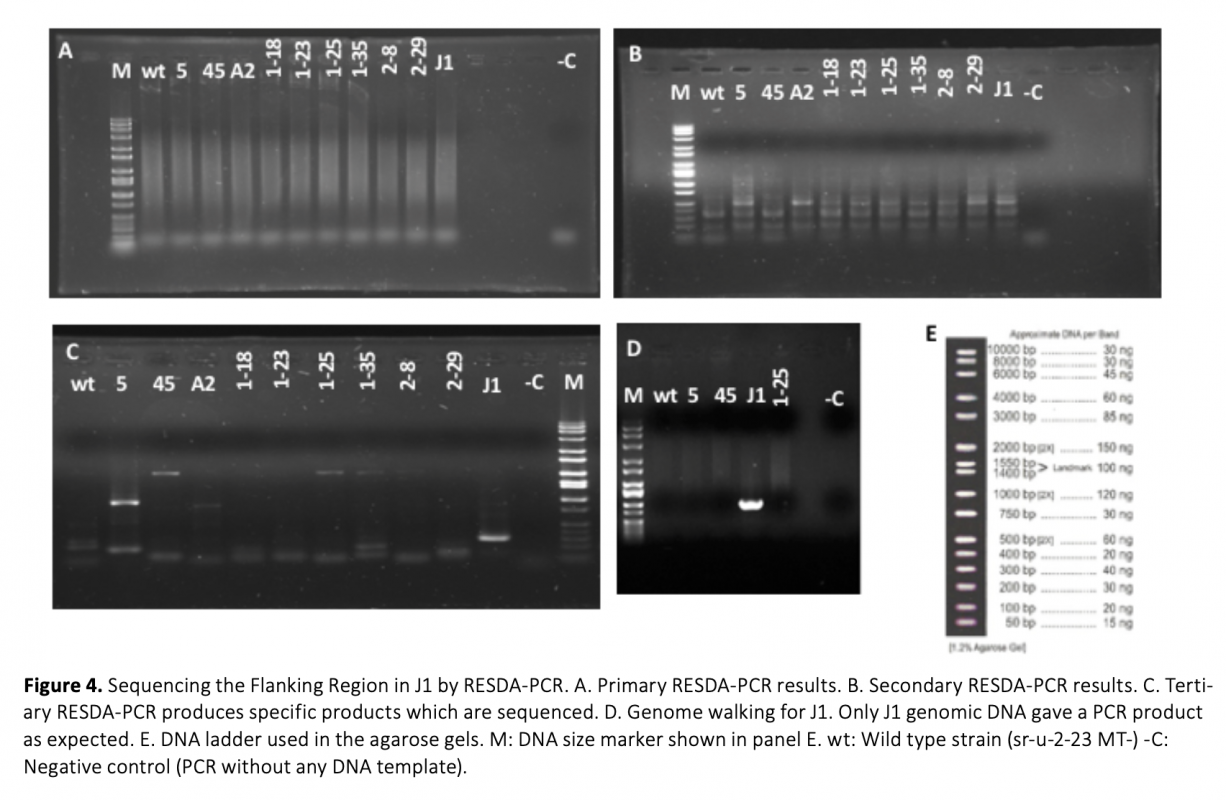
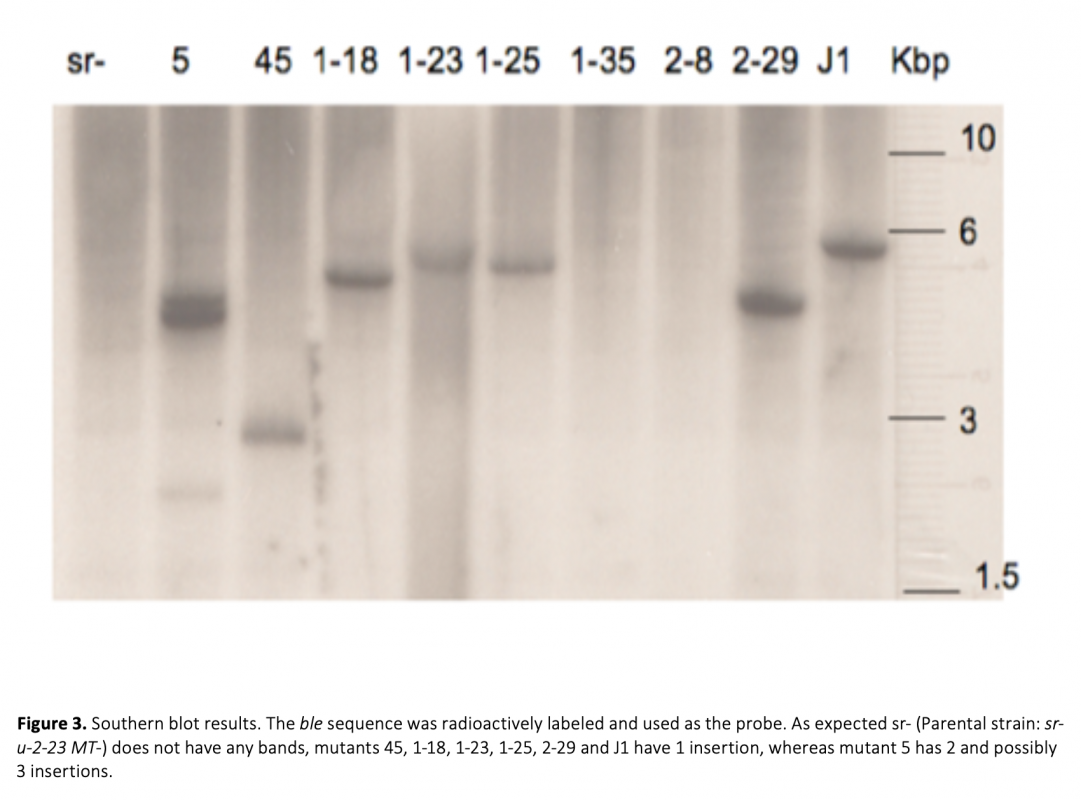
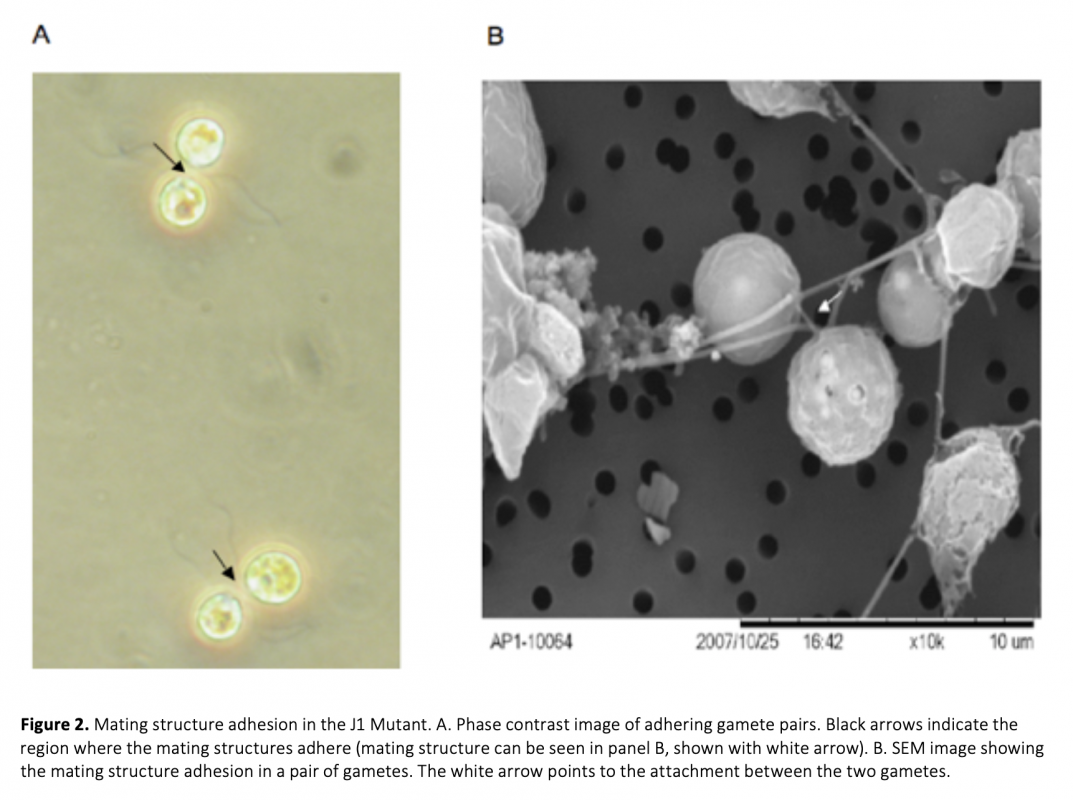
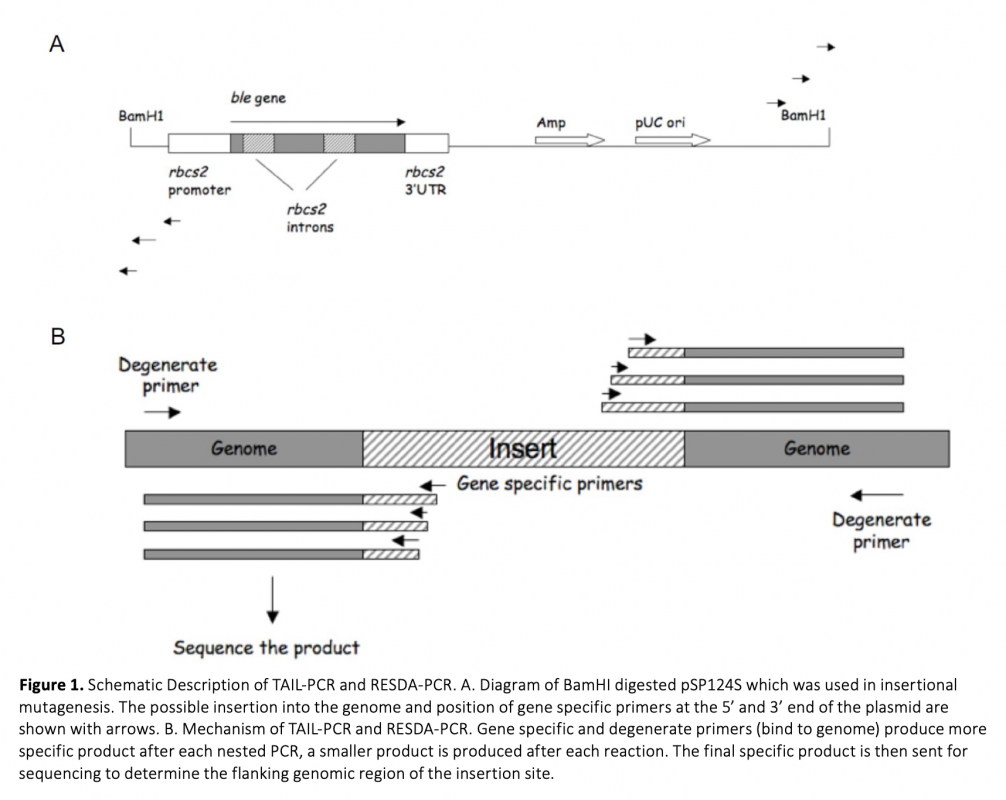
Many biological processes require cell fusion, therefore defects in cell fusion result in many diseases. The unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is an excellent model organism to study cell-cell fusion. The objective of this study was to identify genes that are involved in C. reinhardtii mating type minus (MT_) gamete fusion. A forward genetics approach was taken in our work. We created several MT_ fusion defective mutants using DNA insertional mutagenesis. These mutants were normal in the early stages of mating; they agglutinated with mating type plus (MT+), removed their walls, adhered to their mating