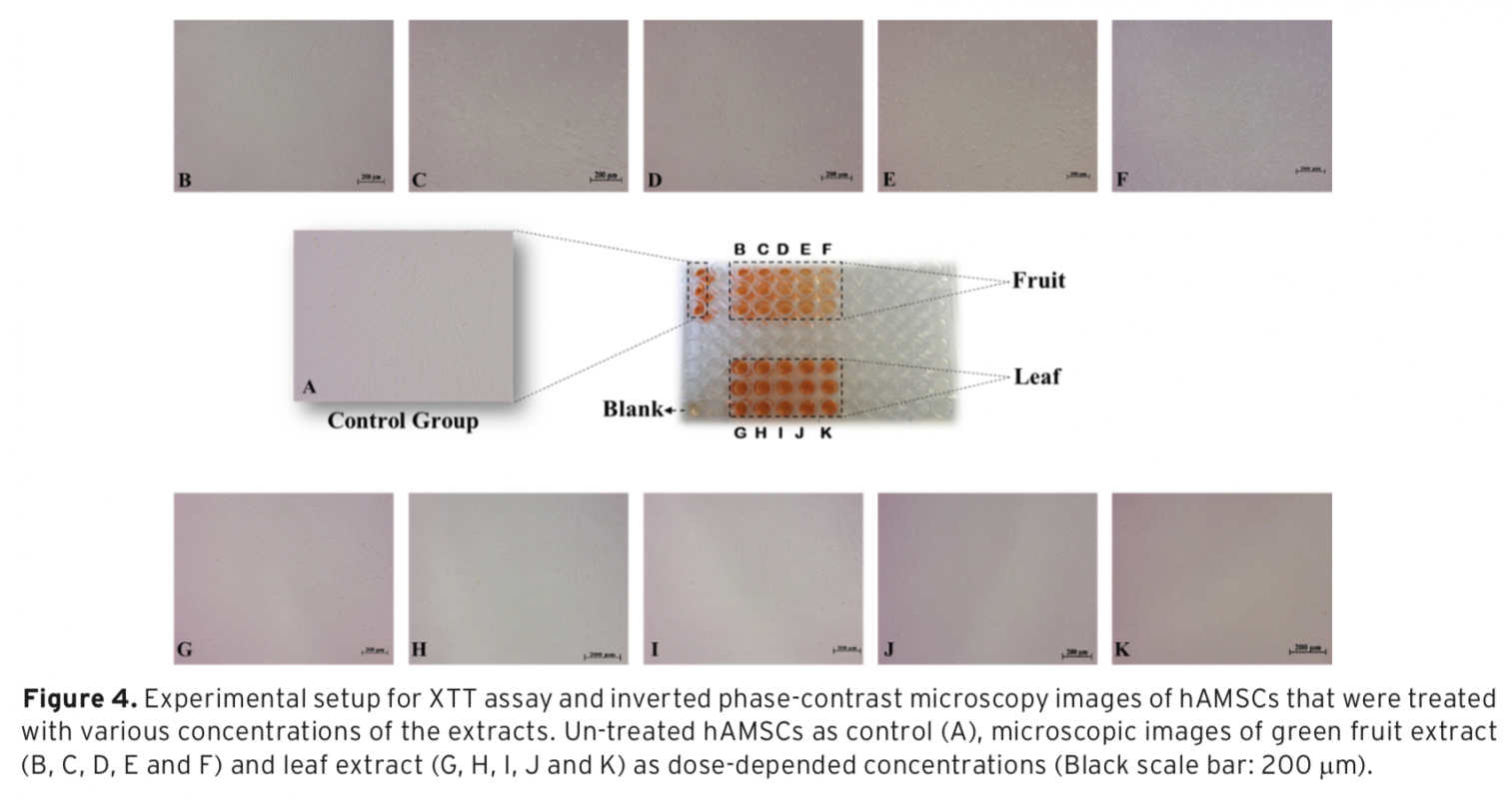
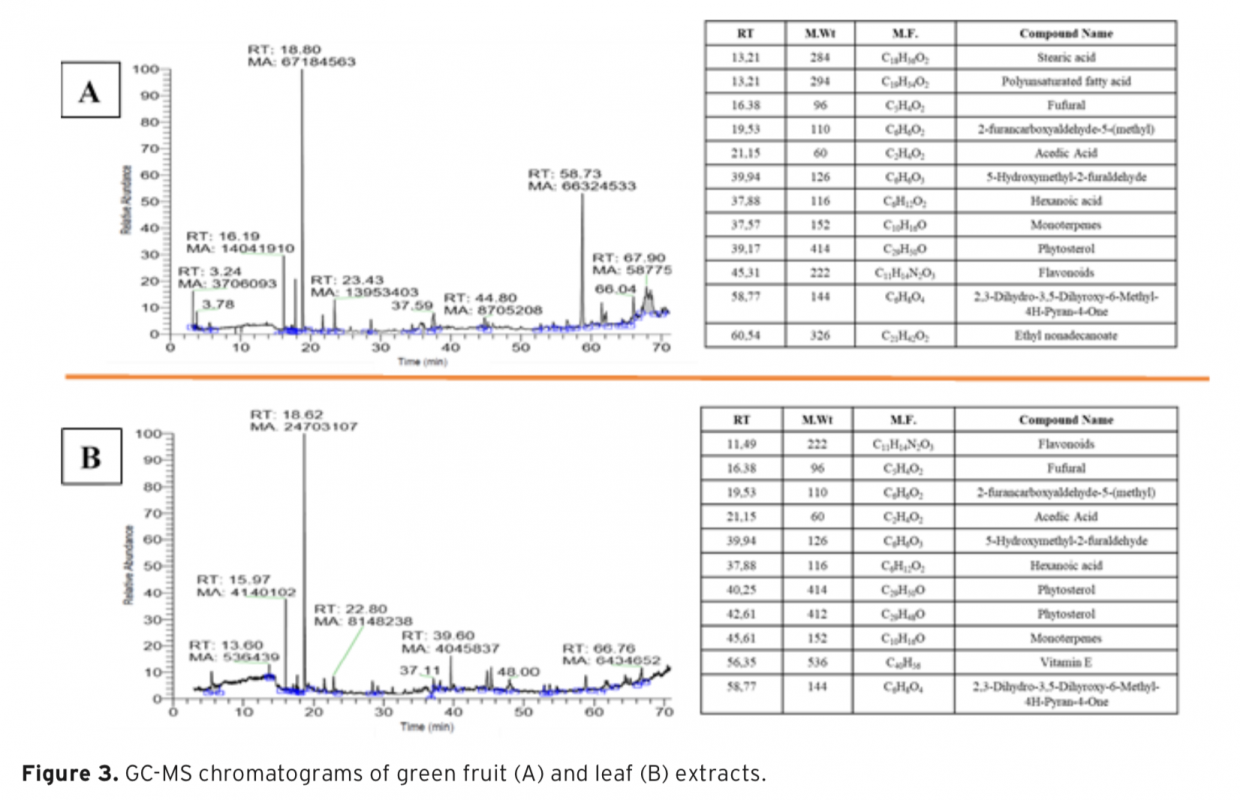
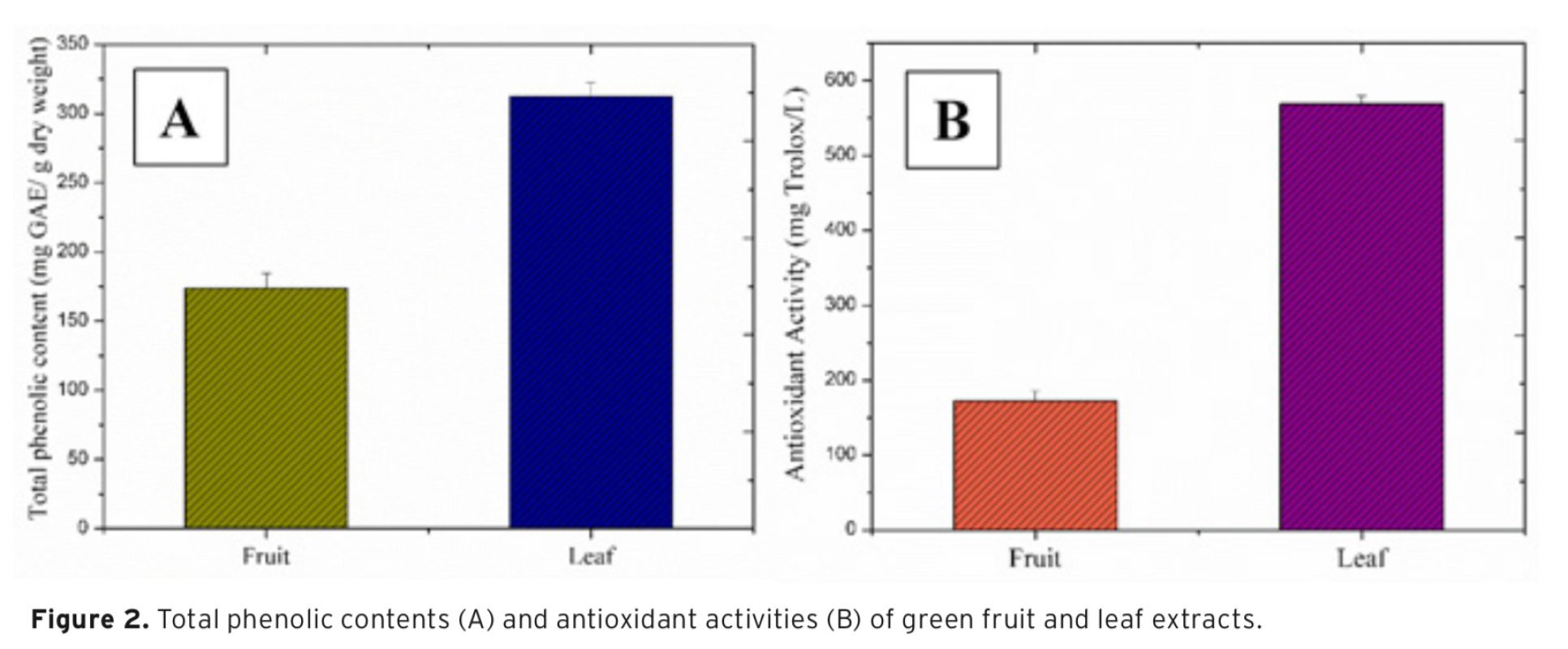
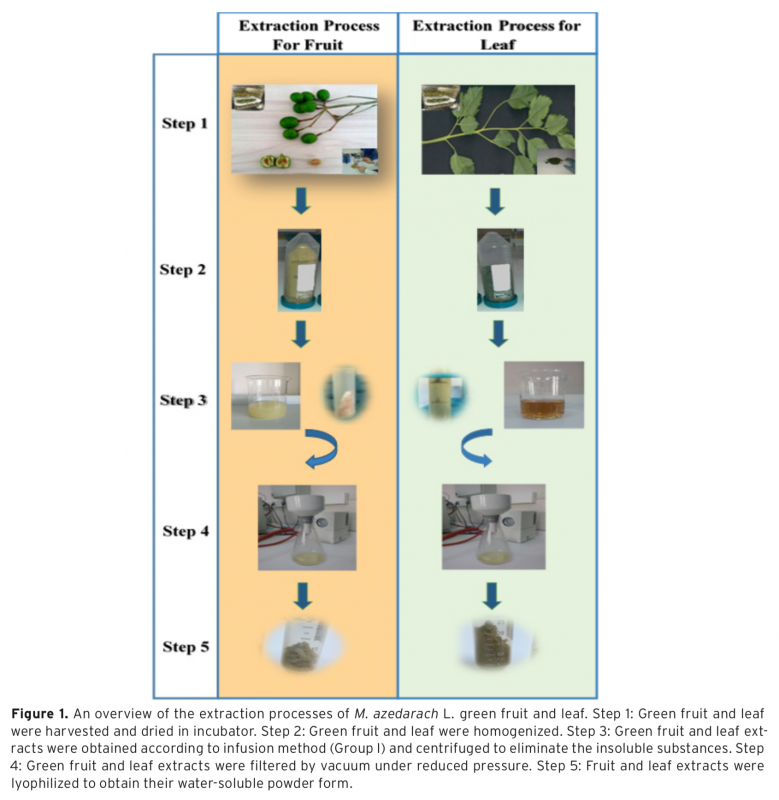
In this study, aqueous extracts of Melia azedarach L. green fruit and leaves were obtained using two different extraction methods. The extraction yields of the green fruit and leaves were found as 24.11% and 37.98% for the infusion method; 17.76% and 27.00% for the rotating method, respectively. The total phenolic content, related to the infusion method, was ascertained for green fruit extract 173.67±10.84 mg Gallic Acid Equivalent (GAE)/g dry weight and leaf extract 312.33±9.81 mg GAE/g dry weight. In other respects, antioxidant activity related to the infusion method was determined for green fruit extract 172.51±13.23 mg Trolox/L and leaf extract 569.16±10.41 mg Trolox/L. