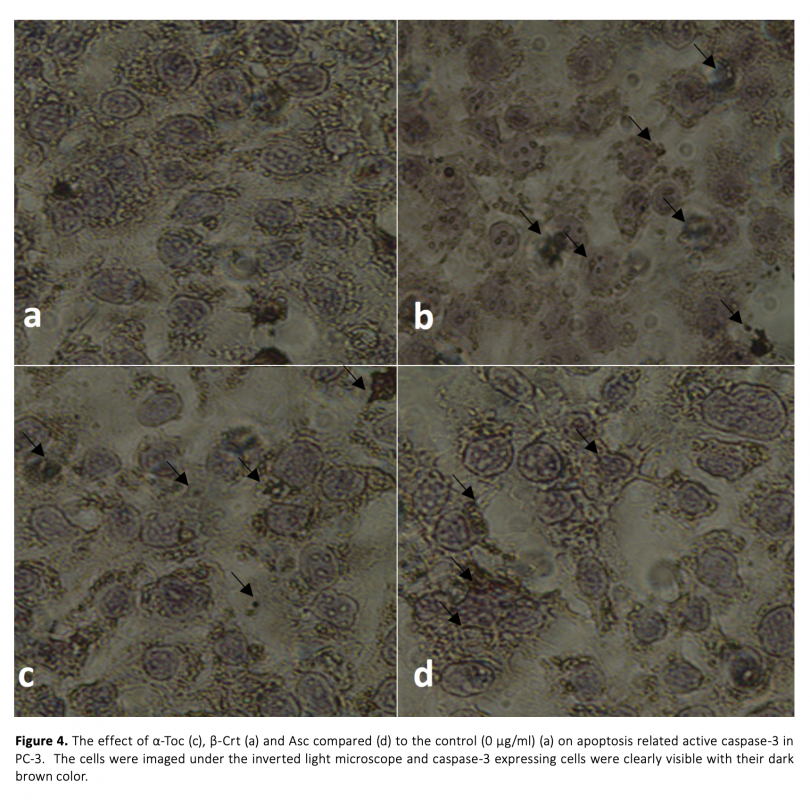
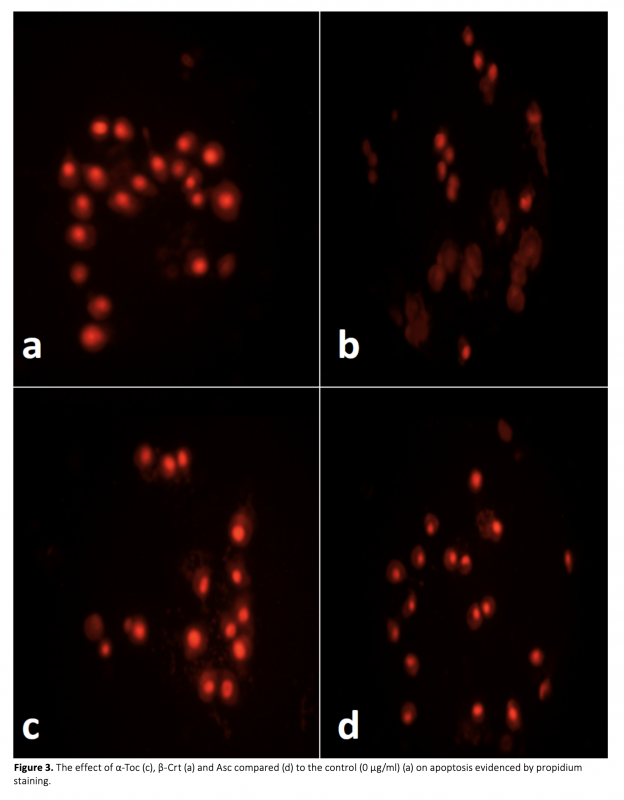
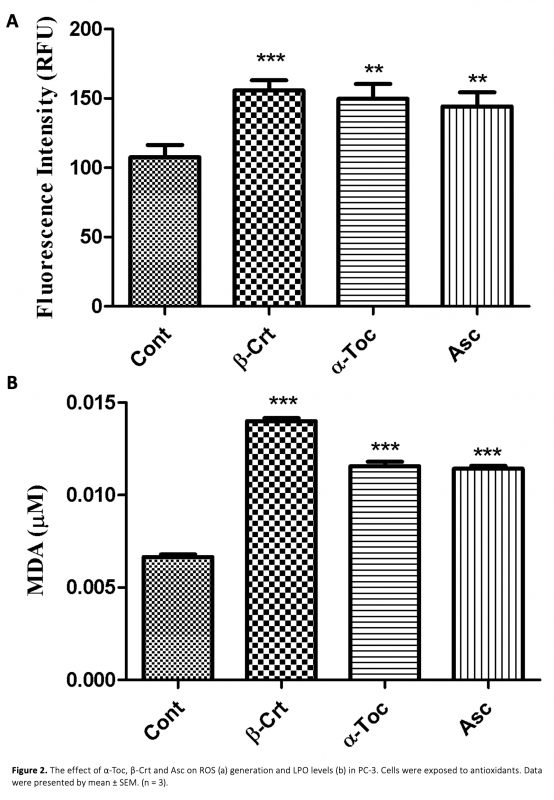
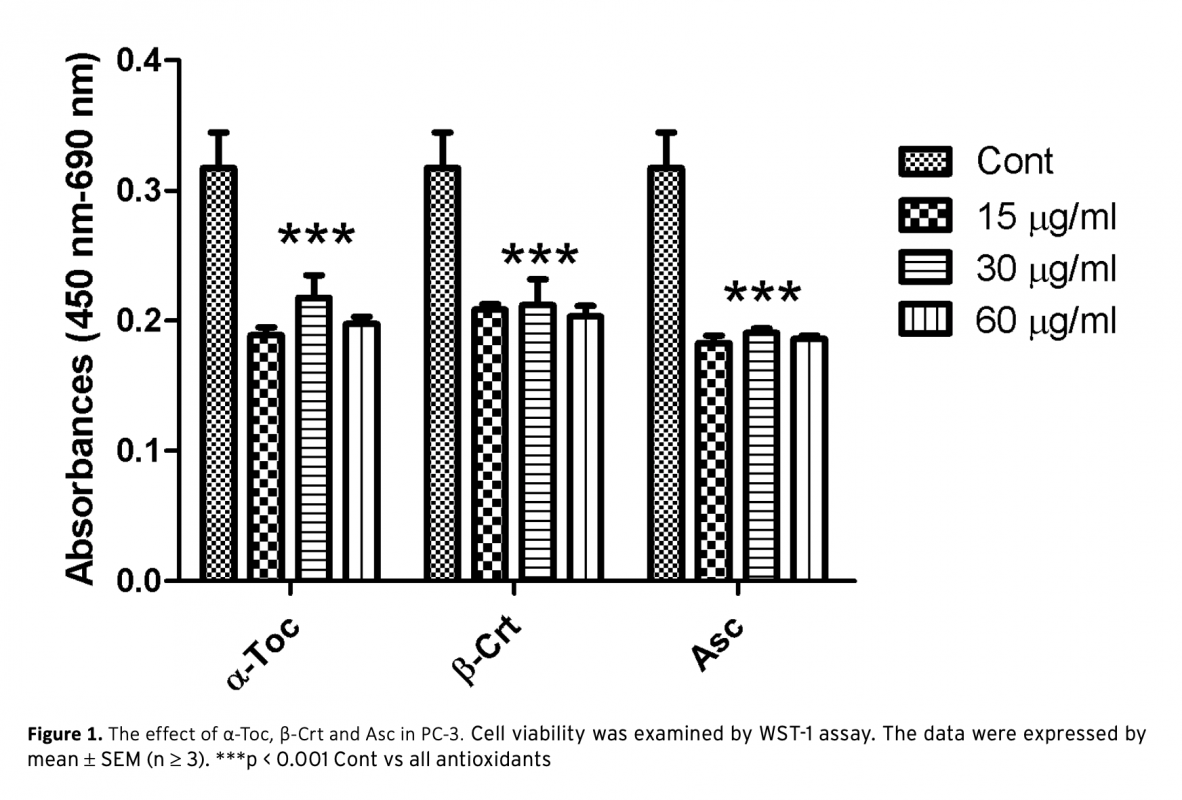
Prostate cancer (PC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancer types being the second major reason of cancer-associated death in male particularly over the age of 50. Accumulating scientific evidences suggest the role oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in prostate cancer. A variety of factors including carcinogenic molecules, infectious diseases and toxic compounds can induce ROS production which turns into a strong contribution to the disturbed homeostasis and genetic mutation. Antioxidants can decrease the negative effects of ROS in vitro. Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid, Asc), vitamin A (beta carotenoids and retinoids, β-Crt) and vitamin E (alpha tocopherol, α-Toc) play an important role in inhibition of oxidative stress and diminishing of free radicals in the body. The aim of this study was to determine the anticancer effect of α-Toc, β-Crt and Asc on PC-3 prostate cancer cells in vitro. This was carried out by cell proliferation, ROS and Lipid Peroxidation assay, caspase-3 and propidium iodide staining experiments. The findings suggest that these agents behave as prooxidant by lowering cell viability and increasing the production of ROS and LPO in prostate cancer. These oxidants induce apoptosis as supported by caspase-3 (the enzyme playing key role in programmed cell death) staining by displaying a marked increase in the expression level of caspase-3 enzyme.
