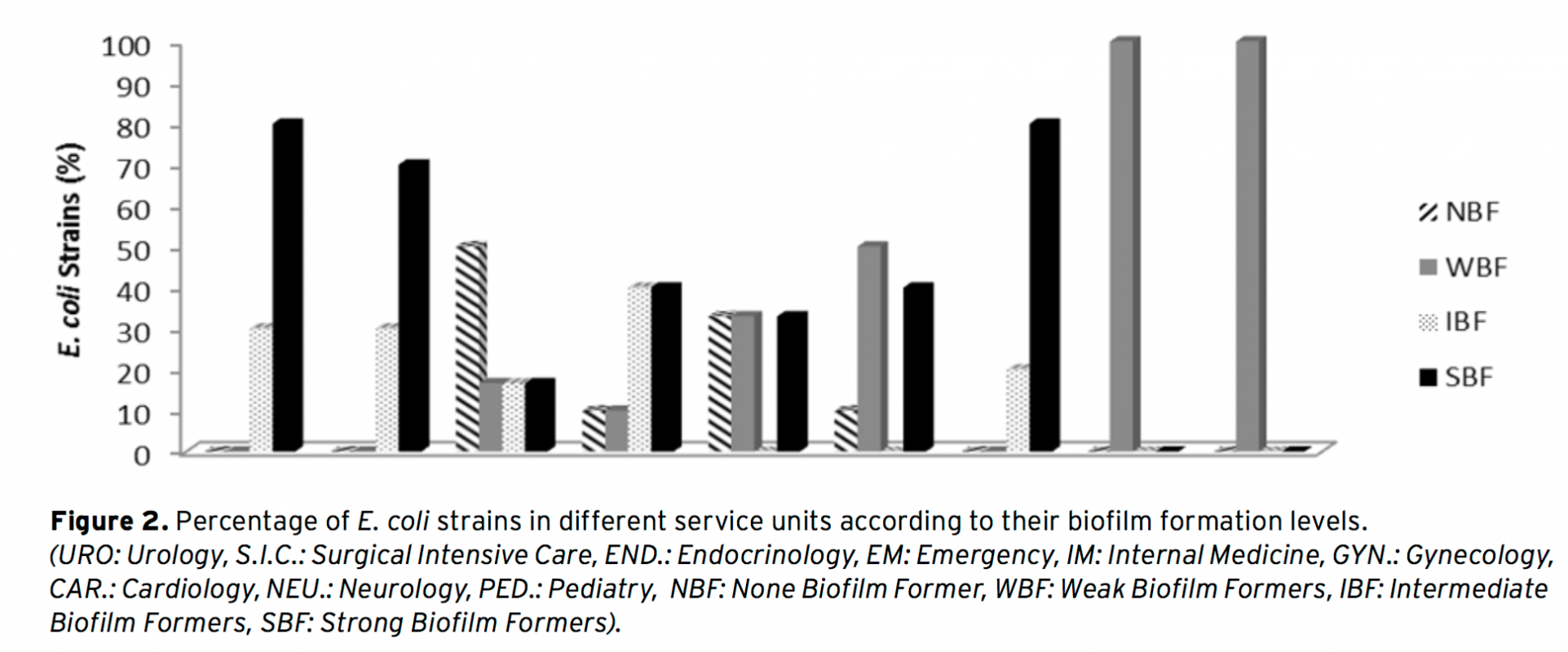
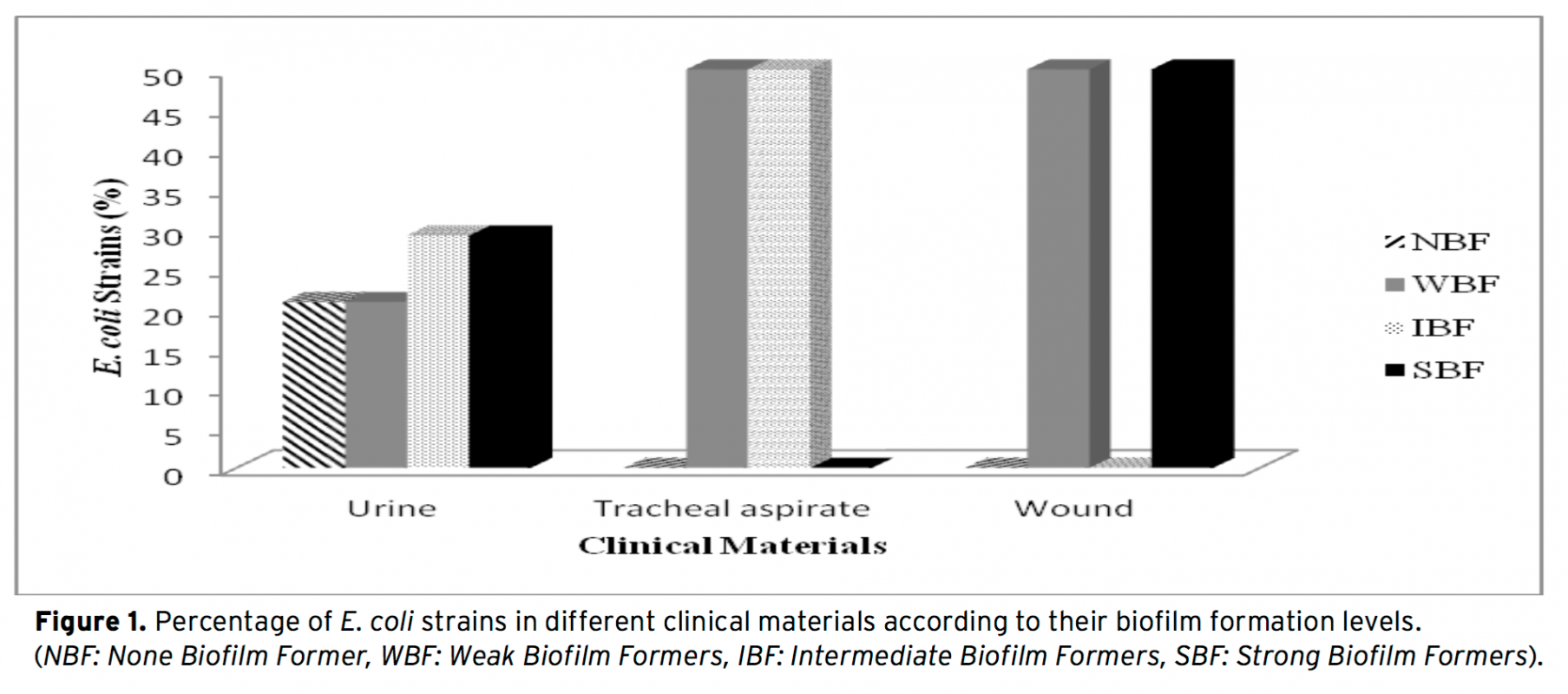
In this study, investigation of biofilm formation levels of clinically acquired Escherichia coli strains and exami- nation of each E. coli strains’ clinical information such as clinical material and service units according to their biofilm formation results were determined. In this respect, according to our results; E. coli strains are grouped as 31% Strong Biofilm Former (SBF), 27% Intermediate Biofilm Former (IBF), 25 % Weak Biofilm Former (WBF) and 17% None Biofilm Former (NBF). In addition to this, clinical materials of wound and urine were found as the most frequent clinical materials from which strong biofilm Former E. coli strains isolated. Besides, urology and cardiology were found as the most SBF isolated service units. Apart from these, E. coli strains were mostly isolated from urinary tract infections and from women who are at the period of post-menopausal. Lastly, the antibiotic susceptibility patterns were investigated and the greatest susceptibility was observed against amika- cin and the least susceptibility was observed against trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Accordingly, NBF strains of E. coli were more susceptible to eight antibiotics than Strong Biofilm Former (SBF) strains.