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis was performed to identify the chemical composition of the extracts. The cytotoxicity levels of the extracts were assessed on human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) using commercially available XTT assay. Consequently, it has been found that the green fruit extract has more cytotoxic activity than the leaf extract on hAMSCs.
Bu çalışmada, Melia azedarach L. yeşil meyve ve yapraklarının sulu özleri iki farklı özütleme yöntemi kullanılarak elde edildi. Yeşil meyve ve yaprakların özütleme verimleri sırasıyla, demleme yöntemi için %24.11 ve %37.98; çalkalama yöntemi için ise %17.76 ve %27.00 olarak bulundu. Demleme yöntemi ile ilgili toplam fenolik içerik, yeşil meyve özü için 173.67±10.84 mg galik asit eşdeğeri (GAE)/g kuru ağırlık ve yaprak özü için 312.33±9.81 mg GAE/g kuru ağırlık cinsinden tespit edildi. Diğer yandan demleme yönteminde, yeşil meyve özü için 172.51±13.23 mg Trolox/L ve yaprak özü için ise 569.16±10.41 mg Trolox/L cinsinden antioksidan aktivite belirlendi. Özütlerin kimyasal bileşimini tanımlamak için gaz kromatografisi-kütle spektrometresi (GC-MS) analizi yapıldı. Özütlerin insan adipoz kaynaklı mezenkimal kök hücreleri (iAMKH’leri) üzerindeki sitotoksisite seviyeleri ticari olarak mevcut olan XTT testi ile değerlendirildi. Sonuç olarak, yeşil meyve özütünün iAMKH’leri üzerine yaprak özütünden daha fazla sitotoksik aktiviteye sahip olduğu bulunmuştur
Download Article in PDF (505.7 kB)