Prostat kanseri (PC), özellikle 50 yaşın üzerindeki erkeklerde kansere bağlı ölümlerin ikinci büyük nedeni olan ve en yaygın olarak teşhis edilen kanser tiplerinden biridir. Bilimsel çalışmalar oksidatif stres ve Reaktif oksijen türlerinin (ROS) prostat kanseri üzerindeki rolünü göstermektedir. ROS, kanserojen moleküller, enfeksiyon, toksi bileşikler gibi homeostaza ve genetik mutasyona neden olabilecek bileşikler tarafından üretilir. Antioksidanlar, ROS’un olumsuz etkilerini in vitro olarak azaltabilir. C vitamini (Askorbik asit, Asc), A vitamini (beta karotenoidler ve retinoidler, β-Crt) ve E vitamini (alfa tokoferol, α-Toc) oksidasyonun önlenmesinde ve vücuttaki serbest radikallerin konsantrasyonunun azaltılmasında önemli rol oynar. Bu çalışmanın amacı, α-Toc, β-Crt ve Asc’nin PC-3 prostat kanseri hücreleri üzerindeki in vitro antikanser etkisini belirlemektir. Bu amaç, hücre çoğalması, ROS ve Lipid Peroksidasyon deneyi, kaspaz-3 ve propidium iyodür boyama deneyleri ile gerçekleştirildi. Bulgular, bu ajanların, prostat kanseri hücrelerinde hücre canlılığını azaltarak ve ROS ve LPO üretimini artırarak proksidan olarak davrandığını göstermektedir. Bu oksidanlar kaspaz-3 (programlı hücre ölümünde rol alan önemli bir enzim) boyamasıyla desteklendiği üzere apoptozu kaspaz-3 enziminin ekspresyonunu artırarak indüklemiştir.
Download Article in PDF (2.8 MB)