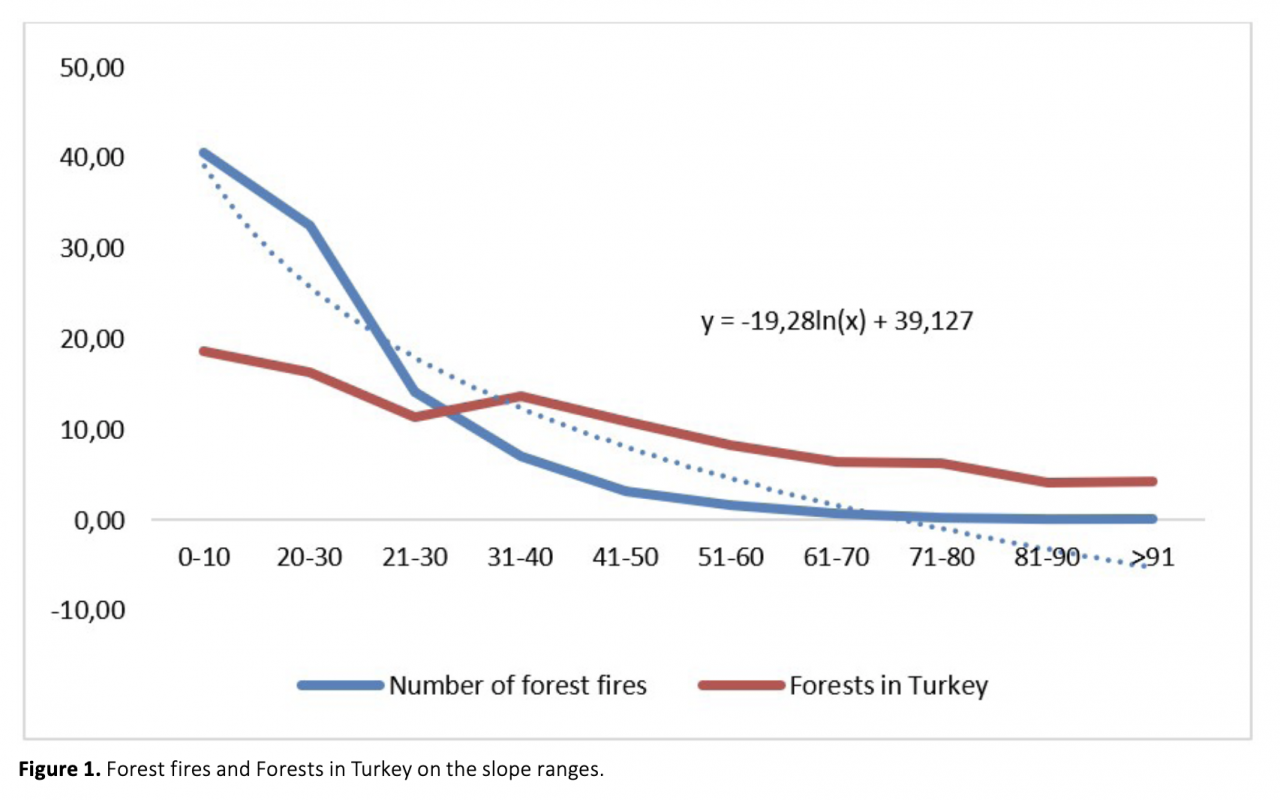
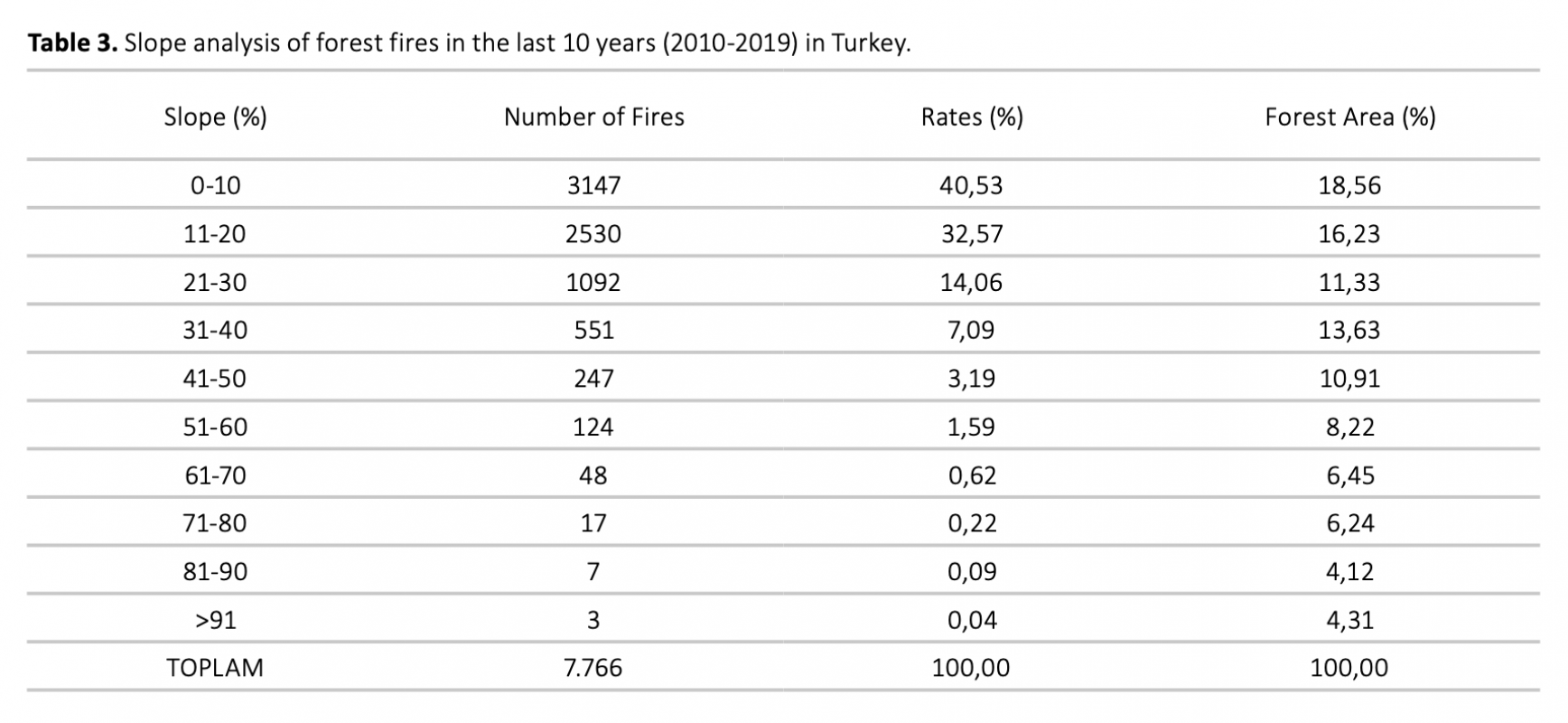
Forest fires are mainly caused by human activities. Therefore, the forest fire risk in an area is under the influence of human activities that may cause forest fires if the vegetation and topographic features are also suitable. While evaluating the effect of slope on forest fire risk in our study, It has been analyzed with geographical information systems (GIS) the starting points of forest fires have occurred in Turkey in the last 10 years. Thus, an objective assessment try to has been made about the effect of slope on forest fire risk. According to the analysis results, 40.53% of forest fires occur in Turkey the range of 0-10% slope. In addition, 87.16% of these fires occur at 0-30% slope. As a result, contrary to the general belief, it has been determined that as the slope increases, the risk of forest fire decreases. The slope affects the fire inversely proportional, On the other hand, it affects the forest fire danger in direct proportion.
Orman yangınlarının ana sebebi insan faaliyetleridir. Bu nedenle bir alanda orman yangını riski, eğer bitki örtüsü ve topoğrafik özellikler de uygunsa, orman yangınına sebep olabilecek insan faaliyetlerinin etkisindedir. Çalışmamızda eğimin orman yangını riskine etkisi değerlendirilirken, son 10 yılda Türkiye’de meydana gelmiş orman yangınlarının başlangıç noktaları coğrafi bilgi sistemleri (CBS) ile analiz edilmiştir. Böylece eğimin orman yangını riskine etkisi konusunda objektif bir değerlendirme yapılmaya çalışılmıştır. Analiz sonuçlarına göre Türkiye’de orman yangınlarının %40,53’ü %0-10 eğim aralığında meydana gelmektedir. Ayrıca bu yangınların %87,16’sı %0-30 eğimde meydana gelmektedir. Sonuç olarak, genel kanıya zıt bir şekilde, eğim arttıkça orman yangını riskinin azaldığı tespit edilmiştir. Eğim orman yangını riskini ters orantılı olarak etkilerken orman yangını tehlikesini ise doğru orantılı olarak etkilemektedir.
Download Article in PDF (448.5 kB)