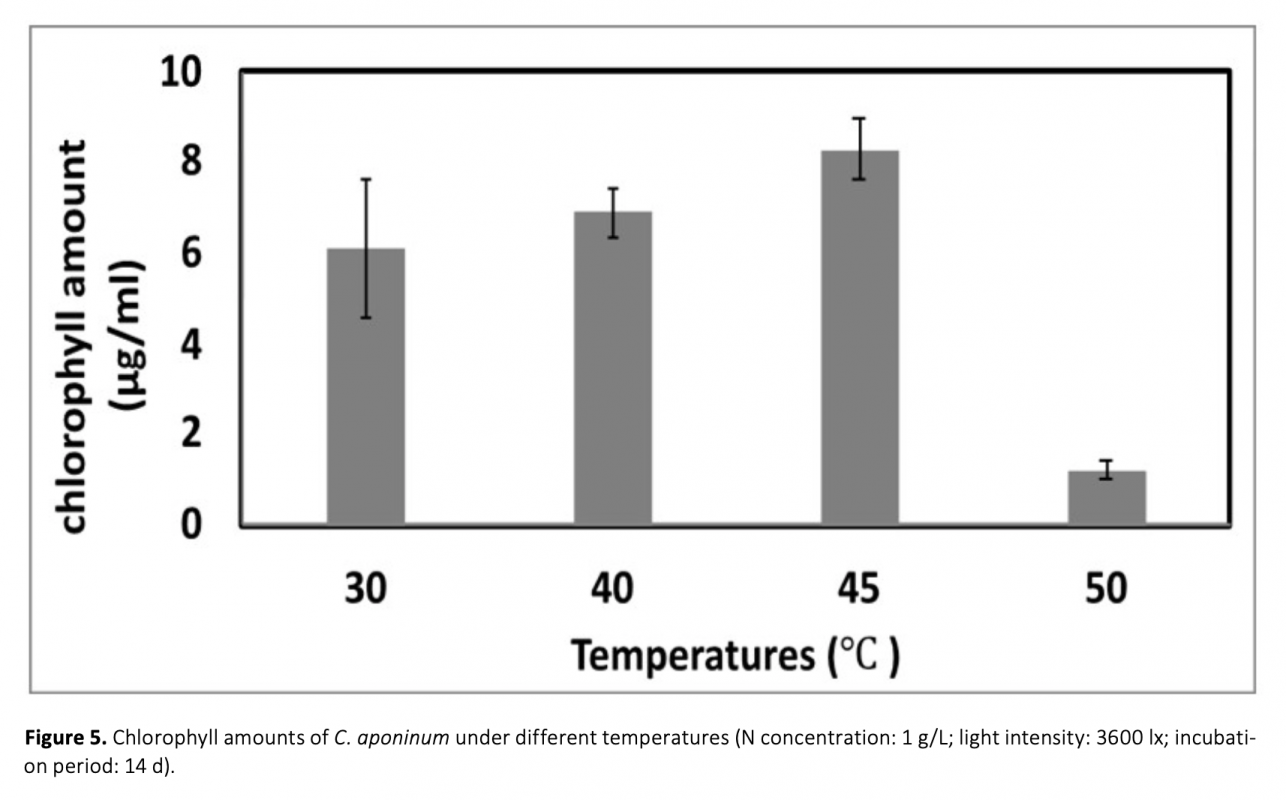
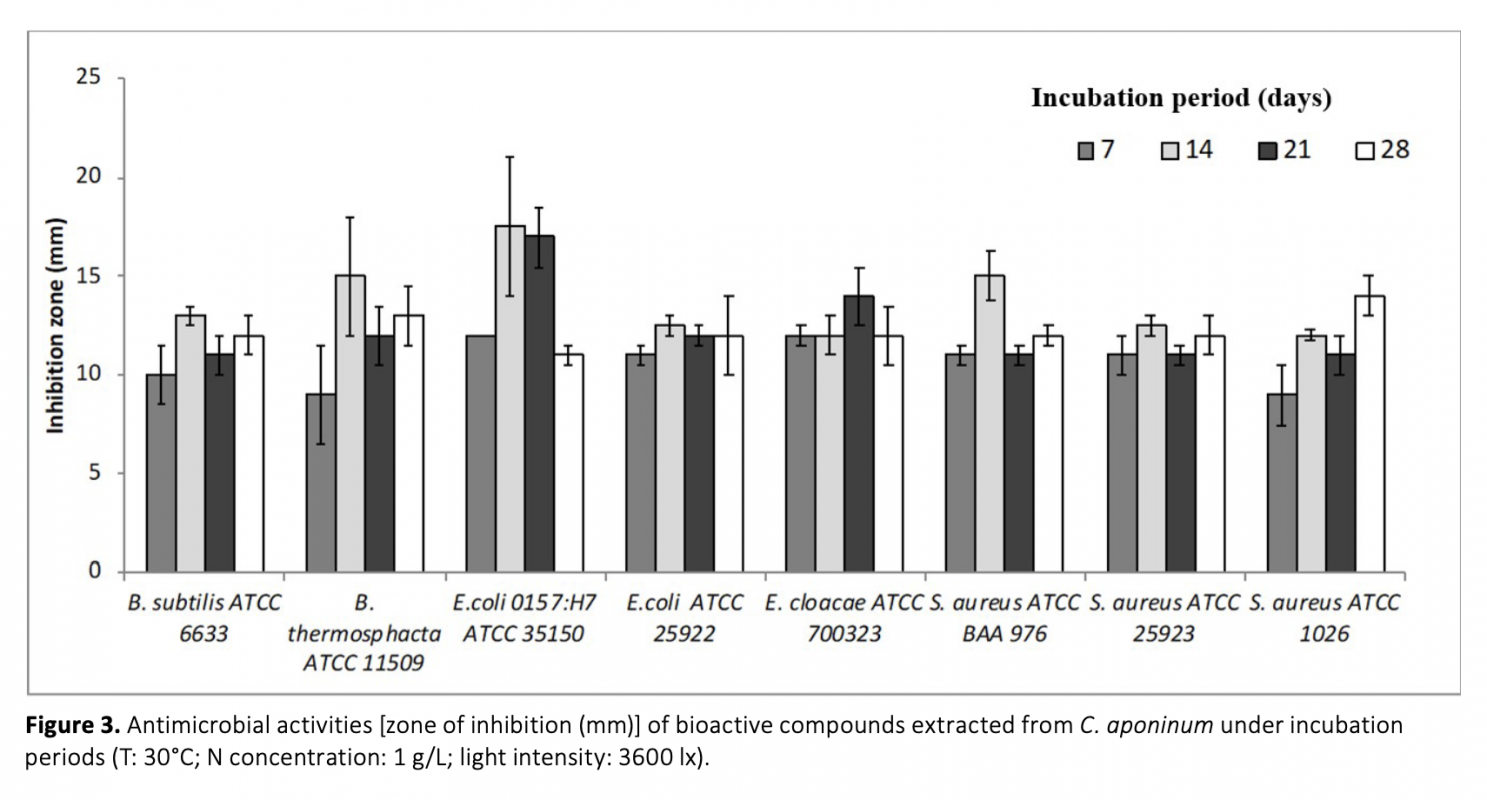
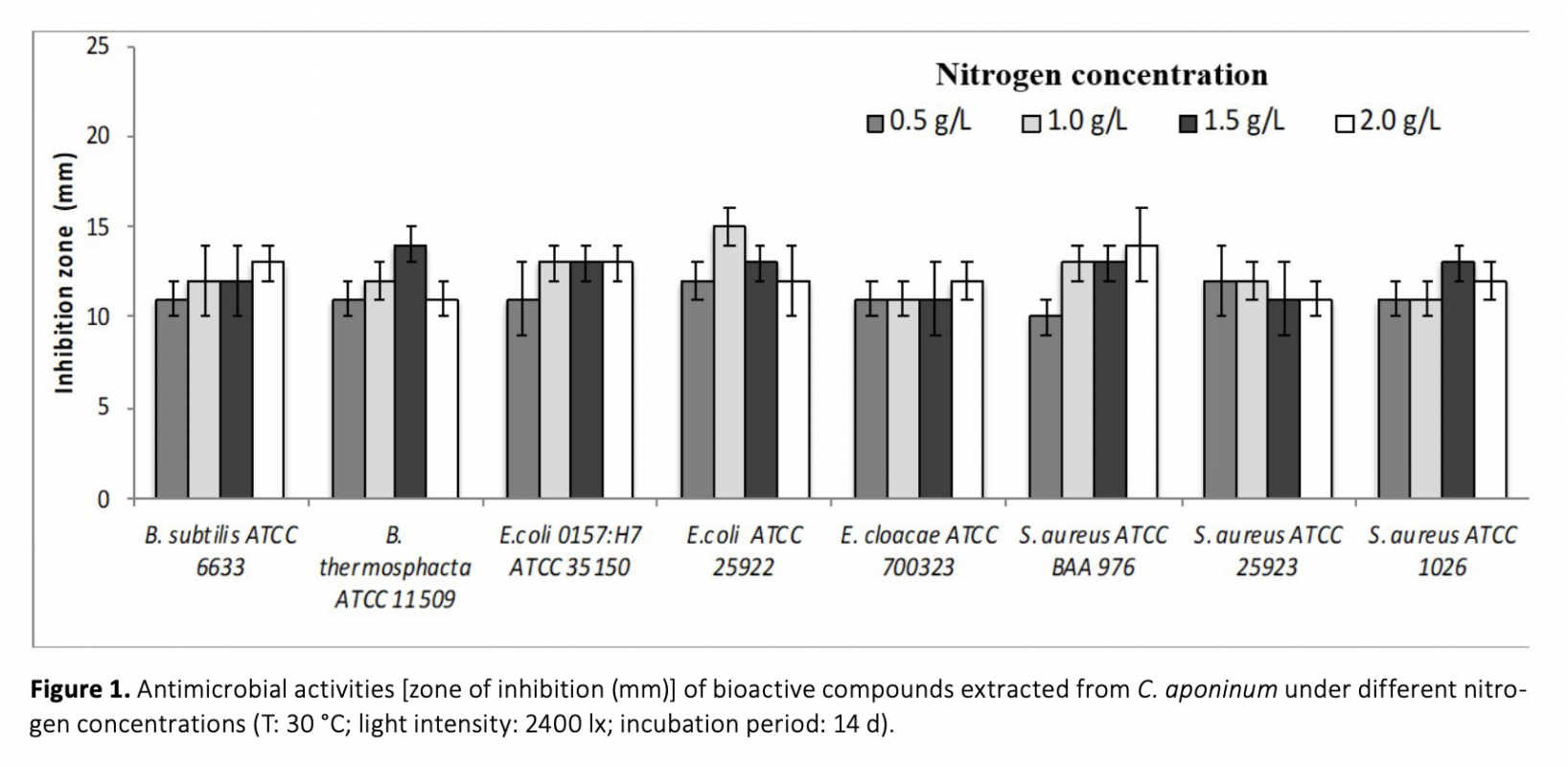
In this report, bioactive properties of 7 thermophile cyanobacteria isolated from thermal springs in Turkey were investigated. Of these, Strain H2 having the highest antimicrobial activity was identified as Cyanobacterium aponium. Bioactive character of cyanobacterial biomass was investigated with regards to different nitrogen concentrations (0.5 g/L, 1.0 g/L, 1.5 g/L, and 2.0 g/L), light intensities (1200lx, 2400 lx, 3600 lx, and 4800 lx), incubation periods (7 d, 14 d, 21 d, and 28 d), and temperatures (30°C, 40°C, 45°C, and 50°C). It was observed that the effectiveness of bioactive substances produced by cyanobacteria was induced by stress conditions. When C. aponinum was exposed to high light intensity or temperature, cyanobacteria produced more efficient bioactive compounds then other