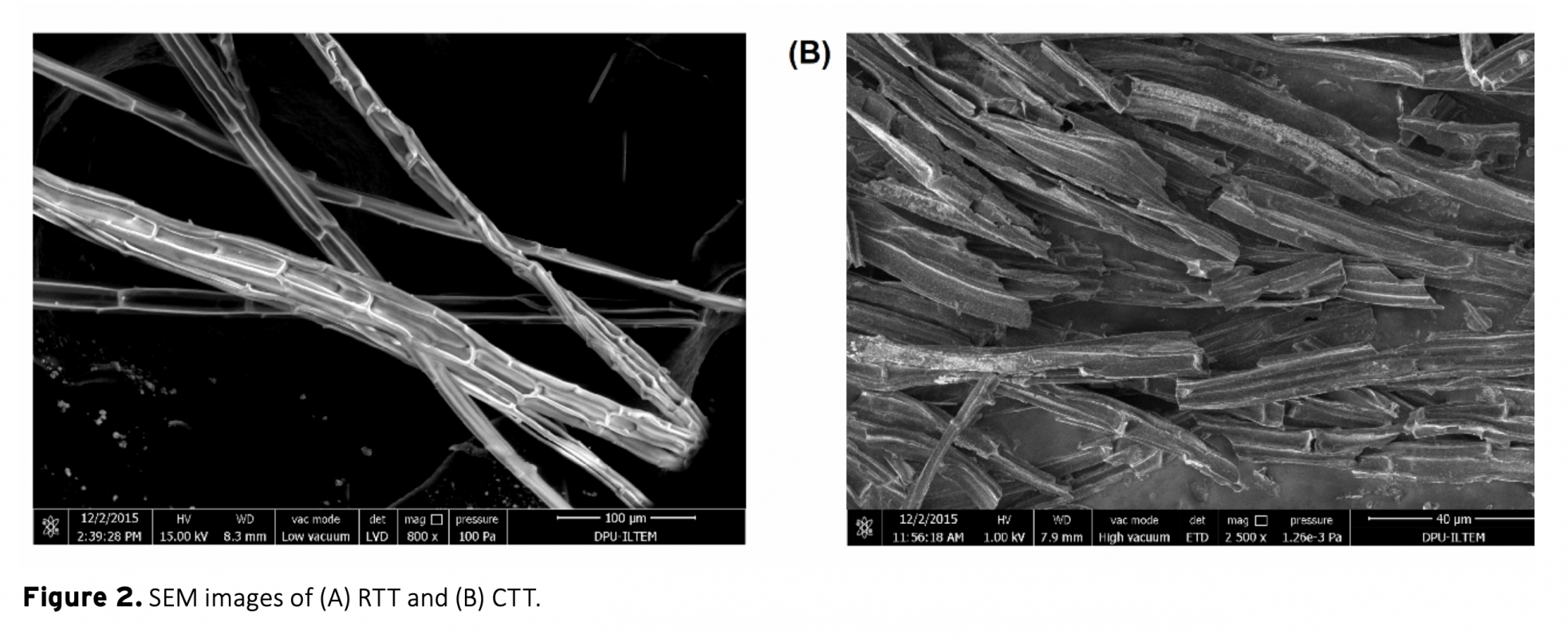
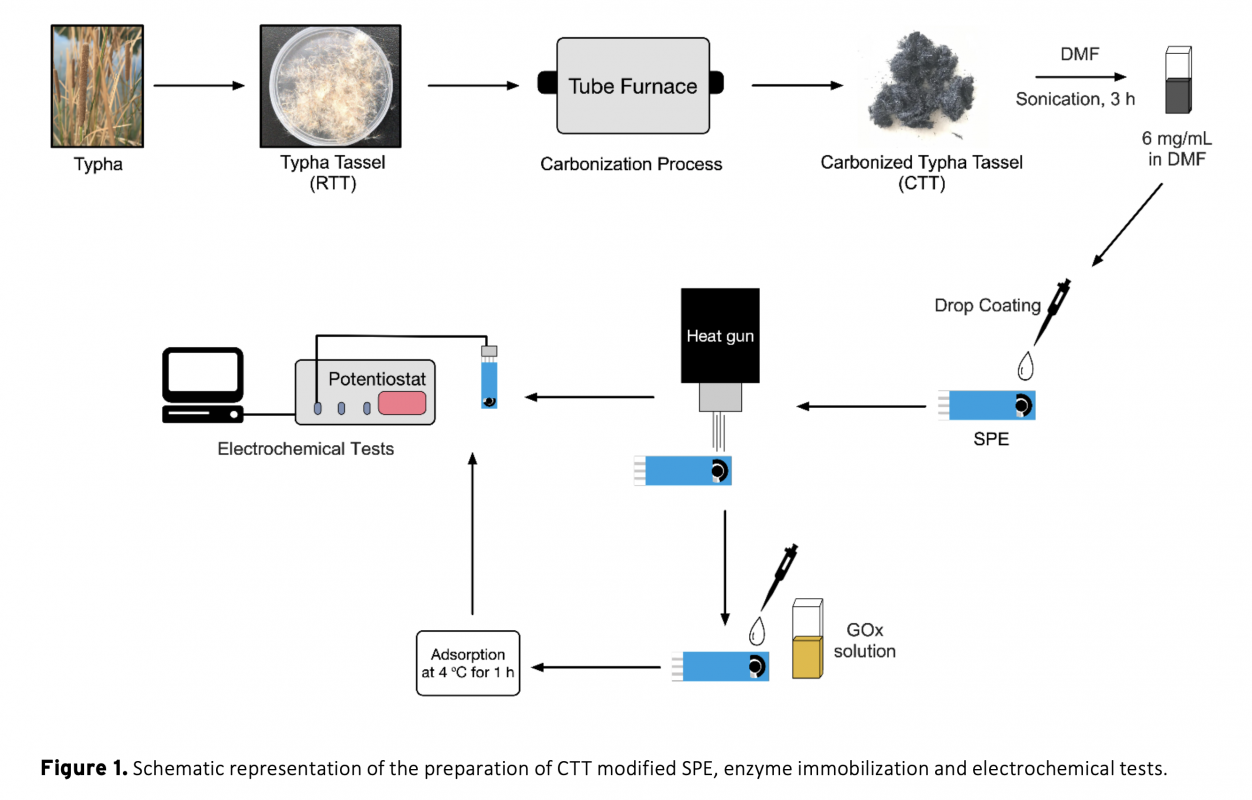
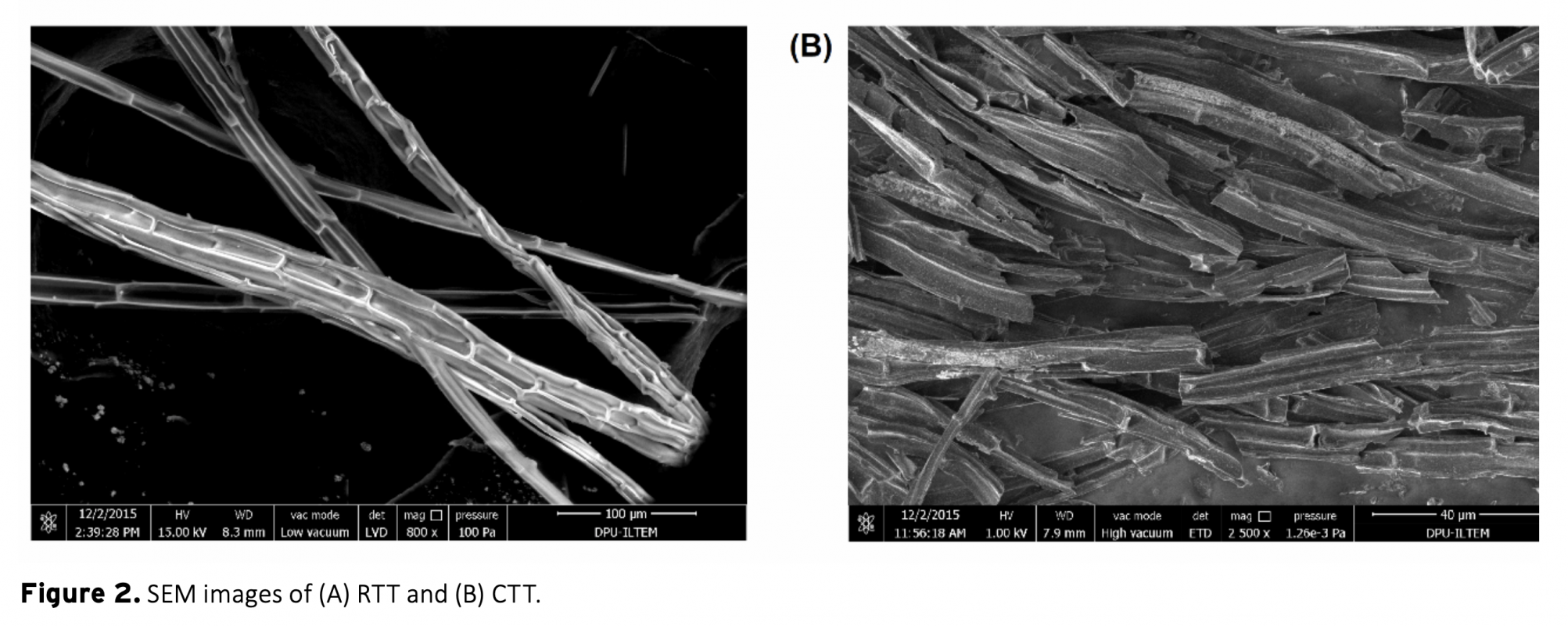
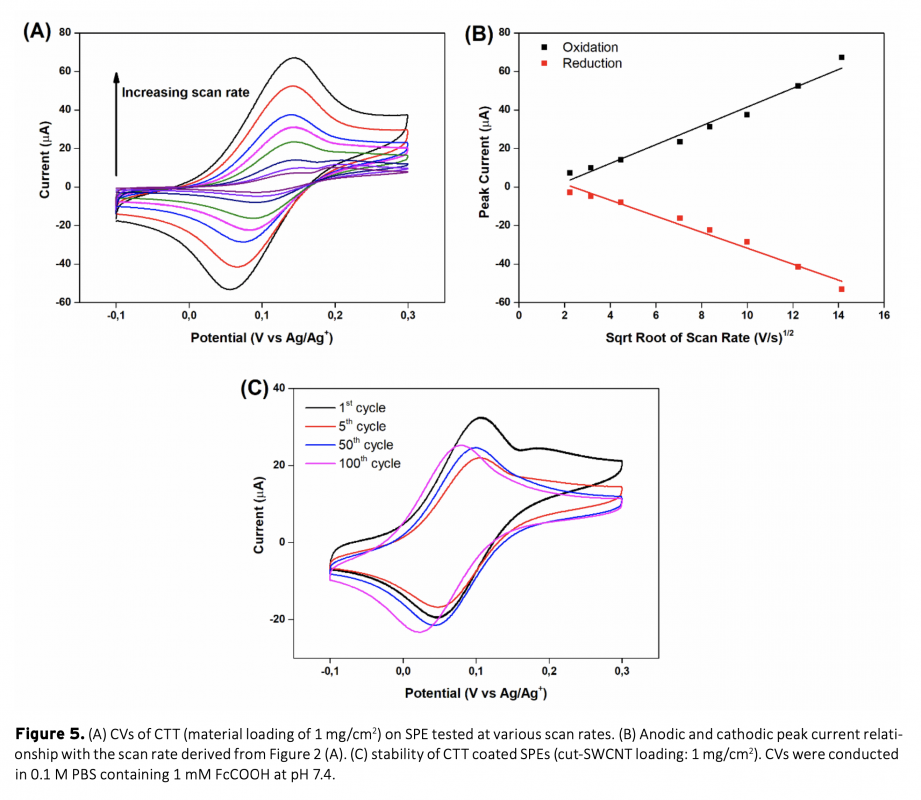
Converting biomass into cheaper but valuable products is very important for a more sustainable world. Especially with emerging technology, the use of hazardous materials in the synthesis of substances such as carbonaceous materials pose a threat to our environment. In this study, electrochemical performance of a carbonaceous material synthesized from typha tassel using a simple and cheap method without any hazardous substances was investigated. It was then used as an enzyme immobilization material for electrochemical glucose oxidation to demonstrate its potential application in bioelectronics. Physical and chemical