Bu çalışmada, klinik materyallerden elde edilen Escherichia coli suşlarının biyofilm oluşturma yetenekleri araştırıldı ve her bir E. coli suşunun klinik materyal ve servis ünitesi bilgileri biyofilm oluşturma sonuçları ile bir arada değerlendirildi. Bu bağlamda çalışmamızın sonuçlarına göre E. coli suşlarının %31’i Yüksek Biyofilm Oluşturan (YBF), %27’si Ilımlı Biyofilm Oluşturan (IBO), %25’i Zayıf Biyofilm Oluşturan (ZBF) ve %17’si ise Biyofilm Oluşturmayan olarak gruplandırıldı. Buna ek olarak klinik materyallerden yara ve idrarın en yüksek sıklıkta izole edilen klinik materyaller olduğu saptandı. Ayrıca Yüksek Biyofilm Oluşturan (YBO) suşların en fazla üroloji ve kardiyoloji servislerinden izole edildiği gözlendi. Bunların yanı sıra, E. coli suşlarının post-menapozal dönemdeki üriner yol enfeksiyonu geçiren kadınlardan en fazla sıklıkta izole edildiği saptandı. Son olarak E. coli suşlarının antibiyotik hassaslık paternleri incelendiğinde en yüksek hassaslığın amikasin antibiyotiğine, en düşük hassaslığın ise trimetoprim sülfametaksazol antibiyotiğine karşı olduğu gözlendi. Bununla ilişkili olarak Biyofilm Oluşturmayan E. coli suşlarının çalışmada kullanılan 8 antibiyotiğe karşı Yüksek Biyofilm Oluşturan (YBF) E. coli suşlarına kıyasla daha hassas oldukları belirlendi.
Download Article in PDF (160.7 kB)