environmental conditions tested. The highest antimicrobial activity was found against E. coli 0157:H7 ATCC 35150 with biomass extracts obtained when cyanobacterium cultivated in media with 1.0 g/L nitrogen, at 45°C, under 3600 lx illumination after incubation for 14 days. For the first time with such an approach as in the current study, production of bioactive compounds by a thermophilic C. aponinum and optimization of the environmental conditions to obtain the most efficient biologically active compounds was investigated.
Bu çalışmada, Türkiye’de kaplıcalardan izole edilen 7 termofil siyanobakterinin biyoaktif özellikleri araştırılmıştır. Bunlardan en yüksek antimikrobiyel aktiviteye sahip olan Suş H2, Cyanobacterium aponium olarak tanılanmıştır. Siyanobakteriyel biyokütlenin biyoaktif karakteri, farklı azot konsantrasyonları (0.5 g/L, 1.0 g/L, 1.5 g/L ve 2.0 g/L), ışık yoğunlukları (1200lx, 2400 lx, 3600 lx ve 4800 lx), inkübasyon süreleri (7 gün, 14 gün, 21 gün ve 28 gün) ve sıcaklıklar (30°C, 40°C, 45°C ve 50°C) açısından araştırılmıştır. Siyanobakteriler tarafından üretilen biyoaktif maddelerin etkinliğinin stres koşulları tarafından tetiklendiği gözlenmiştir. C. aponinum yüksek ışık yoğunluğuna veya sıcaklığa maruz kaldığında, siyanobakteriler test edilen diğer çevresel koşullardan daha verimli biyoaktif bileşikler üretmiştir. En yüksek antimikrobiyel aktivite, siyanobakteri 1.0 g/L azot içeren bir ortamda, 3600 lx ışık şiddeti altında, 45°C’de 14 gün boyunca inkübasyondan sonra elde edilen biyokütleden alınan ekstraktlar ile E. coli 0157: H7 ATCC 35150’ye karşı bulunmuştur. Bu çalışmada ilk kez böyle bir yaklaşımla, termofilik C. aponinum tarafından biyoaktif bileşiklerin üretilmesi ve en etkin biyoaktif bileşikleri elde etmek için çevresel koşulların optimizasyonu araştırılmıştır.

Download Article in PDF (1.3 MB)