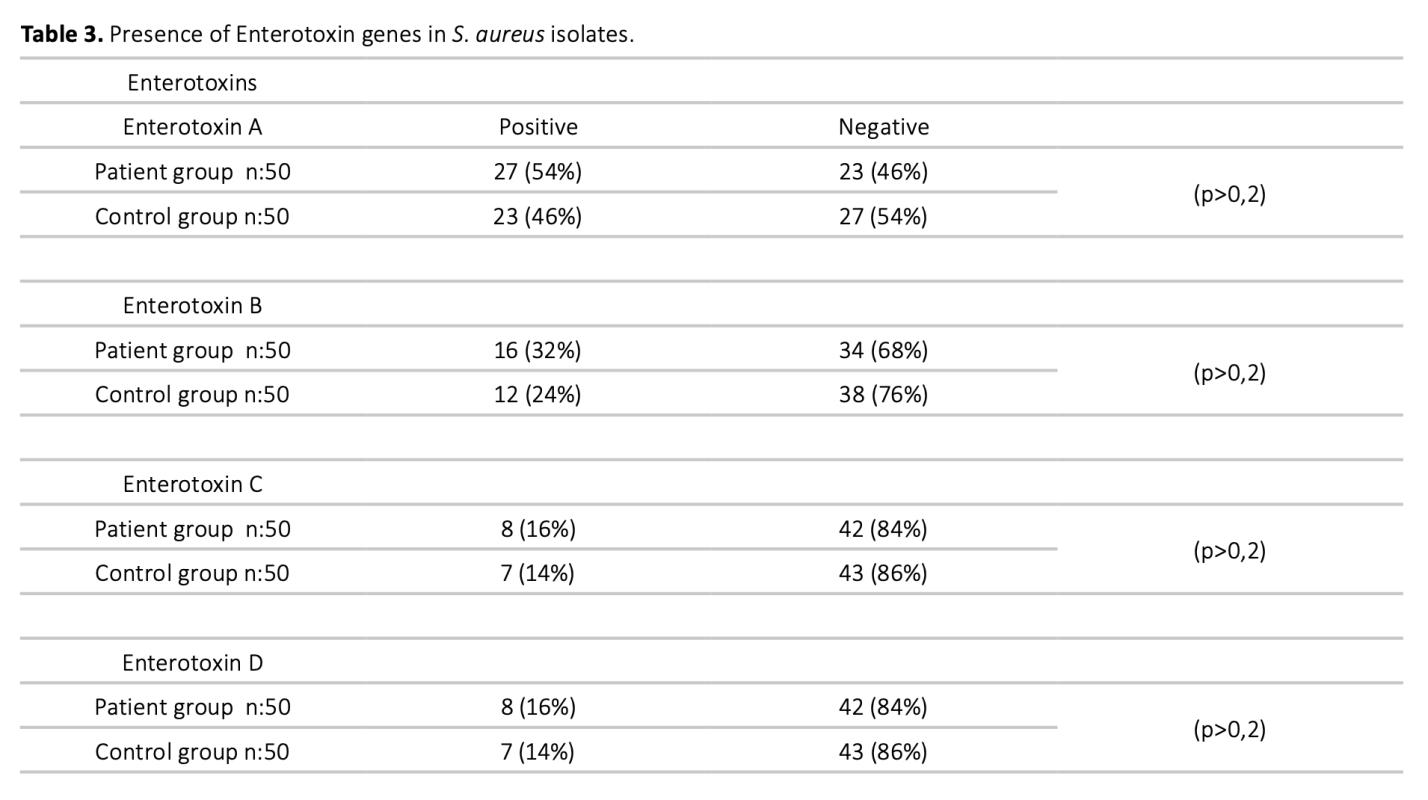
The mechanism of development of chronic rhinosinusitis(CRS) is not fully known. However, bacteria are thought to play an important role in this clinic. It has been suggested that toxins with superantigen(SAgs) properties produced by one of these bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus(S.aureus), play a role in the development of inflammation associated with sinusitis. In this study, S.aureus was isolated by taking endoscopic sinus biopsy samples and nasal swab samples from patients with CRS and the control group. It was aimed to examine the frequency of S.aureus presence in the samples taken, the presence of toxin genes showing superantigen quality in these isolated bacteria, and to evaluate the roles of these parameters in the development of CRS. More S.aureus was isolated in the samples taken from patients with CRS than in the control group. The isolated S.aureus samples were analysed by real-time PCR method. The presence of enterotoxin A, B, C and D genes in the S.aureus samples isolated from the patient group were found at the rates of 54%, 32%, 16% and 16%, respectively, while these rates were 46%, 24%, 14% and 14% in the control group. The Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1(TSST-1) gene was detected in 20% of the samples isolated from the patient and 46% in the control group bacteria. The fact that S.aureus was isolated in 20% of the patients shows that this bacterium is not necessary for CRS. The frequency of superantigen toxin genes in S.aureus isolates shows that these toxins are not necessary for the development of the disease.
Kronik rinosinüzitin gelişim mekanizması tam olarak bilinmemektedir. Bununla birlikte bakterilerin bu klinikte önemli rol oynadıkları düşünülmektedir. Bu bakterilerden biri olan Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus) tarafından oluşturulan süperantijen özelliği gösteren toksinlerin sinüzit ile ilişkili inflamasyonun gelişiminde rol oynadığı ileri sürülmektedir. Bu çalışmada, kronik rinosinüzitli hastalardan ve kontrol grubundan, endoskopik sinüs biyopsi örnekleri ile burun sürüntüsü örnek- leri alınarak S.aureus izole edilmiştir. Alınan örneklerde S. aureus bulunma sıklığı, izole edilen bu bakterilerde süperantijen niteliği gösteren toksin genlerinin varlığının incelenmesi ve bu parametrelerin kronik rinosinüzit gelişimindeki rollerinin değerlendirilmesi amaçlanmıştır. Kronik rinosinüziti olan hastalardan alınan örneklerde, kontrol grubuna göre daha fazla S.aureus üretilmiştir. Üretilen S.aureus örnekleri real-time PCR yöntemiyle incelenmiştir. Hasta grubundan izole edilen S.aureus örneklerinde, enterotoksin A, B, C ve D gen varlığı sırasıyla % 54, % 32, %16 ve %16 oranlarında bulunurken kontrol grubunda bu oranlar % 46, % 24, %14 ve %14 olarak bulunmuştur. TSST-1 geni, hasta grubundan izole edilen örneklerde % 20, kontrol grubu bakterilerinde ise % 46 oranında saptanmıştır. Hastaların % 20’sinde S.aureus izole edilmiş olması bu bakterinin kronik rinosinüzit kliniği oluşumunda mutlak gerekli olmadığını göstermektedir. Süperantijen niteliği gösteren toksin genlerinin S.aureus suşlarında bulunma sıklığı bu toksinlerin hastalık gelişiminde mutlak gerekli olmadığını göstermektedir.

Download Article in PDF (361.5 kB)