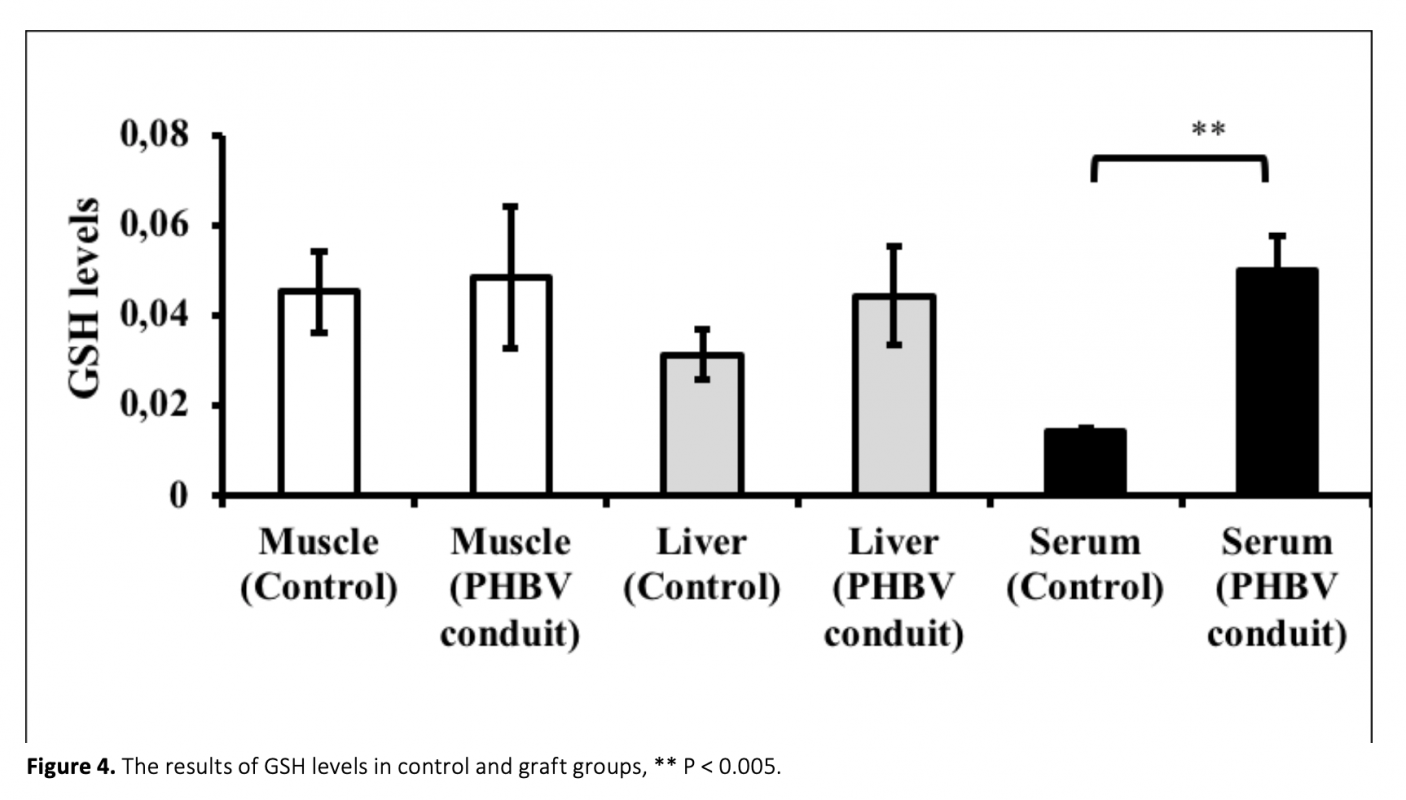
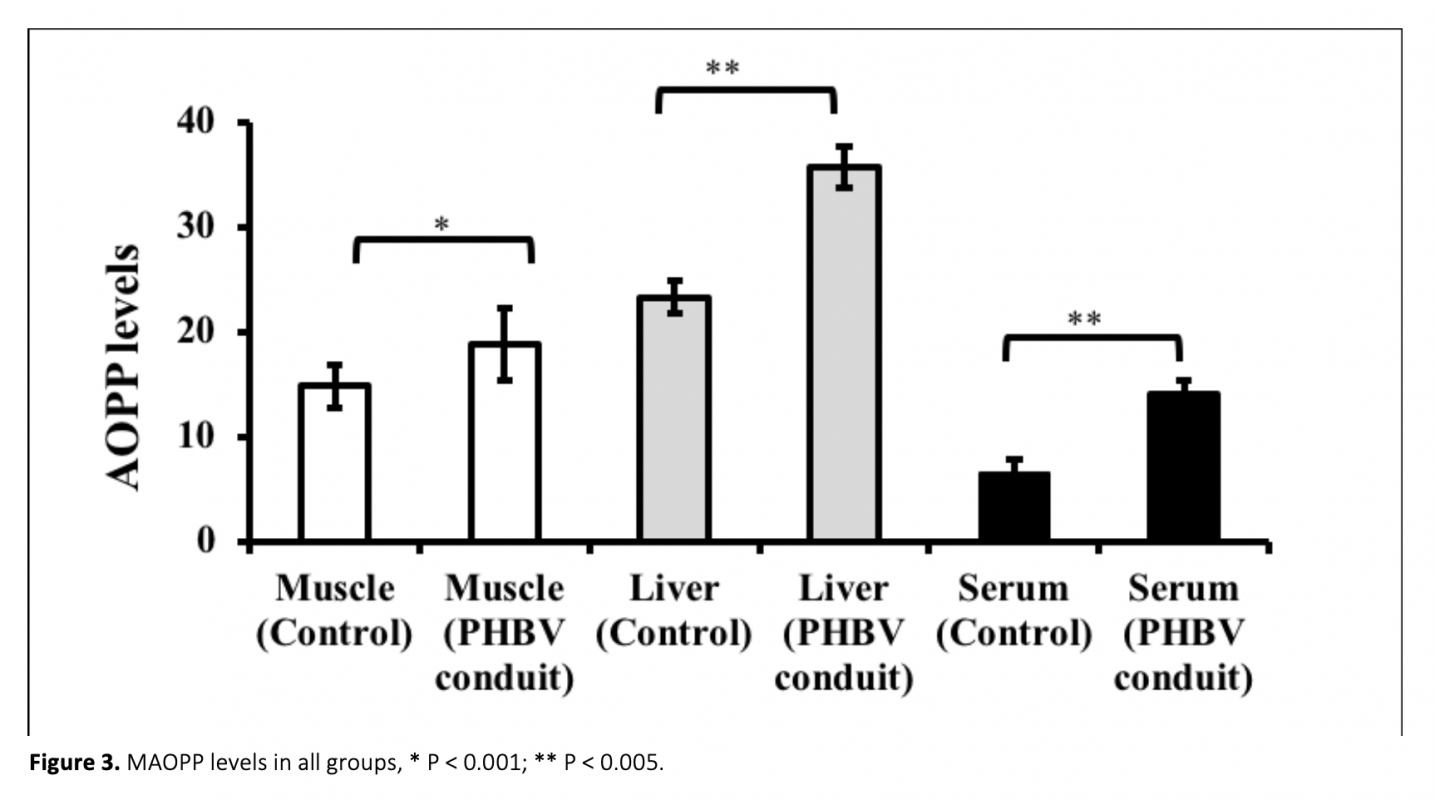
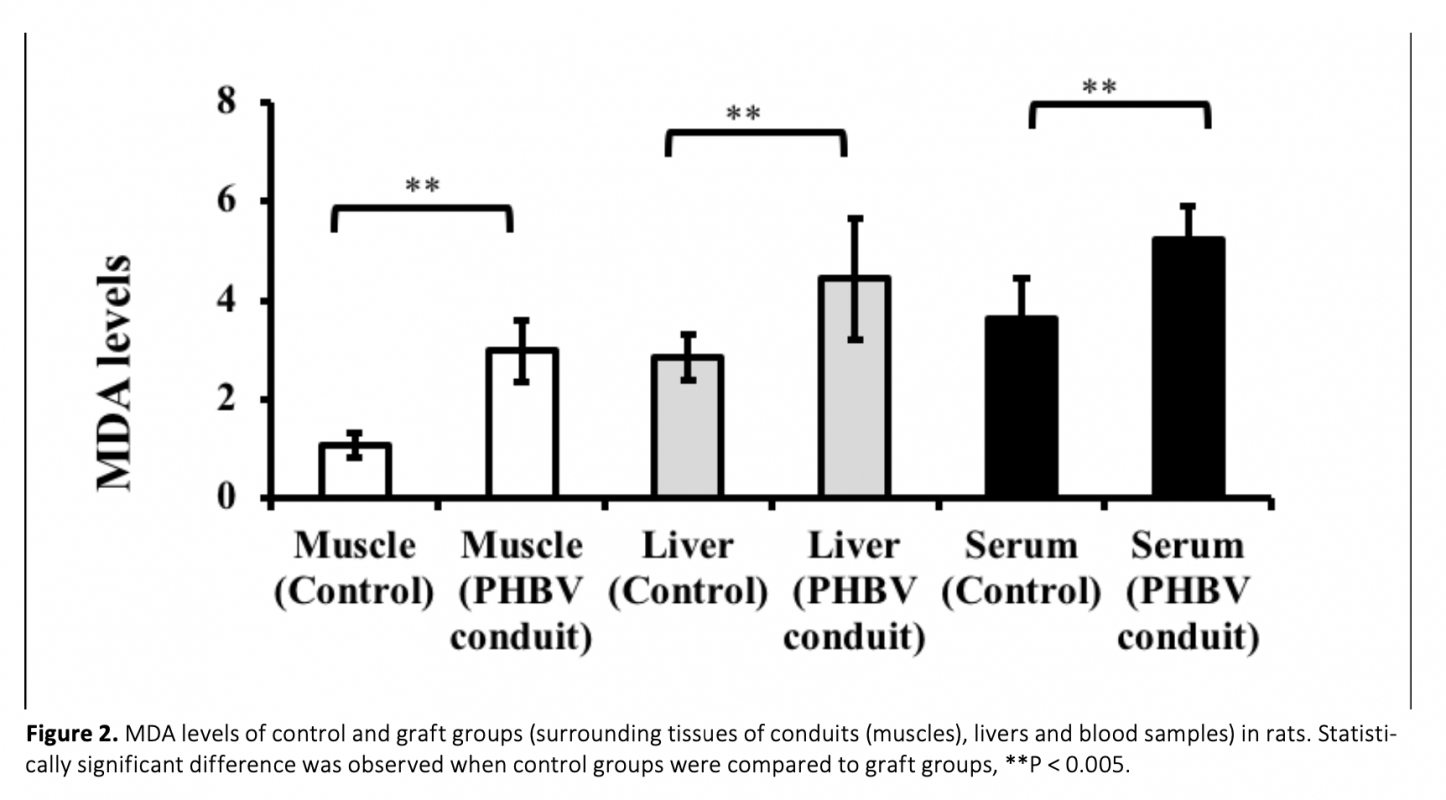
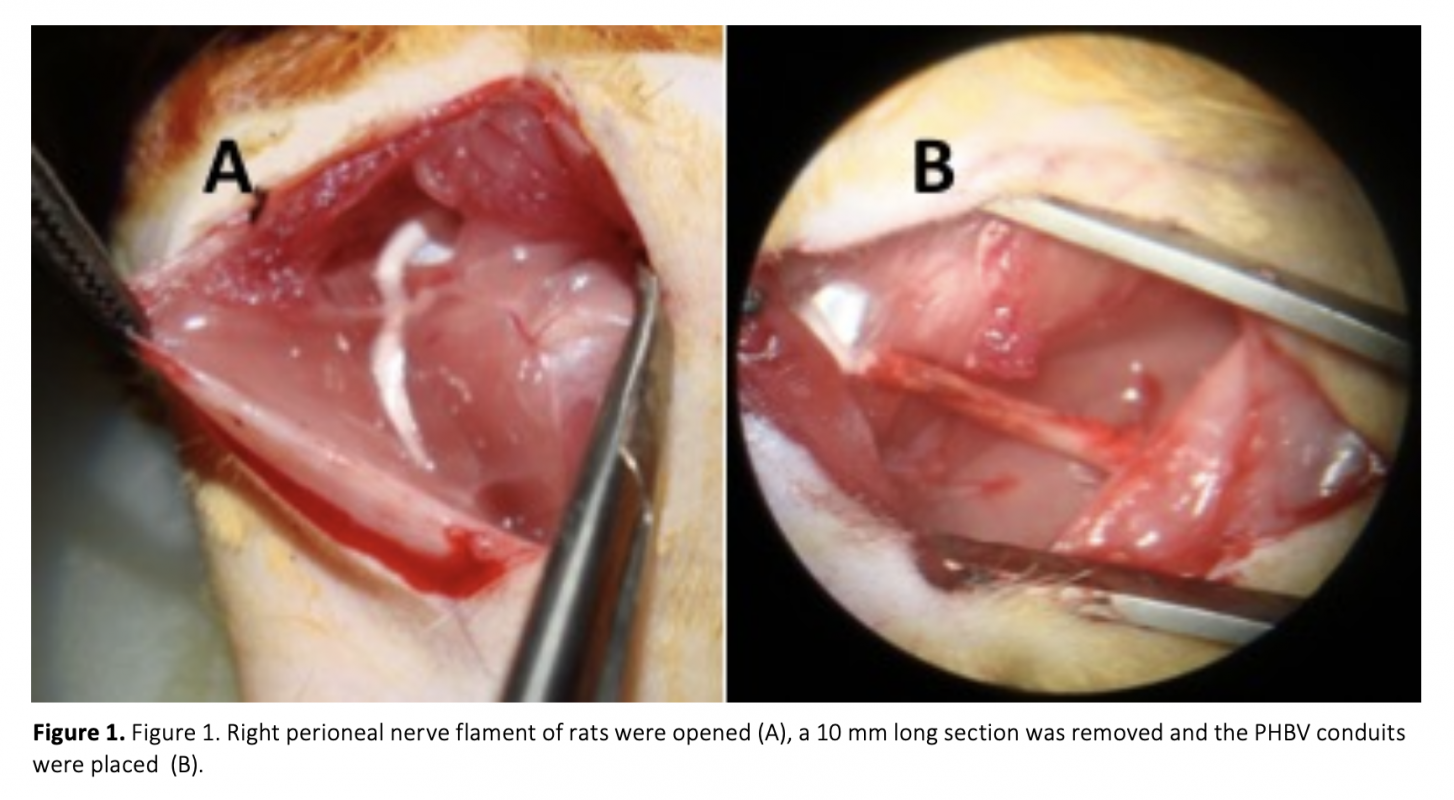
Due to lack of self-repair mechanism in neuronal tissue, biomaterials have been widely studied to regenerate damaged nerve tissue. Despite having advantages, nano materials may cause oxidative stress and this could affect the treatment. In the present study, whether PHBV [poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)] used for axonal regeneration could lead to lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation in rats or not and also its effects on antioxidant molecules was explored. In the study, PHBV nanofiber membranes were formed by electrospinning