partner through their mating structures, but the cells did not fuse, indicating that the DNA insertional mutants were defective in the latest stages of fusion. The number of insertions was confirmed by Southern blots. Mutant J1 had one insertion and the flanking genomic DNA was cloned by TAIL-PCR and RESDA-PCR. The insertion is in a gene predicted to be involved in 5-deoxystrigol biosynthesis.
Birçok biyolojik proses için hücre füzyonu gereklidir, bu yüzden hücre fuzyonu eksikliğinde birçok hastalık görülur. Tek hücreli yeşil alg Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hücre fuzyonu araştırmaları iç mükemmel bir model organizmadır. Bu çalışmanın amacı C. reinhardtii eksi eşey tipinde (MT_) gamet füzyonunda rol alan genlerin belirlenmesidir. Çalışmada ileri genetik tarama (forward genetics) yöntemi kullanılmıştır. DNA insersiyonel mutagenez yöntemi kullanılarak füzyon kapasitesini yitirmiş MT_ mutantlar elde edilmiştir. Bu mutantlar çiftleşmenin erken evrelerinde normal aktivite göstermişlerdir; artı eşey tipi (MT+) ile aglütinasyon göstermişler, hücre duvarlarını çıkartmışlar, karşı eşey tip ile adhezyon yapmışlar fakat hücreler füzyon yapamamışlardır, bu da DNA insersiyonel mutantlarının füzyonun en geç evrelerinde fonksiyon eksikliği taşıdığını göstermistir. DNA insersiyon sayısı Southern blot ile belirlenmiştir. J1 mutantında bir insersiyon görülmüş ve insersiyona komşu genomic DNA bölgesi TAIL-PCR ve RESDA-PCR ile klonlanmıştır. Insersiyonun 5-deoxystrigol biyosentezinde görev alması muhtemel bir gende olduğu belirlenmistir.
Download Article in PDF (1.1 MB)