characterization of raw typha tassel (RTT) and carbonized typha tassel (CTT) were performed using SEM and FTIR techniques. CTT, was then grounded into fine powder, dispersed in DMF and coated onto screen-printed electrodes (SPEs). CTT modified SPEs were electrochemically tested using cyclic voltammetry in 0.1 M phosphate buffer containing 1 mM ferrocene carboxylic acid as a redox mediator at pH 7.4 Finally, glucose oxidase enzyme was adsorbed on CTT modified SPEs to demonstrate its performance in electrochemical enzymatic glucose oxidation reactions. SPE/CTT/GOx system showed promising electrochemical activity and stability at physiological conditions as well as good activity with adsorbed enzyme. This study suggests that CTT is very promising for an easy, effective and cheap ‘biomass to bioelectronics’ construction material.
Biyokütleyi daha ucuz ama değerli ürünlere dönüştürmek, daha sürdürülebilir bir dünya için çok önemlidir. Özellikle ilerleyen teknolojiyle, karbonlu malzemeler gibi ürünlerin sentezinde tehlikeli maddelerin kullanımı çevremizi tehdit etmektedir. Bu çalışmada, herhangi bir tehlikeli madde içermeyen basit ve ucuz bir yöntemle hasır otu püskülünden sentezlenen bir karbonize malzemenin elektrokimyasal performansı araştırılmıştır. Daha sonra biyoelektronik alanındaki potansiyel kullanımını göstermek için elektrokimyasal glikoz oksidasyonu için bir enzim immobilizasyon malzemesi olarak kullanılmıştır. Hasır otu püskülü (RTT) ve karbonize hasır otu püskülünün (CTT) fiziksel karakterizasyonu SEM ve FTIR teknikleri kullanılarak yapılmıştır. CTT, daha sonra ince bir toz halinde öğütülmüş, DMF içinde disperse edilmiş ve baskı-devre elektrotlar (SPE’ler) üzerine kaplanmıştır. CTT modifiye edilmiş SPE’ler, mediyatör olarak 1 mM ferosen karboksilik asit içeren 0.1 M fosfat tamponu (pH 7.4) ile elektrokimyasal olarak test edilmiştir. Son olarak, elektrokimyasal enzimatik glikoz oksidasyon reaksiyonu için performansını göstermek üzere, CTT modifiye SPE’ler üzerinde glikoz oksidaz (GOx) enzimi adsorbe edilmiştir. SPE/CTT/GOx sistemi, adsorbe enzimle iyi aktivite göstermenin yanı sıra fizyolojik şartlar altında iyi elektrokimyasal aktivite ve kararlılık göstermiştir. Bu çalışma, CTT’nin ‘biyokütleden biyoelektroniğe’ gidişte kolay, ucuz ve etkili bir yapı malzemesi olarak kullanılabileceğini göstermektedir.

Download Article in PDF (1.6 MB)