and conduits were formed by using the nanofiber membrane. After the formation of a 1 cm gap in the rat peritoneal nerves, PHBV conduits were placed. Animals were sacrificed at 17th week after the operations. Malondialdehyde (MDA), advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP), glutathione (GSH) levels and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities of livers, as well as surrounding tissues of conduits (muscles) and serums were measured. Compared to control groups, MDA, AOPP and GSH levels and SOD activites in all graft group serums showed a significant increase, while only MDA and AOPP levels in tissues were statistically higher. Therefore, these findings suggest that PHBV nerve graft used for sciatic nerve defects may lead to oxidative stress in rats.
Nöronal hücrelerin kendi kendilerini tamir mekanizmaları olmamasından dolayı, hasarlı sinir dokularının rejenerasyonunda biyomateryaller yaygın bir şekilde çalışılmıştır. Avantajları olmasına rağmen, nanomateryaller oksidatif strese neden olabilir ve bu durum tedaviyi etkileyebilir. Bu çalışmada, aksonal rejenerasyon için kullanılan PHBV [poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)]’nin ratlarda lipid peroksidasyonuna ve protein oksidayonuna neden olup olmadığı ve ayrıca antioksidan molekülleri etkileyip etkilemediği araştırıldı. Çalışmada, elektrospinning ile PHBV yönlendirilmiş nanofiber membranlar hazırlandı ve bunlar kullanılarak graftler oluşturuldu. Sıçan peritoneal sinirlerinde 1 cm boşluk oluşturulduktan sonra PHBV graftler yerleştirildi. Hayvanlar operasyon sonrası 17. haftada feda edildi. Ratların kan, karaciğer ve graft yerleştirilen perioneal sinir demeti çevre kas dokusu malondialdehit (MDA), ileri oksidasyon protein ürünleri (AOPP), glutatyon (GSH) seviyeleri ve süperoksit dismutaz (SOD) aktiviteleri ölçüldü. Kontrol grubu ile karşılaştırıldığında, tüm graft grubu serum MDA, AOPP ve GSH düzeyleri ve SOD aktivitelerinde anlamlı bir artış gözlenirken, dokularda sadece MDA ve AOPP seviyeleri istatistiksel olarak yüksek bulundu. Bu bulgular perioneal sinir defektleri için kullanılan PHBV graftinin sıçanlarda oksidatif strese neden olabileceğini düşündürmektedir.
Download Article in PDF (527.5 kB)