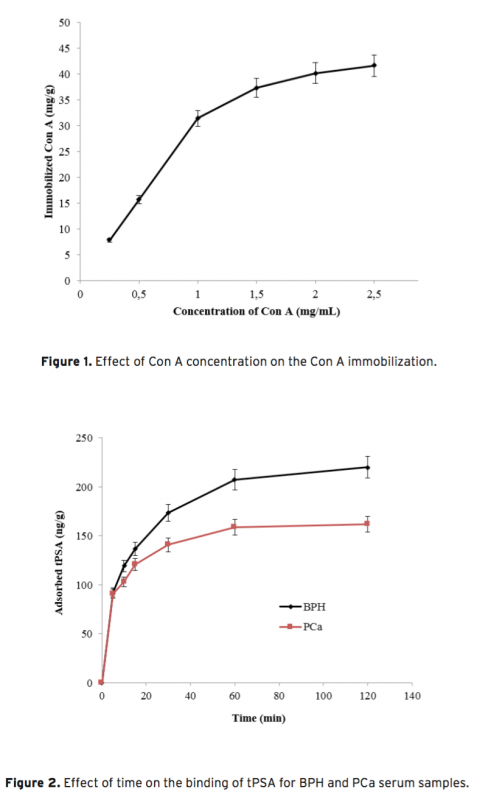
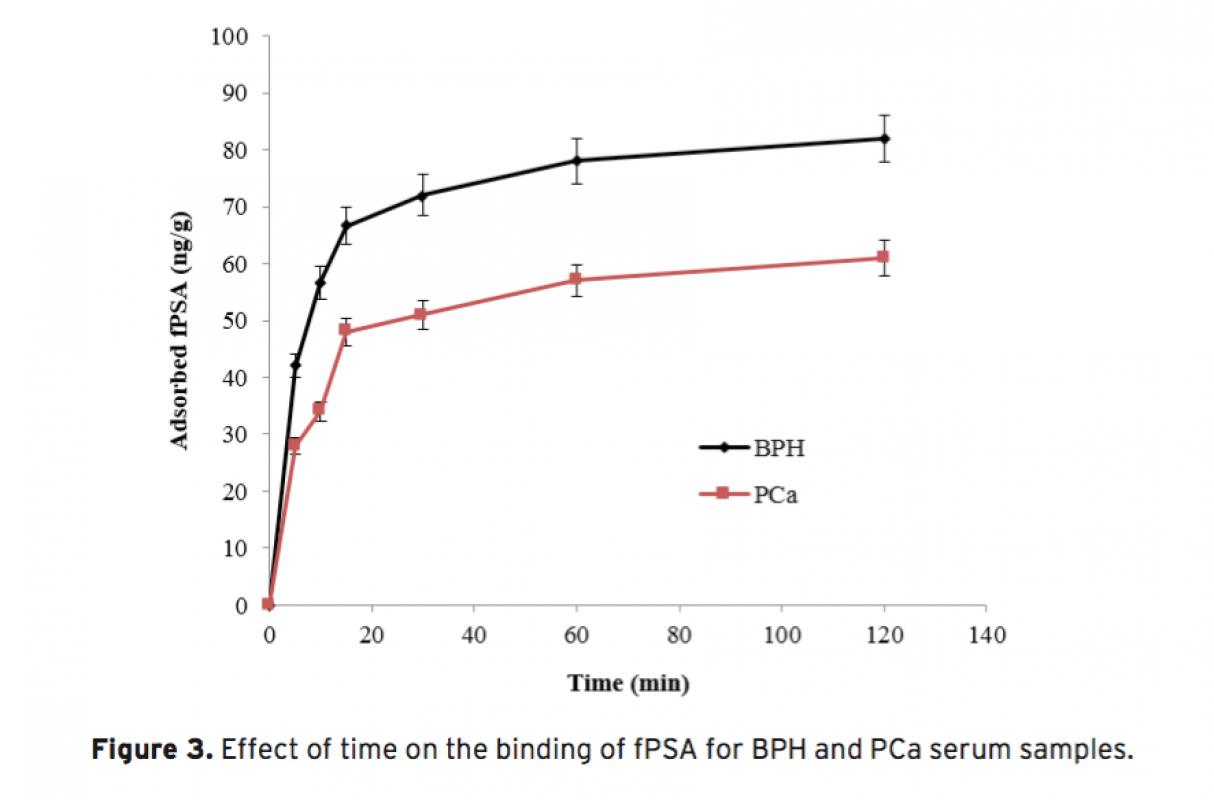
The increased amount of Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) binding capacity is estimated to be associated with the initial concentration of PSA in the serum or cancer-related glycosylation patterns. The aim of this study was to determine tPSA and fPSA binding capacities of mPGMA-HDMA-Con A beads using the serum samples of patients with PCa and BPH having the same concentration of tPSA. Concanavalin A (Con A) is preferred to use as ligand due to the high sugar specificity towards mannose. The initial concentration of the Con A in the medium was changed between 0.25 and 2.5 mg/mL in order to determine the optimum amount of Con A immobilized to the beads. Both tPSA and fPSA adsorption capacity of mPGMA-HDMA-ConA beads performed using the serum sample of patient with BPH were found to be higher than that of PCa. Therefore, the reason of high PSA adsorption capacity observed in patients with BPH could be attribute to the glycosylation changes.
Prostat-spesifik antijen (PSA) bağlanma kapasitesindeki artışın başlangıçta serumda bulunan PSA derişimi ya da kansere bağlı değişen glikozilasyon paternleri ile ilişkili olduğu öngörülmektedir. Bu çalışmada, aynı tPSA derişimine sahip PCa ve BPH’lı hastaların serum örnekleri kullanılarak mPGMA-HDMA-ConA mikrokürelere tPSA ve fPSA bağlanma kapasitesinin belirlenmesi amaçlanmıştır. Concanavalin A (Con A) mannoza karşı özgüllük göstermesi nedeniyle ligand olarak kullanılması tercih edilmiştir. mPGMA mikrokürelere immobilize olan optimum Con A miktarını belirlemek amacıyla ortamdaki Con A miktarı 0.25-2.5 mg/ml arasında değiştirilmiştir. Hem tPSA hem de fPSA için mPGMA-HDMA-ConA mikrokürelerin bağlanma kapasitesinin PCa ile kıyaslandığında BPH’da daha fazla olduğu gösterilmiştir. Böylece, yüksek PSA bağlanma kapasitesinin kansere bağlı değişen glikozilasyondan kaynaklandığı doğrulanmıştır.
Download Article in PDF (145.0 kB)